This FAQ is copyright © 1998 John Savill (SavillTech Ltd) all rights reserved. No part of this document should be reproduced, distributed or altered without my permission. You may print it for your own use personnel use.
The Web version of the Windows NT FAQ is at http://www.ntfaq.com. To subscribe to the Windows NT FAQ send a mail to nt-faq@ed-com.com with subscribe in the body of the message to receive the updated single file version of the FAQ once a week.
This single file version of the FAQ is available for download from http://www.ntfaq.com/faqcomp.zip.
Q. What are the differences between NT Workstation and NT Server?
A. See table Below
| Workstation | Server | |
| Connection to other clients | 10 | Unlimited |
| Connection to other networks | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Multiprocessing | 2 CPUs | 4 CPUs |
| RAS | 1 connection | 255 connections |
| Directory Replication | Import | Import and Export |
| Macintosh Services | No | Yes |
| Logon Validation | No | Yes |
| Disk Fault Tolerance | No | Yes |
| Network | Peer-to-peer | Server |
A. NT actually stands for Northern Telecom but
Microsoft licensed it and in the Windows sense stands for New Technology.
Its also interesting to note its heritage
RSX -> VMS -> ELN -> NT all major designs of David Cutler
Also VMS +1 letter = WNT (Windows NT) :-) (aka HAL and IBM in 2001)
Q. What is the NT Boot Process?
A. Firstly the files required for NT to boot are
The common Boot sequence files are
The boot sequence is as follows
A. Virtual Memory makes up for the lack of RAM in computers by using space on the hard disk as memory, Virtual Memory. When the actual RAM fills up (actually its before the RAM fills) then virtual memory is created on the hard disk. When physical memory runs out, the Virtual Memory Manager chooses sections of memory that have not been recently used and are of low priority and writes them to the swap file. This process is hidden from applications, and applications views both virtual and actual memory as the same.
Each application that runs under Windows NT is given its own virtual address space of 4GB (2GB for the application, 2GB for the operating system).
The problem with Virtual Memory is that as it writes and reads to the hard disk, this is much slower than actual RAM. This is why if an NT system does not have enough memory it will run very slowly.
A. In the late 1980's the Windows environment was created to run on the Microsoft DOS operating system. Microsoft and IBM joined forces to create a DOS replacement that would run on the Intel platform that led to the creation of OS/2, and at the same time Microsoft was working on a more powerful operating system that would run on other processor platforms. The idea was that the new OS would be written in a high level language (such as C) so it would be more portable.
Microsoft hired Dave Cutler (who also designed Digital's VMS) to head the team for the New Technology Operating System (NT :-) ). Originally the new OS was to be called OS/2 NT.
In the early 1990's Microsoft released version 3.0 of its windows OS which gained a large user base, and it was at this point that Microsoft and IBM's split started as the two companies disagreed on the future of their OS's. IBM viewed Windows as a stepping stone to the superior OS/2, where as Microsoft wanted to expand Windows to compete with OS/2, so they split, IBM kept OS/2 and Microsoft change OS/2 NT to Windows NT.
Nt was once called OS/3, and OS/2 V3, I am informed by a alpha tester for IBM & MS, he had a set of 5.25 diskettes from Microsoft, and that's how he got them.
The first version of Windows NT (3.1) was released in 1993 and had the same GUI as the normal Windows Operating System, however it was a pure 32 bit OS, but provided the ability to also run older DOS and Windows apps, as well as character mode OS/2 1.3 programs.
For a detailed history have a look at http://windowsnt.miningco.com
Q. How do I install the SYMBOL files?
A. Symbol files are produced by the linker when a program is built, and are used to resolve global variables and function names in an executable.
For more information see Microsoft Knowledge Base article Q148659
A. Windows NT (both the Workstation and Server) is a 32-bit Operating System. It is a preemptive, multi-tasking Operating System, which means that the Operating System controls allocation of CPU time, not the applications, stopping one application from hanging the OS. NT supports multiple CPU's giving true Multi-tasking, using symmetrical multiprocessing, meaning the processors share all tasks, as opposed to asymmetrical multiprocessing, where the OS uses one CPU and the applications another. NT is also a Fault Tolerant Operating System, with each 32bit application operating in its own Virtual Memory address space (4 GigaBytes) which means one application cannot interfere with another's memory space.
Unlike earlier version of Windows (such as Windows for Workgroups and Windows 95), NT is a complete Operating System, and not an addition to DOS.
NT supports different CPU's: Intel x86, IBM PowerPC (Not to be supported for NT5.0) and DEC Alpha.
NT's other main plus is its Security with a special NT file system (NTFS) that allows permissions to be set on a file and directory basis.
A. Originally there were .ini files in Windows, however the problem with .ini files are many, e.g. size limitations, no standard layout, slow access, no network support etc. Windows 3.1 (yes Windows not Windows NT) had a registry which was stored in reg.dat and could be viewed using regedit.exe and was used for DDE, OLE and File Manager integration. In Windows NT the Registry is at the heart of NT and is where nearly all information is stored, and is split into a number of subtrees, each starting with HKEY_ to indicate that it is a handle that can be used by a program.
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE | This contains information about the hardware configuration and installed software. |
| HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT | This is just a link to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes and contains links between applications and file types as well as information about OLE. |
| HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG | Again this is a link to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Hardware Profiles\Current and contains information about the current configuration. |
| HKEY_CURRENT_USER | This is a link to HKEY_USERS\<SID of User> and contains information about the currently logged on users such as environment, network connections, printers etc. |
| HKEY_USERS | Contains information about actively loaded user profiles, including .default which is the default user profile. |
Each of the subtrees has a number of keys, which in turn have a number of subkeys. Each key/subkey can have a number of values which has 3 parts
To edit the registry there are two tools available, regedt32.exe and regedit.exe.Regedit.exe has better search facilities, but does not support all of the Windows NT registry value types. If you want to just have a look around the Registry:
Q. What files make up the registry, and where are they?
A. The files that make up the registry are stored in %systemroot%/system32/config directory and consist of
There are also other files with different extensions for some of them
Q. How do I restrict access to the registry editor?
A. Using the registry editor (regedt32.exe)
Q. What is the maximum registry size?
A. The maximum size is 102MB, however it is slightly more complicated than this.
The registry entry that controls the maximum size of the registry is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\RegistrySizeLimit. By default this entry will not exist so it will need to be created:
The minimum size is 4MB, and if anything less than this is entered in the registry then it will be forced up to 4MB. The maximum is 80% of the paged pool (which has a maximum size of 128MB, hence 102MB which is 80% of 128MB). If no entry is entered then the maximum size is 25% of the paged pool. The paged pool is an area of physical memory used for system data that can be written to disk when not in use.
An important point to note is that the RegistrySizeLimit is a maximum, not an allocation, and so setting a high value will not reserve the space, and it does not guarantee the space will be available.
This can also be configured using the System Control Panel applet, click on the Performance tab and the maximum registry size can be set there. You would then need to reboot.
For more information see Knowledge Base Article Q124594
There is another complication, during early boot, NTLDR loads some code, allocates working memory, and reads in parts of the registry. All of this has to fit in the first 16MB of memory regardless of how much memory is physically installed. The entire system file is read; enough memory is required to contain the whole file as stored on disk without regard to how much of it is useful.
Some problems
A number of ways to get rid of the excess space:
To turn this off use REGEDT32 to add the value "ReportBootOk:REG_SZ:0" [zero] to HKEY_Local_Machine\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon This will prevent creation of the LastKnownGood ControlSet. If a boot fails because the 16 MB limit with NTLDR is exceeded, no dump can be produced and MS will not solve the problem. This 16 MB problem will not be changed in NT 5.
Q. Should I use REGEDIT.EXE or REGEDT32.EXE?
A. You can use either for NT. REGEDIT does have a few limitations, the largest is that it does not support the full regedit data types such as REG_MULTI_SZ, so if you edit this type of data with REGEDIT it will change its type.
REGEDIT.EXE is based on the Windows95 version and has features that REGEDT32.EXE lacks (such as search). In general REGEDIT.EXE is nicer to work with. REGEDIT.EXE also shows your current position in the registry at the bottom of the window.
Q. How do I restrict access to a remote registry?
A. Access to a remote registry is controlled by the ACL on the key winreg.
It is possible to set up certain keys to be accessible even if the user does not have access by editing the value HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurePipeServers\winreg\AllowedPaths\Machine (use regedt32). You can add paths to this list.
Q. How can I tell what changes are made to the registry?
A. Using the regedit.exe program it is possible to export portions of the registry. This feature can be used as follows:
Q. How can I delete a registry value/key from the command line?
A. Using the Windows NT Resource Kit Supplement 2 utility REG.EXE you can delete a registry value from the command line or batch file, e.g.
reg delete HKLM\Software\test
Would delete the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\test value. When you enter the command you will be prompted if you really want to delete, enter Y. To avoid the confirmation add /f to the command, e.g.
reg delete HKLM\Software\test /f
A full list of the codes to be used with REG DELETE are as follows:
| HKCR | HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT |
| HKCU | HKEY_CURRENT_USER |
| HKLM | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE |
| HKU | HKEY_USERS |
| HKCC | HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG |
To delete a entry on a remote machine add the name of the machine, \\<machine name>, e.g.
reg delete HKLM\Software\test \\johnpc
Q. How can I audit changes to the registry?
A. Using the regedt32.exe utility it is possible to set auditing on certain parts of the registry. I should note that any type of auditing is very sensitive lately and you may want to add some sort of warning letting people know that their changes are being audited.
You will need to make sure that Auditing for File and Object access is enabled (use User Manager - Polices - Audit).
To view the information use Event Viewer and look at the Security information.
Q. How can I clean up/remove invalid entries from the registry?
A. Microsoft have released a utility called RegClean which will go through your machines registry and delete any unused/unnecessary keys. The current version is 4.1a and can be downloaded from http://support.microsoft.com/download/support/mslfiles/RegClean.exe .
Once downloaded just click on the Executable and it will check your registry, once the check is completed you will be given an option to fix errors "Fix Errors" button. You can click the Exit button to exit.
RegClean creates an uninstall file in the directory the image is located in, of the name
"Undo <machine name> <yyyymmdd> <hhmmss>.reg"
e.g. "Undo workstation 19980320 104323.reg"
To undo the changes just double click (or single depending on your config ;-) ) this file.
See http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q147/7/69.asp for more information.
Q. I make changes to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE but they are lost on reboot.
A. This is because HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE is recreated by the system at boot time and this means any settings such as ACL's are lost.
Q. What data types are available in the registry?
A. Below is a table of data types supported by Regedt32.exe, regedit.exe does not support REG_EXPAND_SZ or REG_MULTI_SZ
| REG_BINARY | This is raw binary data |
| REG_DWORD | This is a double word (4 bytes). It can be displayed in binary, hexadecimal or decimal format |
| REG_EXPAND_SZ | An expandable text string that contains a variable (for example %systemroot%) |
| REG_MULTI_SZ | A multiple line string. Each "line" is separated by a null |
| REG_SZ | A text string |
Q. How can I automate updates to the registry?
A. There are 2 main methods you can use to create scripts that can be run to automate the updates. The first is to create a .reg file which can then be run using
regedit /s <reg file>
The format of the file is
REGEDIT4
[<key name>]
"<value name>"="<value>" a
string value
"<value name>"=hex:<value> a binary value
"<value name>"=dword:<value> a dword value
for example
REGEDIT4
[HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Control Panel\Desktop]
"Wallpaper"="E:\\WINNT\\savtech.bmp"
"TileWallpaper"="0"
[HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Control Panel\Colors]
"Background"="0 0 0"
Would set the default background and color before anyone logs on.
The second method is to user a Windows 95 style .inf file. These are run using the command
rundll32 syssetup,SetupInfObjectInstallAction DefaultInstall 128 <inf file>
The format of the file is as follows
[Version]
Signature = "$Windows NT$"
Provider=%Provider%
[Strings]
Provider="SavillTech Ltd"
[DefaultInstall]
AddReg = AddReg
DelReg = DelReg
UpdateInis = UpdateInis
[AddReg]
[DelReg]
[UpdateInis]
Below are the keys to be used
| HKCR | HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT |
| HKCU | HKEY_CURRENT_USER |
| HKLM | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE |
| HKU | HKEY_USERS |
The file below is an .inf file which performs the same as the .reg file described earlier
[Version]
Signature = "$Windows NT$"
[DefaultInstall]
AddReg = AddReg
[AddReg]
HKU,".DEFAULT\Control Panel\Colors","Background",0000000000,"0
0 0"
HKU,".DEFAULT\Control Panel\Desktop","Wallpaper",0000000000,"E:\WINNT\savtech.bmp"
HKU,".DEFAULT\Control Panel\Desktop","TileWallpaper",0000000000,"1"
INF files can be generated automatically using the SYSDIFF utility if you have a difference file (sysdiff /inf <name of difference file> <dir to create to>)
Q. How do I apply a .reg file without the success message?
A. To apply a .reg file (a registry information file) the normal method from the command prompt is to enter
C:\> regedit <registry file>.reg
This applies the change and gives a confirmation message:
"Information is <filename>.reg has been successfully entered into the registry"
If you would like to avoid this confirmation message and apply the change silently use the /s switch, e.g.
C:\> regedit /s <registry file>.reg
Q. What service packs and fixes are available?
A. See table below. All directories are off of ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/fixes/usa/nt40. Just click on the file name for a direct FTP link For people in Europe ftp.sunet.se/pub3/vendor/microsoft/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/fixes may provide faster access.
There are also Microsoft BBS numbers where Service Packs can be downloaded from, e.g. for the UK it is 44 1734 270065, however the fixes tend to be a few days later than on the FTP site.
| File Name | Directory | Description (Microsoft Article No.) |
| Sp1_400i.exe | /ussp1/i386 | Service Pack 1 |
| Sp2_400i.exe | /ussp2/i386 | Service Pack 2 (around 14Mb!) |
| Nt4sp3_i.exe | /ussp3/i386 | Service Pack 3 (around 18Mb!) |
Service Pack 1 Hotfixes /hotfixes-postsp1/
| KRNL40I.EXE | /32proc-fix | Q140065 |
| AFD40I.EXE | /afd-fix | Q140059 |
| CDFS40I.EXE | /cdfs-fix | Q142687 |
| NDIS40I.EXE | /mcanet-fix | Q156324 |
| NDIS40I.EXE | /ndis-fix | Q142903 |
| NTBCKUPI.EXE | /NTBackup-fix | Q142671 |
| NTVDM40I.EXE | /ntvdm-fix | Q134126 |
| PCM40_I.EXE | /pcmcia-fix | Q108261 |
| SCSIFIXI.EXE | /scsi-fix | Q171295 |
| SPX40I.EXE | /spx-fix | Q153665 |
| SYN40I.EXE | /syn-attack | Q142641 |
| NTFS40I.EXE | /toshiba-fix | Q150815 |
| STONE97I.EXE | /winstone97 | Q141375 |
Service Pack 2 Hotfixes /hotfixes-postsp2/
| ALPHA40.EXE | /Alpha-fix | Q156410 |
| DNS40I.EXE | /dns-fix | Q142047, Q162927 |
| IISFIX.EXE | /iis-fix | Q163485, Q164059 |
| KRNL40I.EXE | /krnl-fix | Q135707, **Q141239** |
| TCP40I.EXE | /oob-fix | Q143478 |
| RAS40I.EXE | /ras-fix | Q161368 |
| RPC40I.EXE | /RPC-fix | Q159176, Q162567 |
| SECFIX_I.EXE | /sec-fix | Q143474 |
| SERIALI.EXE | /serial-fix | Q163333 |
| SETUPDDI.EXE | /setupdd-fix | Q143473 |
| SFMSRVI.EXE | /sfmsrv-fix | Q161644 |
| WTCP40I.EXE | /TCPIP-fix | Q163213 |
Service Pack 3 Hotfixes /hotfixes-postsp3/
A number of post Service Pack 3 hotfixes have been replaced by newer fixes and are not listed above, they can be found at ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/fixes/usa/nt40/hotfixes-postSP3/archive . These include
The file names above are for the Intel platform (hence the ending I), but they may also be available for Alpha and PPC, just substitute the I for a A(Alpha) or P(PPC).
I should note a health warning, "If it ain't broke, don't fix it" and I would tend to agree with this, so unless you have a problem, or require a new feature of a Service Pack think if you really want it. Also if you are going to apply it to a live system, try and test it first, as sometimes a Service Pack will introduce new problems.
Q. What are the Q numbers and how do I look them up?
A. The Q numbers relate to Microsoft Knowledge Base articles and can be viewed at http://support.microsoft.com/support/
Q. How do I install the Service Packs?
A. If you receive the Service Pack by downloading from a Microsoft FTP site, then copy the file to a temporary directory and then just enter the file name (e.g. Sp2_400i.exe). The file will be expanded and among the files created a file called UPDATE.EXE will be created. Just run this file. If there is no UPDATE.EXE, just .sym files you have downloaded the symbols version which is used for debugging NT, download the normal version (see above).
If you receive Service Packs via CD, if you just insert the CD (for SP2 and later) and an Internet Explorer page will be shown and you can just click on install for the Service Pack.
Q. How do I install the Hot fix?
A. Again copy the file to a temporary directory and run the file name. A few files will be created, one called HOTFIX.EXE. Run "HOTFIX /install" which will install the Hot Fix.
The newer Hot fixes (Java fix for Service Pack 3 onwards) you just double click on the downloaded file.
A. Use the command Hotfix /remove. To force the remove using the registry editor (regedt32) HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\HOTFIX and delete the entry for the HOTFIX. Then use explorer to goto %SystemRoot%\HOTFIX\HF00?? and copy the backed up files back to their original location.
Q. How do I install Service Pack 3?
A. Before you install Service Pack 3 you must remove Internet Explorer 4.0 preview if installed:
Also before installing SP3 make sure you have an up to date Repair Disk (RDISK /S). To install Service Pack 3 download Nt4sp3_i.exe and follow the instructions below
Q. Emergency Repair Disk issues after installation of Service Pack 3.
A. Due to changes in Service Pack 3 the Emergency Repair Disk process has changed. The file setupdd.sys that is on the 2nd NT installation disk has been superseded by the one supplied with service pack 3. To extract the file from the Service Pack 3 executable, follow the instructions below:
This is discussed in the Service Pack 3 readme file, and also in knowledge base article Q146887.
Q. How do I remove the Java Hotfix for Service Pack 3?
A. Manually unpack the hotfix
javafixi /x
Then type
hotfix -y
And it will remove the hotfix.
This method may become the new standard for hot fixes.
Q. How do I install multiple Hotfixes at the same time?
A. When you extract the files in a hotfix, generally the following will be extracted
The hotfix.exe is the same executable for all the hotfixes, and the hotfix.inf is basically the same, the only difference is the files that are to be copied, e.g. tcpip.sys, and a description of the hotfix. To install multiple hotfixes at the same time all that is needed is to decompress the hotfix files and update the hotfix.inf with the information on which files to copy.
The reason we copied the .inf files is that you can just cut and paste the hotfix specific information to the common hotfix.inf. When you decompressed a hotfix you will see which files were created, you could then search the .inf file for the file name and it would be in two places, the directory it belongs in and the [SourceDisksFiles] section. You could then go to the bottom of the file and cut and paste the HOTFIX_NUMBER and COMMENT and add to the end of HOTFIX.INF.
This is very hard to explain and an example is probably the best way to demonstrate this. Suppose you want to install
The procedure would be as follows
To install just type
hotfix
from the directory created (i.e. hotfix), you will see a dialog copying the files (the ones you have specified in the hotfix.inf file :-) ), and the system will reboot. To see what hotfixes are installed:
Q. How do I install Hotfixes the same time as I install Service Pack 3 onwards?
A. Update.exe that ships with Service Pack 3 checks for the existance of a hotfix subdirectory, and if in that directory the files hotfix.exe and hotfix.inf are present you are asked when running update.exe if you also want to install the hotfixes.
Q. I have installed Service Pack 3, now I cannot run Java programs.
A. Download the updated Java Virtual Machine from Microsoft at http://www.microsoft.com/java/download/dl_vmsp2.htm . Download build 1518 which works with IE3.01, IE 3.02 and IE 4.0 platform preview 1, do NOT install on IE 4.0 PP2 or the release version.
There is also a hotfix for Service Pack 3 available from Microsoft ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/fixes/usa/nt40/hotfixes-postSP3/java-fix/JAVAFIXI.EXE
Q. I have installed Service Pack 3, however the Policy Editor has not been updated.
A. This is caused by a mistake in the Service Pack 3 update.inf file. The entry for poledit.exe (the executable for the policy editor) is specified in the [MustReplace.system32.files] section whereas the file should actually be in the [SystemRoot.files].
To install the new Policy Editor perform the following
Alternatively you can update the update.inf fiile and move the location of poledit.exe from [MustReplace.system32.files] to [SystemRoot.files].
Q. How can I tell if I have the 128 bit version of Service Pack 3 installed?
A. The easiest way to tell this is to examine the secure channel dynamic link library (SCHANNEL.DLL):
Q. How do I install a service pack during a unattended installation?
A. There are various options, however all of them require for the service pack to be extracted to a directory, using
NT4SP3_I /x
and you then enter the directory where you want to extract to.
You could extract to a directory under the $OEM$ installation directory which would then be copied locally during the installation and you could add the line
".\UPDATE.EXE -U -Z"
to CMDLINES.TXT. This will increase the time of the text portion of the installation as the contents have to be copied over the network.
An alternate method is to install from a network drive, this requires a bit more work:
Q. What order should I apply the Hot fixes?
A. The Service Pack 3 hotfixes are, for the most part, cumulative. This means that the latest binary also includes fixes previously made to the same binary.
For example, the 01/09/98 version of Tcpip.sys (teardrop2-fix) also includes previous fixes to Tcpip.sys (such as land-fix, icmp-fix, and oob-fix).
When you apply multiple fixes, please install them in the following order to ensure a newer fix is not replaced by an older one.
For the Microsoft version of the list please see ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/fixes/usa/nt40/hotfixes-postSP3/postsp3.txt
Q. I get an error message when I try to re-apply a hotfix after installing a service pack?
A. If when you try and reinstall a hotfix (after re-applying a service pack etc.) you get the error
Hotfix: The fix is already installed.
Hotfix: Internal consistency error: Invalid Tree pointer = <garbage
characters displayed>.
you need to remove the hotfix before trying to reinstall.
To remove a hotfix you would usually use hotfix /r or hotfix -y (depending on the version, to check how use /? on the hotfix for the syntax) however there are situations where it will refuse to remove the hotfix:
Hotfix: Fix <name of hotfix> was not removed.
All the hotfix actually does when you install one is to check a registry entry so see if it already there, so to get round this problem we can go into the registry and remove the hotfixes corresponding entry.
The fix is still installed on the system, all you have done is removed NT's knowledge of its installation so you will now be able to re-install the hotfix in the normal way.
Q. When will Service Pack 4 be released and what's in it?
A. The Release Candidate for Service Pack is currently with a small handful of testers (I'm one of them :-P) and its looking good. As for details due to the Non Disclosure Agreement all testers have to sign I cannot give details however I can tell you a limited NTFS 5.0 driver is included (the new version of NTFS supplied with Windows NT 5.0).
I would expect the final version to ship by the end of September.
Q. When should I reapply a Service Pack?
A. You should reapply any Service Pack (and subsequent hotfixes) whenever you add any system utilities/services or hardware/software. A good rule of thumb is if the computer says "Changes have been made you must shutdown and restart your computer" reapply your service pack before the reboot.
The only problem is once you reinstall a service pack, unless you uninstall then reinstall, you will lose the ability to uninstall it.
A. Due to a lot of public pressure, Microsoft agreed to no longer include any new functionality in Service Packs, but would rather produce a separate add-on which would update various option components.
Option Pack 4 is the first of these (to keep in step with Service Pack 4) and can be downloaded from http://www.microsoft.com/windows/downloads/contents/updates/nt40ptpk/default.asp or is supplied as part of MSDN. The download is about 27MB.
If you download from the web you have to download a special program, download.exe, which you then run which downloads or installs the software.
Included in Option Pack 4 are:
More information can be found at http://www.microsoft.com/NTServer/Basics/WhatNew.asp
To install the Option Pack you must be running Service Pack 3 or above (I tested with Service Pack 4 and you get warnings that it has not been tested on Service Pack 4 but it works fine) and you must have Internet Explorer 4.01 or above.
Once you start the installation you should click Next to the introduction screen and you will then have two options
If you select Upgrade Only then only existing components on the system will be upgrade to Option Pack 4 version, clicking Upgrade Plus allows you to install extra software.
If you select Upgrade Plus you can then choose which components to install. Items such as IIS have sub-components such as NNTP server (news) which you can optionally install.
Depending on the components you selected you will be asked some minor questions and then the machine will reboot.
Q. How can I tell which version Service Pack I have installed?
A. When a Service Pack is installed using the normal method (e.g. not just copying the files to a build location) the service pack version is entered into the registry value CSDVersion which is under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion.
The value is of the formal "Service Pack n", e.g. "Service Pack 4" but can have extra information if it is a beta or release candidate, e.g. "Service Pack 4, RC 1.99".
To check this from the command line you could use the REG.EXE Resource Kit supplement 2 utility:
C:\>reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
NT\CurrentVersion\CSDVersion"
REG_SZ CSDVersion Service Pack 4, RC 1.99
Make sure you put the value in double quotes (").
Q. What is new in Windows NT 5.0?
A. NT 5.0 is the next major release of NT. It is expected to include the following new features:
For more information on what's new please goto http://www.microsoft.com/NTServer/Basics/Future/WindowsNT5/Features.asp
Q. Where can I get more information on Windows NT 5.0?
A. Below is a list of useful links at Microsoft
Q. How do I get the Microsoft Windows NT 5.0 Beta?
A. Windows NT 5.0 is currently in beta test. The technical beta program is closed and is not accepting additional requests at this time. The Windows NT 5.0 beta is not generally available at present for free. If you want this beta, there are three approaches you can consider taking:-
Did you really want to beta test today?
Q. How can a FAT partition be converted to an NTFS partition?
A. From the command line enter the command convert d: /fs:ntfs . This command is one way only, and you cannot convert an NTFS partition to FAT. If the FAT partition is the system partition then the conversion will take place on the next reboot.
After the conversion File Permissions are set to Full Control for everyone, where as if you install directly to NTFS the permissions are set on a stricter basis.
Q. How can a NTFS partition be converted to a FAT partition?
A. A simple conversion is not possible, and the only course of action is to backup all the data on the drive, reformat the disk to FAT and then restore your data backup.
Q. How do I run HPFS under NT 4.0?
A. If you want NT support for HPFS, you can upgrade from 3.51 to 4.0 which will retain HPFS support. You can manually install the 3.51 driver under NT 4.0, however this is not supported by Microsoft.
Q. How do I compress a directory?
A. Follow instructions below (this can only be done on an NTFS partition)
Q. How do I uncompress a directory?
A. Follow the same procedure above, but uncheck the compress box.
Q. Is there an NTFS defragmentation tool available?
A. There are a number available for NT that I know of.
Q. Can I undelete a file in NT?
A. It depends on the file system. NT has no undelete facility, however if the filesystem was FAT then boot into DOS and then use the dos undelete utility. With the NT Resource kit there is a utility called DiskProbe which allows a user to view the data on a disk, which could then be copied to another file. It is possible to search sectors for data using DiskProbe.
If the files are deleted on an NTFS partition booting using a DOS disk and using the undelete.exe program is not possible since DOS cannot read NTFS partitions. NTFS does not perform destructive deletes which means the actual data is left intact on the disk (until another file is written in its place) and so a new application from Executive Software, Network Undelete can be used to undelete files from NTFS partitions. A free 30-day version can be downloaded from http://www.networkundelete.com/.
It is important that once any file is delete all activity on the machine is stopped to reduce the possibility of other files overwriting the data that wants to be recovered.
A. Native NT does not support FAT32, NT 5.0 provides full FAT32 support. NT Internals have released a read-only FAT32 driver for Windows NT 4.0 from http://www.sysinternals.com/fat32.htm, or a full read/write version can be purchased from http://www.winternals.com.
Q. Can you read an NTFS partition from DOS?
A. Not with standard DOS, however there is a product called NTFSDos which enables a user to read from a NTFS partition. The homepage for this utility is http://www.sysinternals.com.
Q. How do you delete a NTFS partition?
A. You can boot off of the three NT installation disks and follow the instructions below:
Usually a NTFS partition can be deleted using FDISK (delete non-DOS partition), however this will not work if the NTFS partition is in the extended partition.
You can delete an NTFS partition using Disk Administrator, by selecting the partition and pressing DEL (as long as it is not the system/boot partition).
There is also a utility called delpart.exe that will delete a NTFS partition from a DOS bootup.
Q. Is it possible to repartition a disk without losing data?
A. There is no standard way in NT, however there is a 3rd party product called Partition Magic which will repartition FAT, NTFS and FAT32, however there is a bug in the product which makes the boot partition unbootable if it is repartitioned. A fix is available for this from their web site
Q. What is the biggest disk NT can use?
A. The simple answer to this question is that NT can view a maximum partition size of 2 terabytes (or 2,199,023,255,552 bytes), however there are limitations that restrict you well below this number.
FAT has internal limits of 4 GB due to thefact it uses 16-bit fields to store file sizes, 2^16 is 65,536 with a cluster size of 64 KB gives us the 4 GB.
HPFS uses 32bit fields and can therefore handle greater size disks, but the largest single file size is 4GB. HPFS allocates disk space in 512 byte sectors which can cause problems in Asian markets where sector sizes are typically 1024 bytes which means HPFS cannot be used.
NTFS uses 64-bits for all sizes, leading to a max size of..... 16 exabytes!!! (18,446,744,073,709,551,616 bytes), however NT could not handle a volume this big.
For IDE drives, the maximum is 136.9 GB, however for a standard IDE drive this is constrained to 528MB. The new EIDE drives can access much larger sizes.
It is important to note that the System partition (holding ntldr, boot.ini, etc.) MUST be entirely within the first 7.8Gb of any disk (if this is the same as the boot partition this limit applies) This is due to the BIOS int 13H interface used by ntldr to bootstrap up to the point where it can drive the native HDD IDE or SCSI. int 13H presents a 24 bit parameter for cylinder/head/sector for a drive. If say by defragmentation the system are moved beyond this point you will not be able to boot the system.
Q. Can I disable 8.3 name creation on a NTFS?
A. From the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem, change the value NtfsDisable8dot3NameCreation from 0 to 1.
You may experience problems installing Office 97 if you disable 8.3 name creation and may have to re-enable it during the installation of the software.
Q. How can I stop NT from generating LFN's (Long File Names) on a FAT partition?
A. Using the registry editor change the value HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem\Win31FileSystem from 0 to 1 and only 8.3 file names will be created.
The reason for not wanting the LFN's to be created is that some 3rd party disk utilities that directly manipulate FAT can destroy the LFN's. Utilities such as SCANDISK and DEFRAG that come with DOS 6.x and above do not harm LFN's.
Q. I can't create any files on the root of a FAT partition.
A. The root of a FAT drive has a coded limit of 512 entries, so if you have exceeded this you will not be able to create any more files. I don't have this many! Remember Long File Names take up more than one entry, see the next FAQ for more information, so if you have many LFN's on the root this will drastically reduce the number of files you can have.
A. Long File Names are stored using a series of linked directory entries. A LFN will use one directory entry for its alias (the alias is the 8.3 name automatically generated), and a hidden secondary directory entry for every 13 characters in its name, so if you had a 200 character long file name, this would use 17 entries!
The alias is generated using the first six characters of the LFN, then a
~ and a number for the first 4 versions of a files with the same first six
characters, e.g. for the file
john savills file.txt
the names generated would be johnsa~1.txt, johnsa~2 etc.
After the first 4 version of a file, only the first two characters of the file name are used, and the last 6 are generated, e.g. jo0E38~1.txt
Q. How do I change access permissions on a directory?
A. You can only set access permissions on an NTFS volume. Follow the instructions below:
Q. How can I change access permissions from the command line?
A. A utility called CACLS.EXE comes as standard with
NT, and can be used from the command prompt. Read the help with the
CACLS.EXE program (cacls /?). To give user john read access to a directory
called files enter:
CACLS files /e /p john:r
/e is used to edit the ACL instead of replacing it, therefore other
permissions on the directory will be kept. /p sets permission for user:<permission>
Q. I have a CHKDSK scheduled to start next reboot, but I want to stop it.
A. If the command chkdsk /f /r (find bad sectors, recover information from bad sectors and fix errors on the disk) is run, on the next reboot the check disk is scheduled, however you may want to cancel this check disk. To do this perform the following:
Q. My NTFS drive is corrupt, how do I recover?
A. To restore an NTFS drive using the information below, it must have been created using Windows NT 4.0, if it was not created using NT 4.0 you should see Knowledge base article Q121517. To restore an NTFS partition you must locate the spare copy of the boot sector and copy it to the correct position on the drive. You need the NTdiskedit utility (you can also use Disk Probe that comes with the resource kit or Norton disk edit) which is available from Microsoft Support Services.
Q. How can I delete a file without it going to the recycle bin?
A. When you delete the file, hold down the shift key.
Q. How can I change the serial number of a disk?
A. The serial number is located in the boot sector for a volume. For FAT drives its 4 bytes starting at offset 0x27; for NTFS drives its 8 bytes starting at offset 0x48. You'll need a sector-level editor to modify the number (like the Resource Kit's Diskprobe).
Q. How can I backup the Master Boot Record?
A. The Master boot record on the hard disk used to start the computer (the system partition) is the most critical sector so make sure this is the sector you backup. The boot partition is also very important (where %systemroot% resides). You need the DiskProbe utility that comes with the Resource Kit.
Q. How do I restore the Master Boot Record?
A. Follow the instructions below, however be very careful!!!
Q. What CD-ROM file systems can NT read?
A. NT's primary file system is CDFS a read only file system, however it can read any file system that is ISO9660 compliant.
Q. How do I disable 8.3 name creation on VFAT?
A. Start the registry editor (regedit.exe) and set the value HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem\Win95TruncatedExtensions to 0.
Q. How do I create a Volume Set?
A. A volume set allows you to take all the unused space on one or more drives (up to 32 drives per volume set) and combine it into a single, large, system recognizable drive. To create a volume set:
The main problem with volume sets is that if one drive in the volume set fails, the entire volume set becomes unavailable.
Q. How do I extend a Volume Set?
A. Extending a volume set is very simple, however a reboot will be required
The reboot will take longer than normal as the new area added has to be formatted to the same file system as the rest of the volume set.
Note: Only NTFS Volume Sets can be extended.
Q. How do I delete a Volume Set?
A. When you delete a volume set all the data stored will be lost. To delete a volume set:
Q. What is the maximum number of characters a file can be?
A. This depends on if the file is being created on a FAT or NTFS partition. The maximum file length on a NTFS partition is 256 characters, and 11 characters on FAT (8 character name, . , 3 character extension). NTFS filenames keep their case, whereas FAT filenames have no concept of case (however the case is ignored when performing a search etc on NTFS). There is the new VFAT which also has 256 character filenames.
NTFS filenames can contain any characters, including spaces, uppercase/lowercase except for the following
" * : / \ ? < > |
which are reserved for NT, however the file name must start with a letter or number.
VFAT filenames can also contain any characters except for the following
/ \ : | = ? " ; [ ] , ^
and once again the file name must start with a letter or number.
NTFS and VFAT also creates a 8.3 format file name, see Q. How to LFN's work?
Q. How can I stop chkdsk at boot time from checking volume x?
A. When NT boots it performs a check on all volumes to see if the dirty bit is set, and if it is a full chkdsk /f is run. To stop NT performing this dirty bit check you can exclude certain drives. The reason you may want to do this is for some type of removable drive, e.g. Iomega drives:
Where x is the drive letter, e.g. if you wanted to stop the check on drive f: you would type autocheck autochk /k:f *. To stop the check on multiple volumes just enter the drive names one after another, e.g. to stop the check on e: and g: autocheck autochk /k:eg *, you do not retype the /k each time.
If you are using NT 4.0 with Service Pack 2 or above, you can also use the CHKNTFS.EXE command which is also used to exclude drives from the check and updates the registry for you. The usage to disable a drive is
chkntfs /x <drive letter>:
e.g. chkntfs /x f: would exclude the check of drive f:
To set the system back to checking all drives just type
chkntfs /d
Q. How can I compress files/directories from the command line?
A. A utility is supplied with the resource kit called compact.exe which can be used to view and change the compression characteristics of a file/directory.
Q. What protections can be set on files/directories on a NTFS partition?
A. When you right click on a file in Explorer and select properties (or select Properties from the File menu) you are presented with a dialog box telling you information such as size, ownership etc. If the file/directory is on a NTFS partition there will be a security tab, and within that dialog, a permissions button. If you press that button you can grant access to users/groups on the resource at various levels.
There are six basic permissions
These can be assigned to a resource, however they are grouped for ease of use
The permissions above can all be set on a directory, however this list is limited for a file, and permissions that can be set are only No Access, Read, Change and Full Control.
Another permission exists called "Special Access" (on a directory there will be two, one file files, one for directories), and from this you can set which of the basic permissions should be assigned.
Q. How can I take ownership of files?
A. Sometimes you may want to take ownership of files/directories, usually as someone has removed all access on a resource and can't see it. You would log on as the Administrator and take ownership. You cannot give ownership to someone else using standard NT functionality, only take ownership.
Q. How can I view the permissions a user has on a file from the command line?
A. A utility is supplied with the resource kit called perms.exe which can be used to view permissions on files/directories. The usage is
perms <domain>\<user> <file>
e.g. perms savilltech\savillj d:\file\john\file.dat
You can add /s to also show details of sub files/directories. The permissions shown equate to
| R | Read |
| W | Write |
| X | Execute |
| D | Delete |
| P | Change Permission |
| O | Take Ownership |
| A | All |
| None | No Access |
| * | User is the owner |
| # | A group the member is a member of owns the file |
| ? | Permissions cannot be determined |
To output to a file just add > filename.txt at the end, e.g.
perms <user> <file> > file.txt
Q. How can I tell the total amount of space used by a folder (including sub folders)?
A. There are two ways of doing this (there are more!), one using explorer and one from the command line. Using Explorer
From the command line you can just use the dir command
with /s qualifier which also lists all sub-directories,
e.g.
dir/s d:\savilltechhomepage
would list all files/folders in the savilltechhomepage directory
and at the end the total size.
Q. There are files beginning with $ at the root of my NTFS drive, can I delete them?
A. NO!!! These files hold the information of your NTFS volume. Below is a table of all the files used by the file system:
| $MFT | Master File Table |
| $MFTMIRR | A copy of the first 16 records of the MFT |
| $LOGFILE | Log of changes made to the volume |
| $VOLUME | Information about the volume, serial number, creation time, dirty flag |
| $ATTRDEF | Attribute definitions |
| $BITMAP | Contains drive cluster map |
| $BOOT | Boot record of the drive |
| $BADCLUS | A list of bad clusters on the drive |
| $QUOTA | Quota information (used on NTFS 5.0) |
| $UPCASE | Maps lowercase characters to uppercase version |
If you want to have a look at any of these files use the command
dir /ah $mft
Its basically impossible to delete these files anyway as you can't remove the hidden flag and if you can't remove the hidden flag you can't delete it!
Q. What file system do Iomega ZIP disks use?
A. By default, the formatted ZIP disks are FAT, however you can format these with NTFS is you want. NTFS has a higher overhead than FAT on small volumes (an initial 2MB) which is why you don't have NTFS on 1.44 floppy disks.
Q. What cluster size does a FAT/NTFS partition use?
A. The default cluster size for a FAT partition is as follows:
| Partition size | Sectors per cluster | Cluster size |
| <32MB | 1 | 512 bytes |
| <64MB | 2 | 1K |
| <128MB | 4 | 2K |
| <255MB | 8 | 4K |
| <511MB | 16 | 8K |
| <1023MB | 32 | 16K |
| <2047MB | 64 | 32K |
| <4095MB | 128 | 64K |
This is why FAT volumes larger than 511MB are not recommended due to the amount of potentially wasted space due to the 16KB and above cluster size.
The default for NTFS is as follows:
| Partition size | Sectors per cluster | Cluster size |
| <512MB | 1 | 512 bytes (or hardware sector size if greater than 512 bytes) |
| <1024MB | 2 | 1K |
| <2048MB | 4 | 2K |
| <4096MB | 8 | 4K |
| <8192MB | 16 | 8K |
| <16384MB | 32 | 16K |
| <32768MB | 64 | 32K |
| >32768 MB | 128 | 64K |
NTFS better balances the trade off between disk defragmentation due to smaller cluster size and wasted space due to a large cluster size.
When formatting a drive you can change the cluster size using the /a:<size> switch, e.g.
format d: /a:1024 /fs:ntfs
Q. How much free space do I need to convert a FAT partition to NTFS?
A. The calculation below can be used for disks of a standard 512 bytes per sector:
To summarize:
Free space needed = (<size of partition in bytes>/100) + (<size of partition in bytes>/803) + (<no of files & directories> * 1280) + 196096
For more information see Knowledge Base article Q156560 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q156/5/60.asp
Q. NT becomes unresponsive during an NTFS disk operation such as a dir.
A. When you perform a large NTFS disk operation such as a dir/s *.* or a ntbackup :\*.* NT can sometimes become unresponsive because NT updates NTFS files with a last access stamp and if viewing thousands of files the NTFS log file can become full and waits to be flushed to the hard disk, this can cause NT to become unresponsive. To stop NTFS updating the last access stamp perform the following:
This should improve the performance of your NTFS partitions.
Q. I have missing space on my NTFS partitions (Alternate Data Streams).
A. Its possible to hide data from both explorer and the dir command within an NTFS file that you cannot see unless you know its stream name. NTFS allows multiple streams to a file in the form of <filename>:<stream name>, you can try it
You can have as many streams as you want. If you copy a file it keeps the streams, so copying normal.txt to john.txt, john.txt:hidden would exist. You cannot use streams from the command prompt as it does not allow : in files names except for drive letters.
Microsoft provide no way of detecting or deleting these streams. The two ways to delete are
One application I have found to detect alternate data steams is by Frank Heyne and can be downloaded from http://www.heysoft.de/nt/ep-lads.htm.
Alternatively you can use Lizp which is downloadable from http://www.lizp.com. I have not used it in earnest, however what I have seen looks very good. An example use would be
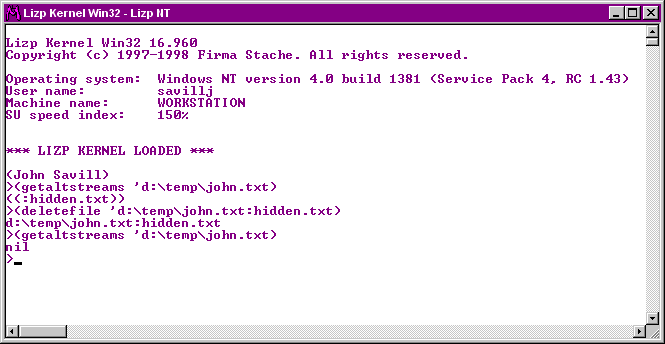
Its also possible to write a function to enumerate every altstream in
every file matching c:\winnt\*. To do this, let's define a function, we'll
call it las, and it'll take one argument, the wild path. Then we could
type
(las 'c:\winnt\*)
and we'd get what we wanted.
Here's such a function definition:
(sequence
(define
(las Dir)
(filter
'(lambda
(o)
(cdr o) )
(mapcar
'(lambda
(FileInfo)
(if
(getfilesize
(car FileInfo) )
(cons
(car FileInfo)
(getaltstreams
(car FileInfo) ) )
(cons nil nil) ) )
(dirlist Dir) ) ) )
'(Enhanced with las) )
Even though you could type all this in at the prompt, on one long line, it's easier to save the code above to a file. Let's call the file las.lzp.
Now, from the Lizp prompt, you could type
(eval (load 'las.lzp))
and voila, you'll have a new function, las. Now try the thing above:
(las 'c:\winnt\*)
Suppose we think our Lizp should have this functionality always. Then type
(Compile (load 'las.lzp) 'Lizp_with_las.exe true)
and we'll have a new version of Lizp, called Lizp_with_las.exe.
Finally, suppose we wanted a GUI application which asked us for the wild path, and then displayed the alternate streams in a window. Save the following lines to a file, let's call it las_gui.lzp:
(local
(Result)
(setq Result
(las
(inputbox
'((Wild path to check for Alt Streams)) ) ) )
(messagebox
(if Result Result
'((No Alt Streams found in path.)) ) )
(exit) )
Now, from Lizp_with_las' prompt, type
(Compile (load 'las_gui.lzp) 'Las.exe nil
and you'll have a new program, Las.exe, doing what we want. Note the last argument to the Compile function: the first time we compiled, we used "true", this last time we used "nil". This is because the first time we wanted the new program to create a console when run (because it was going to be our new Lizp interpreter). The second time we don't need a console.
Another way to delete these streams is to edit them in notepad and delete all the text. When you quit notepad NT tells you that the file is empty and will be deleted and you only have to confirm.
If you want to write your own programs to detect streams have a look at
Basically the only reliable way of handling streams is to use the BackupRead() function. The only "problem" is that BackupRead() requires SeRestorePrivilege/SeBackupPrivilege rights which most users will not have
BackupRead() actually does is to turn a file and its associated metadata (extended attributes, security data, alternate streams, links) into a stream of bytes. BackupWrite() converts it back.
Q. How can I change the Volume ID of a disk?
A. Windows NT provides functionality to change the volume name of a disk by using the command
label <drive>: <label name>
Windows NT does not provide built in functionality to change Volume ID's, however NT Internals has produced a free utility that can be downloaded from http://www.sysinternals.com/misc.htm called VolumeID which can change the volume ID of a FAT or NTFS volume. To view a drives current Volume ID you can just perform a dir <drive>: and the volume serial number is shown on the second line down, e.g.
Volume in drive E is system
Volume Serial Number is BC09-8AE4
To change enter the command
volumeid <drive letter>: xxxx-xxxx
Q. How do I read NTFS 5.0 partitions from Windows NT 4.0?
A. Service Pack 4 includes a read/write driver for NTFS 5.0 volumes (an updated ntfs.sys driver). More details will follow once Service Pack 4 is released, the non-disclosure agreement limits me from saying any more.
Q. How do share and file system protections interact?
A. In general when you have protections on a share or on a file/directory the privileges are added, for example if user John was a member of 2 groups, one with read access and another with change the user would have read and change access. The exception to this if a group has "no access" which means no mater what other group memberships there are, any user in that group will have no access.
The opposite is true when protections are set on the file system and on the share where the most restrictive policy is enforced, e.g. if the file has full control set for a user and the share only has read then the user will be limited to read-only privileges, likewise if the file had only read-only but the share had full the user would still be limited to read-only.
Share protections are only used when the file system is accessed through a network connection, if the user is using the partition locally then the share protections will be ignored.
Q. How can I backup/restore my Master Boot Record?
A. The Windows NT Resource kit supplies a utility DISKSAVE.EXE which enables a binary image of the Master Boot Record (MBR) or Boot Sector to be saved.
DISKSAVE has to be run from DOS and so you will need to create a bootable DOS disk and copy DISKSAVE.EXE to the disk. To create a DOS bootable disk just use the command
C:\> format a: /s
from a DOS machine (do not do it from a Windows NT command session).
Once you boot with the disk you will have a number of options:
F2 - Backup the Master Boot Record - This function will prompt for a path and filename to save the MBR image to. The path and filename are limited to 64 characters. The resulting file will be a binary image of the sector and will be 512 bytes in size. The MBR is always located at Cylinder 0, Side 0, Sector 1 of the boot disk.
F3 - Restore Master Boot Record - This function will prompt for a path and filename for the previously save Master Boot Record file. The only error checking is for the file size (must be 512 bytes). Copying and incorrect file to the MBR will permanently destroy the partition table information. In addition, the machine will not boot without a valid MBR. The Path/filename is limited to 64 characters.
F4 - Backup the Boot Sector - This function will prompt for a path and filename to save the Boot Sector image to. The path and filename are limited to 64 characters. The resulting file will be a binary image of the sector and will be 512 bytes in size. The function opens the partition table, searches for an active partition, then jumps to the starting location of that partition. The sector at that location is then saved under the filename the user entered. There are no checks to determine if the sector is a valid boot sector.
F5 - Restore Boot Sector - This function will prompt for a path and filename for the previously save Boot Sector file. The only error checking is for the file size (must be 512 bytes). Copying and incorrect file to the Boot Sector will permanently destroy Boot Sector information. In addition, the machine will not boot without a valid Boot Sector. The Path/filename is limited to 64 characters.
F6 - Disable FT on the Boot Drive - This function may be useful when Windows NT will not boot from a mirrored system drive. The function looks for the bootable (marked active) partition. It then checks to see if the SystemType byte has the high bit set. Windows NT sets the high bit of the SystemType byte if the partition is a member of a Fault Tolerant set. Disabling this bit has the same effect as breaking the mirror. There is no provision for re-enabling the bit once it has be disabled.
Q. How do I convert an NTFS partition to NTFS 5.0? - NT 5.0 only
A. Windows NT 5.0 introduces NTFS 5.0 which enables a number of new features. By default when you install Windows NT 5.0 it will automatically convert any NTFS 4.0 partitions to NTFS 5.0 (however this may change).
During the installation of Windows NT 5.0 if it detects any Windows NT 4.0 installations it will upgrade their NTFS.SYS (providing the systems are Service Pack 3 or above) so they to will be able to read the NTFS 5.0 partitions. Service Pack 4 also has an updated NTFS.SYS which can read NTFS 5.0 partitions.
To check the version of an NTFS partition use the CHKNTFS.EXE utility.
C:\> chkntfs <drive>:
The type of the file system is NTFS 5.0.
or
The type of the file system is NTFS 4.0
<drive>: is not dirty
If the file system is not NTFS 5.0 and you want to upgrade it use the command
C:\> chkntfs /e <drive>:
The machine will need to be rebooted for the upgrade to take place.
Q. I cannot compress files on an NTFS partition.
A. If when you try and compress files on an NTFS partition using Explorer (right click on a file/directory, select properties and check the compress box) the option is not available or when you try from the command prompt using the command:
C:\> compact /c ntfaq.txt /s
you get the error
"The file system does not support compression"
the cause is normally that the cluster size of the NTFS partition is greater than 4096. To check the cluster size of your NTFS partition use the CHKDSK command, e.g.
C:\> chkdsk <disk>: /i /c
The /i /c are used to speed up the chkdsk and at the end of the display it will tell you the bytes in each allocation unit:
2048 bytes in each allocation
unit.
1012032 total allocation units on disk.
572750 allocation units available on disk.
If this number is greater than 4096 you will need to backup all the data on the disk and then reformat the partition using any of the following methods:
Once reformatted you can then restore your backed up data.
To understand more about the 4,096 limit please read Knowledge base article Q171892 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q171/8/92.asp
Q. How can I modify the CHKDSK timer?
A. Service Pack 4 introduces a new feature which before performing a chkdsk of a disk if its dirty bit is set a 30 second countdown timer is given allowing you to cancel to chkdsk from running.
If you want to modify this 30 second value perform the following:
The change will take effect at the next reboot
Q. How can I view the current owner of a file?
A. The normal method would be to right click on the file in Explorer, select Properties, click the Security tab and click Ownership. This will then show the current owner and give the option to take ownership.
To view from the command line you can use the SUBINACL.EXE utility that is shipped with the Windows NT Resource Kit Supplement 2. To view the current owner use as follows:
C:\> subinacl /file <file name>
//++++
// D:\Documents\<file name>
//----
+ Owner = builtin\administrators
+ Primary Group= lnautd0001\domain users
+ System ACE count =0
+ Disc. ACE count =1
lnautd0001\saviljo ACCESS_ALLOWED_ACE_TYPE FILE_ALL_ACCESS
You could perform on *.* to list owners for all files in all subdirectories (no need for any /s switch).
Q. What is Distributed File System?
A. Distributed File System (or Dfs) is a new tool for NT server that was not completed in time for inclusion as part of NT 4.0, but is now available for download. It basically allows Administrators to simulate a single server share environment that actually exists over several servers, basically a link to a share on another server that looks like a subdirectory of the main server.
This allows a single view for all of the shares on your network, which could then simplify your backup procedures as you would just backup the root share, and Dfs would take care of actually gathering all the information from the other servers across the network.
You do not have to have a single tree (Dfs directory structures are called trees), but rather could have a separate tree for different purposes, i.e. one for each department, but each tree could have exactly the same structure (sales, info. etc).
For more information on DFS see http://www.microsoft.com/windows/downloads/contents/Other/NTSDistrFile/AdminGuide.asp
A. Dfs is available for download from Microsoft http://www.microsoft.com/ntserver/dfs/dfsb2.asp . Follow the instructions at the site and fill in the form about your site. The file you want for the I386 platform is dfs-v41-i386.exe.
Once downloaded just double click on the file, and agree to the license. It will then install files to your drive which you need to install.
A. Follow the instructions below, you must have first downloaded and expanded the file dfs-v40-i386.exe:
Q. How do I create a new folder as part of the Dfs?
A. Once Dfs is installed a new application, the Dfs Administrator, is created in the Administrative Tools folder. This app should be used to manage Dfs. To add a new area as part of the Dfs tree follow the procedures below:
A. Follow the procedure below:
Q. How do I assign User Rights for a standalone server (not the PDC/BDC) in a domain?
A. In NT Workstation, User Manager/Policies/User Rights... assigns the privileges (e.g. the Shutdown or Log On Locally privilege) for the local machine. However, in NT Server the User Rights you assign with User Manager for Domains affect the Domain Controller(s). To modify privileges for the local machine, first choose Select Domain... from the User menu, and type in the name of the computer at the Domain prompt (you cannot browse the domain).
Q. I can't FTP to my server, although the FTP service is running?
A. Have you unchecked the "Allow only anonymous connections" option, but still receive a "530 User xyz cannot log in. Login failed." message? To log on to the FTP server with your domain account, it is not sufficient to specify your name at the User prompt. The FTP service checks local accounts only, even if the computer is participating in a domain. Use domainname\username instead, e.g. if the domain name was savilltech and the user was john, enter savilltech\john as the username.
Q. How do I validate my NT Logon against a UNIX account?
A. There is software to do this available at
Q. Can I synchronize the time of a NT Workstation with a NT Server?
A. Yes, enter the command
NET TIME \\<name of the server to set time to> /SET /YES
Please note that users will require "Change System Time" user right, via User Manager\User rights. There is a utility on the resource kit called TimeServ which runs the time synchronization as a service and works even when there are no logged on users.
Also see Q. How do I configure a user so it can change the system time?
Q. How can I send a message to all users?
A. Ensure the "Messenger" service is started
(Control Panel - Services - Messenger - Auto). To send a message type:
c:> net send <machine name> "<message>"
Or instead of a machine name type * to broadcast to all stations
There are also various GUI utilities, and one of the best is NT Hail at http://www.geocities.com/SiliconValley/Bay/1999/NT_Hail.html
Q. How do I change a Workstations Name?
A. Follow the steps below
Q. How do I stop the default admin shares from being created?
A. This can be done through the registry.
This can also be done using the policy editor. Start the policy editor (poledit.exe), load the default computer profile, and expand the Windows NT Network tree, then Sharing and set "Create hidden drive shares" to blank for server/workstation.
There are a few other options though. The first is to use NTFS and set
protections on the files so people may be able to connect to the share,
but they will not be able to see anything. The second is to delete the
shares each time you logon, this can be done through explorer, but it
would be better to have a command file run each time with the lines
net share c$ /delete
and for all the other shares, however these shares are there for a reason
so your machine can be administered by the servers, so if you delete them
system managers may have something to say about it!
Q. How do I disconnect all network drives?
A. Use net use * /del /yes
Q. How do I hide a machine from Network Browsers?
A. Using the registry editor set the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanManServer\Parameters and set value Hidden from 0 to 1. You should then reboot. You can also type
net config server /hidden:yes
You can still connect to the computer, but it is not displayed on the browser.
A. NT does not support remote boot. It is possible to reboot a machine from another computer using the Shutdown Manager that comes with the NT resource kit.
You could also reboot by using the shutdown.exe resource kit utility and specify another machine name.
C:\>shutdown \\<machine name> /l /r /y /c
Software such as PC Anywhere can also remotely reboot machines.
Q. How can I get a list of users currently logged on?
A. Use the net sessions command, however this will only work if you are an Administrator. You can also use control panel and choose server.
Q. How do I configure NT to be a gateway to an ISP?
A. Firstly the hardware required would be a network and a modem. The network card would be so the other clients in the network can communicate with the "to be" gateway, and the modem to connect to the gateway. Dial-up networking is not covered here, and you should first be confident with dial-up networking before attempting this.
This would enable the machines to send out IP packets to the internet, however the packets would have no way of finding there way back, as the ISP would not know to route them through the gateway, so you ISP will have to either a) have host entries for each of the machines or b) point to the gateway as another DNS.
Other things to check are as follows:
Have a look at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q121/8/77.asp for more information.
Q. How do I install the FTP server service?
A. In prior version of NT, the FTP server service was installed as part of TCP/IP, however as of NT 4.0, it became part of IIS/PWS, so it needs to be installed manually. Before you install the FTP server, TCP/IP must be installed.
Q. How do I get a list of all connections to my PC?
A. Use the command netstat -a
Q. How can I get the Ethernet address of my Network card?
A. Type ipconfig /all from a command box.
Q. How can I configure the preferred Master Browser?
A. On the NT server you want to be the preferred master browser change the registry setting HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Browser\Parameters\IsDomainMaster to True
Q. Is it possible to protect against Telnet attacks?
A. There was a recent well-known problem that a telnet client could connect to an NT machine on port 135, type 10 characters and it would hang NT. There is no simple way to protect NT from a certain port attack. It is possible to configure NT to only accept incoming packets from a set of configured ports, however you have to name the ports you want to accept input from:
To protect against the port 135 attack, install the RPC hotfix for Service Pack 2.
Service Pack 3 and some its Hotfixes are also highly desirable, and address a number of Internet attack methods.
Q. What Telnet Servers/Daemons are available for Windows NT?
A. A Telnet Server on NT allows connection to an NT machine using a Telnet client from any hardware platform. Products are available from:
Q. How do I install MSN under NT?
A. The new MSN 2.0 only runs under Windows 95, however a version for NT 4.0 is being developed. In the mean time it is possible to use MSN to connect to the Internet, however you cannot read Mail
Q. What FireWall products are available for NT?
A. Below are a selection of FireWall systems for NT:
Q. How do I install the Remoteboot Service?
A. Before installing the Remoteboot service you must have both the NetBEUI and DLC protocols installed. The remoteboot service will only run on NT server.
Q. How many connections can NT have?
A. NT workstation can have up to 10 concurrent connections, with one exception, Peer Web Services which allows unlimited concurrent connections.
Q. How can I secure a server that will be a Web Server on the Internet?
A. Below are points to be aware of
Q. How can I stop a user logging on more than once?
A. There is no way in NT to stop a user logging on more than once, however it is possible to restrict a workstation so that only a certain user can login, and with this method each user would be tied to one workstation and thus could only logon once.
This solution is far from ideal, and it may be plausible to write a login script that checked if a user was currently logged on and if so, logoff straight away (using the logout command line tool).
Q. How can I get information about my domain account?
A. From the command prompt type
net user <username> /domain
And all your user information will be displayed including last logon time, password change etc.
Q. A machine is shown as Inactive in Server manager when it is not.
A. Sometimes Server Manager fails to see a machine has
become active, you can attempt to force it to see the machine by typing
net use \\<machine name>\IPC$
If this fails it may be the machine has been configured to be invisible
to the network.
Q. How do I automatically FTP using NT?
A. I use a basic script to update my main site and the mirrors using two batch files. The first consists of a few lines:
d:
cd \savilltechhomepage
ftp -i -s:d:\savmanagement\goftp.bat
The -i suppresses the prompt when performing a multiple put, and the -s defines an input file for the FTP like:
open ftp.savilltech.com - the name of the FTP
server
johnny - username
secret - password
cd /www - remotely move to a base directory
lcd download - locally change directory
cd download - remotely move to a sub directory of the
current directory
binary - set mode to binary
put faqcomp.zip - send a file
cd .. - move down a directory remotely
lcd .. - move down a directory locally
cd ntfaq
lcd ntfaq
mput *.html - send multiple files (this is why we needed
-i)
close - close the connection
Q. How can I change the time period used for displaying the password expiration message?
A. Follow Instructions below:
Q. How can I modify share permissions from the command line?
A. The Windows NT resource kit ships with a utility called RMTSHARE.EXE that is used to modify permissions on shares, the syntax to grant access to a share is as follows
rmtshare \\<server name>\<share> /grant <username>:<permission>,
e.g.
rmtshare \\bugsbunny\movies /grant savillj:f
Valid permissions are f for full, r for read, c for change and n for none. To revoke access to a share type
rmtshare \\<server name>\<share> /grant <username>,
e.g.
rmtshare \\bugsbunny\movies /grant savillj
This would remove savillj's access to the share. To view share permissions enter:
rmtshare \\<server name>\<share> /users, e.g.
rmtshare \\bugsbunny\movies /grant
RMTSHARE.EXE also allows the creation and deletion of shares. Type rmtshare /? for help.
Q. How can I change the protocol binding order?
A. Network bindings are links that enable communication between the network adapter(s), protocols and services. If you have multiple protocols installed on a machine you can configure NT to try a certain protocol first for communication:
Q. What criteria are used to decide which machine will be the Master Browser?
A. There are 5 roles a machine can have
When an election takes place, a number or criteria are used. Firstly the browser type
If two machines have the same role then the operating system is used
If there is still a tie, the Windows NT version is used
To set a machine as a certain type of browser perform the following
Q. How can I get a list of MAC to IP addresses on the network?
A. An easy way to get a list of MAC to IP addresses on the local subnet is to ping every host on the subnet and then check you ARP cache, however pinging every individual node would take ages and the entries only stay in the ARP cache for 2 minutes. An alternative is to ping the broadcast mask of your subnet which will ping every host on the local subnet (you can't ping the entire network as you only communicate directly with nodes on the same subnet, all other requests are via the gateway so you would just get a ARP entry for the gateway).
What is the broadcast mask? The broadcast mask is easy to calculate if the subnet mask is in the format 255.255.255.0 or 255.255.0.0 etc. (multiples of 8 bits). For example if the IP address was 134.189.23.42 and the subnet mask was 255.255.0.0 the broadcast mask would be 134.189.255.255, where 255 is in the subnet mask the number from the IP address is copied over, where 0 it is replaced with 255, basically the network id part is kept. If the subnet mask is not the basic 255.255 format, you should use the following, all you need is the IP address and the subnet mask
for example, IP address 158.234.24.98 and subnet mask 255.255.248.0
|
Network |
Host |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
|
Byte 1 |
Byte 2 |
Byte 3 |
Byte 4 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The first row is the subnet mask 255.255.248.0, the second row the IP address 158.234.24.98 and the third row is the broadcast mask, 158.234.31.255.
To get the MAC to IP addresses, you would therefore perform the following
ping <broadcast mask>
arp -a
Voila, a list of IP addresses and their MAC address (you can add > filename to get the list to a file, e.g. arp -a > iptomac.lst). You could repeat this exercise on the various subnets of your organization.
Unfortunatly due to limitations in NT's implementation of PING the above will not work correctly so put the following into a file
REM arpping.bat
ping -n 1 -l 1 %1.%2
arp -a %1.%2
You can then call the batch file as follows:
C:\> for /l %i in (1,1,254) do arpping 160.82.220 %i
In this case it would generate a list of all MAC to IP addresses for 160.82.220.1 to 160.82.220.254. Again you could put this all in a file, redirect to a file and then search, e.g.
REM test.bat
for /l %%i in (1,1,254) do arpping.bat 160.82.220 %%i
Notice you have to use two %%. You could run as
C:\> test.bat > file.txt
Then search listing.txt for (example) dynamic
C:\> findstr dynamic file.txt
160.82.220.1 00-00-0c-60-8b-41 dynamic
160.82.220.9 00-60-97-4b-bf-4c dynamic
160.82.220.13 00-10-4b-49-94-e1 dynamic
160.82.220.17 00-80-5f-d8-a4-8b dynamic
160.82.220.22 00-a0-d1-02-a4-cf dynamic
160.82.220.25 00-60-08-75-0d-7a dynamic
160.82.220.26 00-10-4b-44-e4-73 dynamic
160.82.220.33 00-10-4b-44-d6-33 dynamic
160.82.220.34 00-10-4b-4e-67-6a dynamic
160.82.220.35 00-60-97-4b-c4-53 dynamic
160.82.220.39 00-10-4b-44-eb-ae dynamic
160.82.220.41 00-10-4b-49-7b-f7 dynamic
160.82.220.42 00-00-f8-21-7a-7f dynamic
160.82.220.43 08-00-20-88-82-57 dynamic
160.82.220.221 00-80-5f-88-d0-55 dynamic
Q. How can I control the list of connections shown when mapping a network drive?
A. When you map a network drive (Explorer - Tools - Map network drive), if you click the down arrow on the path, a list of previous connections will be shown. These are stored on the registry and can be edited
Q. How do I grant users access to a network printer?
A. The same way as files have security information, so do printers, and you need to set which users can perform actions on each network printer
Q. How can I create a share on another machine over the network?
A. From a Windows NT Server machine a share can be created by opening Server Manager, highlight the target system, select Computer, Shared Directories, and click on New Share.
The Windows NT Resource kit comes with a utility called RMTSHARE.EXE and this can be used to create shares on other machines providing you have sufficient privilege. The basic syntax is as follows
rmtshare \\<computer name>\"<share name to be
created>"="<path>" /remark="<share
description>"
e.g. rmtshare \\savillmain\miscfiles=d:\files\misc /remark="General
files"
You only need to use double quotes around the share to be created and the path if there are spaces in the share/file name, e.g. if the share was to be called misc files instead of miscfiles it would have to be in quotes, e.g.
rmtshare \\savillmain\"misc files"="d:\my files\misc" /remark="With space share"
Q. I get errors accessing a Windows NT FTP Server from a non Internet Explorer browser.
A. If you run the Microsoft FTP Server Service then you may find problems accessing an area other than the root from a non Internet Explorer browser. This is because most other FTP Servers use the UNIX type naming conventions and that is what browsers such as Netscape expect, however the Microsoft FTP service outputs using dos naming conventions. This can be resolved by forcing the FTP server service to use Unix conventions rather than dos
You will need to stop and start the FTP server service for this change to take effect (Start - Settings - Control Panel - Services - FTP Service - stop - start)
Q. How can I view which machines are acting as browse masters?
A. There are 2 utilities shipped with the NT resource kit (one GUI, on command line) which can be used to view current browse master status.
BROWMON.EXE - Select from the Diagnostics Resource Kit menu. The master browser will then be displayed for each domain. Double clicking on a machine will then list the other machines that are browsers and a subsequent double click on these machines will tell their status, e.g. backup browser.
BROWSTAT.EXE - Start a command session. There are a
number of commands that can be used, however to get a general view enter
the command
browstat status <domain name>
Browsing is active on domain.
Master browser name is: PDC
Master browser is running build 1381
2 backup servers retrieved from master PDC
\\PDC
\\WORKSTATION
As can be seen the master browser name is shown, as are backup servers.
Q. Is there any way to improve the performance of my modem internet connection?
A. By default, NT will use a Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) (packet size) over the path to a remote host of 576. Problems can arise if the data is sent over routes etc that cannot handle data of this size and the packets get fragmented.
The parameter EnablePMTUDiscovery set to 1 forces NT to discover the maximum MTU of all connections that are not on the local subnet. To change this perform the following:
By discovering the Path MTU and limiting TCP segments to this size, TCP can eliminate fragmentation at routers along the path that connect networks with different MTUs. Fragmentation adversely affects TCP throughput and network congestion.
Q. How can I remotely tell who is logged on at a machine?
A. The easiest way to do this is to use the NBTSTAT command. There are two ways to use this command depending on if you know the machines name or just its IP address. If you know the machines name enter the command
nbtstat -a <machine name>
e.g. nbtstat -a pdc
The output will be of the format:
NetBIOS Remote Machine Name Table
Name Type Status
---------------------------------------------
PDC <00> UNIQUE Registered
PDC <20> UNIQUE Registered
SAVILLTECH <00> GROUP Registered
SAVILLTECH <1C> GROUP Registered
SAVILLTECH <1B> UNIQUE Registered
SAVILLTECH <1E> GROUP Registered
PDC <03> UNIQUE Registered
SAVILLJ <03> UNIQUE Registered
SAVILLTECH <1D> UNIQUE Registered
INet~Services <1C> GROUP Registered
..__MSBROWSE__.<01> GROUP Registered
IS~PDC.........<00> UNIQUE Registered
MAC Address = 00-A0-24-B8-11-F3
The user name is the <03>.
If you only know the IP address use the command
nbtstat -A <IP address>
e.g. nbtstat -A 10.23.23.12
The output is the same and notice we just use a capital A instead of a lowercase a.
Q. How do I remove a NT computer from a domain?
A. The first way would be to logon to the machine you wish to remove from the domain and start the Network Control Panel Applet (Start - Settings - Control Panel - Network or just right click on Network Neighborhood and select properties). Select the Identification tab and click Change. Just enter a different domain or workgroup, you will receive a notice welcoming you to the new domain/workgroup. The problem with this is the machine can still rejoin the domain as its account has not been removed from the domain.
To actually remove the computer account from the domain perform the following:
Alternatively you can remove a computer from the command line using the Resource Kit utility NETDOM
netdom /Domain:<domain> MEMBER <machine name>
/delete
e.g. netdom /Domain:savilltech MEMBER kevinpc /delete
You can use this command from any machine workstation or server as long as you are logged on as an administrator. When you enter the command it will find the PDC and delete, the output is as follows:
Searching PDC for domain SAVILLTECH ...
Found PDC \\PDC
Member \\KEVINPC successfully deleted.
Q. How can I shutdown a number of machines without going to each machine?
A. I have a number of machines setup in my Lab and at the end of an entertaining evening of computing I don't want to have to goto each machine and shut them down so I wrote a small batch file that uses the shutdown.exe resource kit utility. Just enter the following into a file with a .bat extension:
rem Batch file to shutdown local machine and the PDC, BDC
shutdown \\pdc /t:2 /y /c this shuts down a machine called
PDC in 2 seconds, repeat with other machine names
shutdown \\bdc /t:2 /y /c this shuts down a machine
called BDC in 2 seconds
shutdown /l /y /c /t:5 this line shuts down the
local machine in 5 seconds
You can then just right click the file in explorer and drag onto the desktop, release and select "Create shortcut". Clicking this icon will then shutdown all the machines in the file.
Q. How can I close all network sessions/connections?
A. The command below will close all network sessions
net session /delete
Q. How can I connect to a server using different user accounts?
A. It is possible to specify a user account to use when connecting to a share using the /user switch, e.g.
C:\> net use k: \\server\share /user:domain\user
If you then attempt to connect to the server again with a different username an error will be given. A workaround is to connect to the server using its IP address rather than its NetBIOS name, e.g.
C:\> net use l: \\<ip address>\share /user:domain\user
Q. How do I set the comment for my machine that is displayed in Network Neighborhood?
A. There are 3 ways to set this, from the command line, edit the registry or via the GUI.
The easiest way is via the Server control panel applet
An alternative method is from the command prompt using the "net config" command.
C:\> net config server /srvcomment:"machine comment"
Note that even if you are performing this on a workstation machine you still use "net config server" as this is a configuration on the server service of the machine.
Both of the methods shown update a single registry value so this can also be edited directly.
You can remotely change the comment of other machines by using the NT Server utility "Server Manager". Double click on a machine and you will then be presented with the same dialog box as with the Server control panel applet. This has the advantage of allowing the Administrator to set a common description format.
Q. How can I define multiple NetBIOS names for a machine?
A. This would be useful if, for instance, you wanted to migrate a number of shares to a different machine and rather than having to switch all clients to the new machine instantly you could define the new machine to also answer to the old machines NetBIOS name and then slowly migrate the machines. To define extra names for a machine perform the following:
Q. How can I manage my NT domain over the net?
A. Microsoft have released "Web Administrator 2.0 for Microsoft Windows NT Server" which allows you to use to manager the following via the web
The additional software required has to be installed on a server (though it does not have to be a domain controller) with
Internet Information Server 4.0 is available as part of Option Pack 4 which can be obtained from http://www.microsoft.com/windows/downloads/contents/updates/nt40ptpk/default.asp or as part of MSDN. Option Pack 4 has its own requirement that Internet Explorer 4.0 be installed.
Once all the software is installed you can download the Web Admin tools from
To begin the installation just execute the required executable and the installation wizard will begin.
Once the installation is complete you will be able to administer your domain by connecting to http://<the server name>/ntadmin/default.asp. For example if I had installed the software on titanic in the savilltech.com I would connect to http://titanic.savilltech.com/ntadmin/default.asp.
You will need Internet Explorer 4.0 or above to use the site and once connected you can perform a number of options. Below is an example of viewing/changing users.
Q. How can I remotely manage services?
A. The Windows NT Resource kit has two utilities, SC.EXE and NETSVC.EXE, which allow remote services to be managed. The resource kit has help on both on these but we will only look at NETSVC.EXE.
To view the services on a remote machine use
C:\> netsvc /query \\<server name> /list
To see the current state of a service use
C:\> netsvc <service name> \\<server> /query
You can then modify the state of the service using the /start, /stop, /pause and /continue switches, e.g.
C:\> netsvc <service name> \\<server> /stop
A. Below is a summary of all the net.exe usage methods.
net accounts
Used to modify user accounts. Specified on its own will give information about the current logon.
Options:
| /forcelogoff:<minutes or no> | Minutes until the user gets logged off after logon hours expire. No means a forced logoff will not occur |
| /minpwlen:<length> | Minimum number of characters for the password. Default is 6, valid range is between 0 and 14 |
| /maxpwage:<days> | Maximum number of days a password is valid. Default is 90, valid range is between 0 and 49710 |
| /minpwage:<days> | Number of days that must occur before the password can be changed. Default is 0, valid range is between 0 and maxpwage |
| /uniquepw:<number> | Password may not be reused for number attempts |
| /sync | Forces a domain sync |
| /domain | Performs any of the above actions on the domain controller |
net computer
Used to add and remove computer accounts from the domain.
Options:
| \\<computer name> | Name of the computer to be added or removed |
| /add | Add the specified computer |
| /del | Removes the specified computer |
net config server
Allows modifications to the server service. Entered with no parameters give details of the current configuration
Options:
| /autodisconnect:<minutes> | Number of minutes an account may be inactive before disconnection. Default is 15, valid range between 1 and 65535. -1 means never disconnected. |
| /srvcomment:"text" | Set the comment for the machine |
| /hidden:<yes or no> | Specified is the computer is hidden in the listing of computers |
net config workstation
Allows modifications to the workstation service. Entered with no parameters give details of the current configuration
Options:
| /charcount:<bytes> | Number of bytes to be collected before data is sent. The default is 16, valid range is between 0 and 65535. |
| /chartime:<msec> | Number of milliseconds NT waits before sending data. If charcount is also set whichever is satisfied first is used. Default is 250, valid range is between 0 and 65535000. |
| /charwait:<seconds> | Number of seconds NT waits for a communications device to become available. Default is 3600, valid is between 0 and 65535. |
net continue <service name>
Restarts the specified paused service.
net file
Lists any files that are open/locked via a network share.
Options:
| id | Identification of the file (given by entering net file on its own) |
| /close | Close the specified lock |
See Q. How can I tell who has which files open on a machine? for more details.
net group
Adds/modifies global groups on servers. Without parameters will list global groups.
Syntax:
net group <group name> [/command:"<text>"]
[/domain]
net group <group name> [/add [/comment:"<text>"] or
/delete] [/domain]
net group <group name> <user name> /add or /delete [/domain]
Options:
| groupname | Name of the global group |
| /comment:"<text>" | Comment if a new global group is created. Up to 48 characters |
| /domain | Performs the function on the primary domain controller |
| username | Username to which apply the operation |
| /add | Adds the specified user to the group or the group to the domain |
| /delete | Removes a group from a domain or a user from a group |
net localgroup
Performs actions on local groups. Same parameters as net group.
net name
Adds/removes a name to which messaging may be directed to. Running the command on its own will list all messaging names eligible on the machine.
Options:
| name | The messaging name to be added/removed |
| /add | Add the name |
| /delete | Remove the name |
net pause <service name>
Used to pause a service from the command line.
net print
Used to list/modify print jobs.
Options:
| \\computername | Indicates the computer that hosts the printer queue |
| sharename | Name of the printer queue |
| job | The job number to modify |
| /hold | Pauses a job on the print queue |
| /release | Removes the hold status of a job on the print queue |
| /delete | Deletes a job off of the print queue |
net send
Sends a message to a computer, user or messaging name.
Options:
| name | Name of the user, computer or messaging name. Can also use * to send to everyone in the group |
| /domain:<domain name> | All users in the current domain or the specified domain |
| /users | To all users connected to the server |
| message | The message to send |
net session
Lists or disconnects sessions. Used with no options lists the current sessions.
Options:
| \\<computer name> | The computer of whose session to close |
| /delete | Closes the session to the computer specified. Omitting a computer name will close all sessions |
net share
Used to manage shares from the command line.
Syntax:
net share <sharename>=<drive>:\<directory> [/users=<number>
or /unlimited] [/remark:"text"]
net share <sharename> [/users=<number> or /unlimited]
[/remark:"text"]
net share <sharename or device name or drive and path> /delete
Options:
| <sharename> | Name of the share |
| <device name> | Used to specify the printer name if specifying a printer share |
| <drive>:<path> | Absolute path |
| /users:<number> | Number of simultaneous connections to the share |
| /unlimited | Unlimited usage |
| /remark:"<text>" | Comment for the share |
| /delete | Delete the specifed share |
net start <service name>
Start the specified service
net statistics [workstation or service]
Gives information about either the server or workstation service.
net stop <service name>
Stops the specified service
net time
Used to synchronize the time of a computer.
Options:
| \\<computer name> | The name of the computer to which synchronize the time |
| /domain:<domain> | Synchronize the time with the specified domain |
| /set | Sets the time |
net use
Connects or disconnects to a network share. Used with no qualifiers lists the current network mappings.
Syntax:
net use <device name> or * \\<computer name>\<share name>
[password or *] [/user:[domain\user] /delete or [persistent:[yes or no]]
net use <device name> /home /delete or /persistent:[yes or no]
Options:
| <device name> | Name of the device to map to. Use * to use the next available device name |
| \\computer name | The name of the computer controlling the resource |
| \sharename | Name of the share |
| \volume | Name of the volume if on a NetWare server |
| password | Password to which to map |
| * | Gives a prompt to which to enter the password |
| /user:<domain>\<user> | Specifies the user to connect as |
| /home | Connects to a users home directory |
| /delete | Closes a connection |
| /persistent:[yes or no> | Sets if the connection should be reconnected at next logon |
net user
Used to add/create/modify user accounts
Syntax:
net user <username> [password or *] [/add] [options] [/domain]
net user <username] /delete /domain
| username | The name of the account |
| password | Assigns or changes a password |
| * | Gives a prompt for the password |
| /domain | perform on a domain |
| /add | Creates the account |
| /delete | Removes the account |
| /active:[yes or no] | Activates or deactivates the account |
| /comment:"<text>" | Adds a descriptive comment |
| /counterycode.nnn | nnn is the number operating system code. Use 0 for the operating systems default |
| /expires:<date or never> | The expiry date of the account. Date format is mm,dd,yy or dd,mm,yy which is determined by the country code |
| /fullname:"<name>" | The full name of the account |
| /homedir:<path> | Path for the users home directory |
| /passwordchg:[yes or no] | Used to specify if the user can modify the password |
| /passwordreq:[yes or no] | Used to determine if the account needs a password |
| /profilepath:<path> | Used to specify the profile path |
| /scriptpath:<path> | Path of the logon script |
| /times:<times or all> | Hours user may logon |
| /usercomment:"<text>" | A comment for the account |
| /workstations:<machine names> | Names the user may logon to. * means all. |
net view
Lists shared resources on a domain. Used with no parameters lists all machine accounts in a domain.
Options:
| \\computer name | Specifies the computer whose resource should be viewed |
| /domain:<domain name> | The domain to be used |
| /network:<NetWare network> | A NetWare network to be used |
Q. How can I make net.exe use the next available drive letter?
A. The normal syntax to map a network drive is
C:\> net use <drive letter>: \\<server>\<share>
however this can be modified to
C:\> net use * \\<server>\<share>
which will make the net use command utilize the next available drive letter.
Q. How can I check if servers can communicate via RPC's?
A. Exchange ships with RPINGS.EXE and RPINGC32.EXE which can be used to test RPC communication between two servers. These programs are located in the SERVER\SUPPORT\RPCPING directory of the Exchange CD. Test as follows:
The connection will then be checked. Once complete close the RPINGC32.EXE utility by clicking Exit and on the target machine enter the sequence '@q'.
Below is an example of a successful test.
Q. How do I change Domain Names?
A. This is not so much a procedure but things to think about.
Q. How do I move a Workstation to another Domain?
A. Logon to the Workstation locally as Administrator (i.e. name of machine) and goto Control Panel. Double click Network and click change. Enter the new Domain name and click OK. You will receive a message "Welcome to Domain x". Reboot the machine and you are part of the new domain.
If you wish to administer this box from the new domain you will need to add <Domain>\DomainAdmins to the local administrators group by connecting to the local user database via User Manager for Domains (i.e. \\computername)
Q. How many user accounts can I have in one Domain?
A. The real problem is that each user account and machine account takes up space in the SAM file, and the SAM file has to be memory resident. A user account takes up 1024 bytes of memory (a machine account half as much), so for each person (assuming they each had one machine) would be 1.5 KB. This would mean for a 10,000 user domain each PDC/BDC would need 15MB of memory just to store the SAM! Imagine a network with 100,000 people. This is one of the reasons you have multiple domains and then setup trust relationships.
Q. How to I change my server from Stand Alone to a PDC/BDC?
A. You cannot change the role of a NT server, you will need to reinstall NT.
A. A PDC is a Primary Domain Controller, and a BDC is a Backup Domain Controller. You must install a PDC before any other domain servers. The Primary Domain Controller maintains the master copy of the directory database and validates users. A Backup Domain Controller contains a copy of the directory database and can validate users. If the PDC fails then a BDC can be promoted to a PDC. Possible data loss is user changes that have not yet been replicated from the PDC to the BDC. A PDC can be demoted to a BDC if one of the BDC's is promoted to the PDC.
Q. How many BDC's should I have?
A. Microsoft say one BDC for every two thousand users. This is fine considering a 486DX2 with 32MB of RAM can, on average, perform at least 10 logons per minute, however if everyone in your company arrives at 9:00 on the dot and log on (except for the helpful people who arrive half an hour late) there will be a surge of logon requests to deal with, resulting in large delays. To try and improve on this, it is possible to configure the Server service to throughput for Network Applications rather than File Applications. Remember the more powerful the processor, the more logons (for a Pentium 133, would be able to logon at least 30 people).
Q. How do I configure a Trust Relationship?
A. Domains by default are unable to communicate with other domains, which means somewhere in domain x cannot access any resource that is part of domain y. Before a trust relationship is configured
After a trust relationship is defined, say x trusts y the following happens
In the example above x is the trusting domain, and y is the trusted domain. Also the above is a one-way trust relationship, i.e. while domain y users can use domain x resources, users of domain x cannot use domain y resources. A two-way relationship would allow each domain to access resources of the other (if given permission).
The basics of a trust relationship is to first configure domain y to allow domain x to trust it, and then configure domain x to trust domain y:
Q. How do I terminate a Trust Relationship?
A. Firstly you have to stop domain x trusting domain y, then remove domain x's ability to trust domain y:
Q. How can I join a domain from the command line?
A. The NT Resource Kit Supplement 2 ships a new utility called NETDOM.EXE which can be used to not only join domains, but create computer account and trust relationships.
To join a domain there are 2 paths, the first is to just add the computer to the domain and create the computer account simultaneously which is OK if you are logged on as a domain administrator, if you are not a domain administrator the account needs to be added in advance and then you join the domain.
If you are logged on as a domain administrator then enter the command below to create the account and join the domain
netdom /domain:savilltech /user:savillj /password:nottelling
member <computer name> /joindomain
where <computer name> is the name of your machine, e.g.
johnstation
If you are not an administrator the domain admin people will have to add you an account first using either server manager or using NETDOM.EXE
netdom /domain:savilltech /user:savillj /password:nettelling member <computer name> /add
Once the account has been add the normal user could join the domain using the first command shown.
Q. How do I demote a PDC to a BDC?
A. Normally when you promote a BDC to the PDC, the existing PDC is automatically demoted to a BDC, but in the event that the PDC was taken off line and then a BDC promoted when the old PDC is restarted it will still think its the PDC and when it detects another PDC it will simply stop its own netlogon service.
To actually modify the machine to be a BDC the registry needs to be changed directly:
Q. How can I configure a BDC to automatically promote itself to a PDC if the PDC fails?
A. There is no way to do this, the assumption is that the PDC would be configured to write out the dump information and then reboot itself thus coming back online. You configure this behavior using the System Control Panel Applet - Startup/Shutdown tab.
A. To rename a Primary Domain Controller perform the following:
To Rename a Backup Domain Controller
Note: If the BDC begins to receive 7023 or 3210 errors after synching the domain in server manager, on the PDC choose the BDC and then synch that specific BDC with the PDC. After an event indicating that the synch is complete, restart the BDC.
Q. Can I move a BDC to another domain?
A. Normally no, the BDC shares a common SID with the PDC of the domain and so there is no way to move a BDC to another domain, you would need to reinstall the BDC.
System Internals have released NewSID 3.0 ( from http://www.sysinternals.com) which has a SID-synchronizing feature that let's you have one machine copy the SID of another. This makes it possible to move a BDC to a new domain. On the BDC start NewSID and click "Synchronize SID", enter the name of the PDC and click OK.
Q. Can I change a PDC/BDC into a stand-alone server?
A. No, the PDC/BDC registry is different from that of a stand alone server, again a reinstallation would be needed.
Q. Can I administer my domain from an NT Workstation?
A. Yes, if you install the NT Server client based Administration tools:
Q. In what order should I upgrade my PDC and BDC's from 3.51 to 4.0?
A. The two different versions can coexist happily so you can upgrade in order you want however the safest option may be the following schedule:
Q. What tuning can I perform on PDC/BDC Synchronization?
A. There are several registry settings that can be configured for PDC/BDC Synchronization :
These are all values under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Netlogon\Parameters
| ChangeLogSize (REG_SZ) | Default size for the Change Log. By default 64KB with a maximum of 4MB |
| Pulse | This determines the gap in seconds between replication from the PDC to the BDC's. The lowest value is 60, and the max is 3600 (1 hour). The default is 300 (5 minutes). You may want to increase this time if the BDC's are over a slow WAN link. |
| PulseConcurrency | The number of BDC's that the PDC sends pulses to concurrently. By default this is 10. |
| PulseMaximum | The PDC performs a check that the BDC's are still there every so often. This is in seconds and once again the minimum is 60 and the maximum is 86,400. |
| Randomize | The number of seconds a BDC waits after an announcement before answering. 1 by default. |
| ReplicationGovernor | This is a percentage of the 128K blocks that are sent. If you had a slow link you may not want the PDC sending 128K blocks so you could change this to 25, meaning only 32K would be sent at a time. This will mean that the blocks are sent more frequently (25 would mean 4 times as often). |
| Update | By default this is set to no, which means only changes are replicated. Setting this to Yes will cause everything to be replicated even if there is no change. This needs to be set on the import server. |
Q. I cannot add a BDC over a WAN.
A. To add a BDC to a domain, the PDC has to be contactable. Therefore the first task is to check that communications are working.
If you are using TCP/IP then ensure you can PING the PDC,
ping <ip address of the PDC>
If this is OK then the problem is at the NetBIOS level. If you have WINS on the network ensure the BDC is configured to use the WINS server as when the PDC starts it will register the WINS name <domain><1Bh> which is used to identify the domain controller.
Alternatively the LMHOSTS file can be updated.
To use the lmhosts file during installation you should create the file on another machine and copy it over when the BDC is being installed.
Q. How can I synchronize the domain from the command line?
A. To force a domain synchronization use the command
net accounts /sync
Q. How can I force a client to validate its logon against a specific domain controller?
A. Before answering this is is best to understand what happens when a login occurs.
When a logon request is made to a domain, the workstation sends out a request to find a domain controller for the domain. The domain name is actually a NetBIOS name that is a 16-character name with the 16th character used by Microsoft networking services to identify the NetBIOS type.
The type used for a domain controller is <1C> and so the NetBIOS name for domain controller of domain "SAVILLTECH" would be "SAVILLTECH <1C>" The NetBIOS type has to be the 16th character, hence the name of the domain has to be filled with blanks to make its length up to 15 characters.
If the client is WINS enabled then a query for the resolution of "<domain name> <1C>" will be sent to the WINS server as defined in the clients TCP/IP properties. The WINS server will return up to 25 IP addresses that correspond to domain controllers of the requested domain, a \mailslot\net\ntlogon is broadcast to the local subnet and if the workstation receives a response then it will attempt logon with the local domain controller.
If WINS is not configured then it is possible to manually configure the LMHOSTS file on the Workstations to specify the Domain Controller. This file is located in the %systemroot%\system32\drivers\etc directory.
An example entry in LMHOSTS would be as follows
200.200.200.50 titanic #PRE #DOM:savilltech #savilltech domain controller
The above sets up IP address 200.200.200.50 to be host Titanic, which is the domain controller for savilltech and instructs the machine that this entry is to be preloaded into the cache.
To check the NetBIOS name cache you can use command nbtstat -c, which will show all the entries including their type. If WINS is not configured and there is no entry in LMHOSTS then the Workstation will send out a series of 3 broadcasts. In the situation where no response is received and WINS is configured to use DNS for WINS resolution a request to the DNS server will be sent and finally the HOSTS file checked. If all of this fails then an error "A domain controller for your domain could not be contacted.
To force a client to use a specific domain controller we need only do the following:
The machine is now configured to broadcase for a domain controller on a local subnet and then query a name server. If no domain controllers are found on the WINS server, or WINS is not used it will then search the LMHOSTS file. The next stage is to edit this file.
Q. How do I promote a server to a domain controller? - NT 5.0 only
A. Windows NT 5.0 ships with a utility, DCPROMO.EXE, which is used to promote a stand-alone/member server to a domain controller and vice-versa.
In Windows NT 5.0 domains are DNS names which means you can have a hierarchy of domains leading to parent-child domain relationships. The advantage of these parent-child relationships is that there have a bidirectional transitive trust which means that if domain b is a child of domain a, and domain c is a child of domain b, domain c implicitly trusts domain a. This is very different from the way trusts work in earlier versions of Windows NT.
Since Windows NT 5.0 domains rely on DNS it is vital that DNS is correctly configured to enable the domain to be created (if you are creating a new top level domain). Information on configuring DNS for a domain can be found here.
A final pre-requisite is that an NTFS 5.0 volume is required to house the SYSVOL volume and so ensure you have at least one NTFS 5.0 volume (use CHKNTFS to check the versions of your partitions).
To upgrade a stand-alone/member server to a domain controller perform the following:
You now have a Windows NT 5.0 domain controller. Additional domain controllers (old BDC's) can be added by performing the above and selecting "Replica domain controller in existing domain" in step 3. It would then ask you the name of the domain to replica.
Q. How can I generate a list of all computer accounts in a domain?
A. The normal method under Windows NT 4.0 and earlier is to use Server Manager (Start - Programs - Administrative Tools - Server Manager) and computer accounts can be viewed/added/deleted.
Under Windows NT 5.0 this information can be viewed using the Active Directory MMC (Microsoft Management Console) snap-in and browse the domain/Computers group. Of course under Windows NT 5.0 and the Active Directory computers can also be created in Organisation Units so would not all be shown under this tree (as shown below the computer account in the law OU would not be listed in the Computers group).
A more complete method is to use the Windows NT Resource Kit NETDOM.EXE utility (which runs under Windows NT 5.0) to generate the list, e.g.
C:\> netdom member
Searching PDC for domain SAVILLTECH ...
Found PDC \\TITANIC
Listing members of domain SAVILLTECH ...
Member 1 = \\ODIN
Member 2 = \\garfield
It is also possible to list other domains using a mixture of command line switches, e.g.
C:\> netdom /d:<domain name> [/u:<domain>\<user to which query> /p:<password] member
The information in the [] is only needed if your account does not have privileges in the requested domain.
The advantage of the command line tool is it lists all computer accounts, even those in OU's in the Active Directory.
An alternative method is to use the net view /domain:<domain> command which has the advantage that you can pipe the output to a file or another command, e.g.
C:\> net view /domain:savtech
Q. How can I verify my Windows NT 5.0 domain creation? - NT 5.0 only
A. To verify the tcp/ip configuration is OK check for the ldap.tcp.<domain> service record, e.g. ldap.tcp.savilltech.com
C:\> nslookup
> set type=srv
> ldap.tcp.savilltech.com
Server: [200.200.200.50]
Address: 200.200.200.50
ldap.tcp.savilltech.com SRV service location:
priority = 0
weight = 0
port = 389
svr hostname = titanic.savilltech.com
titanic.savilltech.com internet address = 200.200.200.50
Also make sure the NetBIOS computer name is OK
C:\> net view \\<computer name>
Finally check the NetBIOS Domain name works
C:\> usrmgr <domain name>
The NetBIOS domain name is used for backwards compatibility.
Q. How do I connect two Workstations using RAS?
A. NT Workstation supports one inbound RAS connection so one NT station will be the RAS server, and one will be the client. The procedure below is what I did to connect two machines.
Server
If RAS is already installed
If RAS is not already installed, goto “My Computer” and double click “Dial-up Networking”, it will then detect your modem and then take you to step 3 as above.
Client
This assumes RAS is not installed
Q. Is it possible to dial an ISP using the command line?
A. Yes, use RASPHONE -d <entry>. To disconnect you can type RASPHONE /disconnect.
Q. How can I stop the RAS connections closing when I logoff?
A. Perform the following:
Q. How can I create a RAS Connection Script?
A. It is possible to write a script that will run when you connect during a RAS connection to automate actions such as entering your username and password. To specify a script perform the following
An example addition to the SWITCH.INF would be
; the phonebook entry
[Savill1]
; send initial carriage return
COMMAND=<cr>
; wait for : (after username, may be different at your site) omit the U
as it may be capitals. You could just have :
OK=<match>"sername:"
LOOP=<ignore>
; send username as entered in the connection dialog box, alternaticly you
could just enter the username e.g. savillj<cr>
COMMAND=<username><cr>
; wait for : (after password this time, may be different at your site)
OK=<match>"assword:"
LOOP=<ignore>
; send the password entered in the connection dialog box, again you could
just manually enter the password, e.g. password<cr>
COMMAND=<password><cr>
NoResponse
; send the "start ppp" command
COMMAND=ppp default<cr>
OK=<ignore>
In depth information on all of the commands can be found in the SWITCH.INF file.
Q. How can I debug the RAS Connection Script?
A. It is possible to create a log file of the connection by performing the following steps
Each dial-up session will now be appended to the file %systemroot%/system32/RAS/device.log. To stop logging perform the steps above but set the value back to 0.
Q. How do I configure RAS to connect to a leased line?
A. The method will vary depending on your systems current setup, however assuming you have RAS already installed below are the actions needed to configure in your leased line. It is assumed the modems (at both ends) are configured correctly for leased line usage (&D0 for DTR override).
You should now configure the RAS connection (server/client) in the normal way (use the RAS service properties).
Once this has been done you may also want a phonebook entry for outgoing use as you would normally except under the Dialing section check the "Persistent connection" box.
Q. How can I disable RAS AutoDial?
A. The easiest way to do this is to disable the RAS AutoDial service:
To re-enable you would repeat the above but change the startup to automatic.
Q. RAS tries to dial out even on local resources.
A. Perform the following:
You may also wish to add addresses to the disabled list:
You will need to reboot the machine in both of the above cases.
A. When you configure the RAS server you set for each protocol the scope of the connection, the server or the whole network. To change this perform the following:
Clients should now be able to view the entire network.
Q. How do I force the "Logon Using Dialup Networking" to be checked by default on the logon screen?
A. This can be accomplished with a registry change on each client machine.
Q. Where are the RAS phone book entries and settings stored?
A. The actual phone book entries are stored in the file %systemroot%/system32/ras/rasphone.pbk (pbk - phone book). You could therefore copy this file to another machine to copy the phone book entries.
Another important file is %systemroot%/system32/ras/switch.inf which is used to create terminal login scripts (as discussed earlier in this section), and you may find phone book entries may refer to an entry in this file at the end of the entry:
DEVICE=switch
Type=Terminal
In this case, Type=Terminal means bring up a terminal window after connection so it does not use switch.inf,
DEVICE=switch
Type=Pipex
would cause the script "Pipex" (which is in switch.inf) to be run once a connection has been made. If these two lines are missing don't worry, it just means you don't need a terminal window once you have connected (probably means you are connecting to a Windows NT box). Usually if you connect to a non-NT machine you have to send it a username and password, along with the connection type (protocol), which is usually PPP on most modern systems, SLIP is an older option.
RAS information relating to phone book entries and outbound connections in the registry is actually stored under HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\RAS Phonebook, and contains details about redial attempts, display settings etc. Again you export this section of the registry to a reg file (using regedit.exe) and import into another machine to copy the machine specific settings.
Q. How can I change the number of rings that RAS server waits for before answering?
A. The normal method is to edit the file %systemroot%\system32\ras\modem.inf. Edit the file, find the sections relating to your modem and find the line
COMMAND_LISTEN=ATS0=1<cr>
Change the numeric value to the number of rings to answer after, e.g.
COMMAND_LISTEN=ATS0=10<cr>
would answer after 10 rings (you must really hate your users, don't we all :-) ). You must restart Windows NT for this change to take effect.
The above does not work if RAS is using any TAPI (Telephony Application Programming Interface )/Unimodem-based devices. If this is the case perform the following:
A. By default the RAS Server will wait 12 seconds before calling back a RAS client however this can be changed by editing the registry.
Q. Whenever I connect via RAS I cannot connect to local machines on my LAN.
A. To enable WWW and FTP browsing when you connect via RAS you enable the "use default gateway on remote network" of the RAS options. This has the effect of when the connection is made a new route is added to the route list superseding the existing LAN routes so any traffic destined for a node outside your local subnet will attempt to be sent using the RAS route. This is because a metric is used to identify the number of hops needed and once connected to RAS it will have a metric 1 and existing routes will be bumped out to a metric of 2.
To solve this a persistent route can be manually added for your LAN's subnet and the associated subnet gateway. While not connected via RAS you can examine your route information using the ROUTE PRINT command:
If your network was 160.82.0.0 (your company has a class B address) and the gateway was 160.82.220.1 for your local subnet you can add a route for the LAN only and all addresses outside of 160.82.0.0 will be routed using the RAS gateway.
C:\>route -p add <ip network> mask <subnet mask>
<local gateway for the route>
e.g. C:\>route -p add 160.82.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
160.82.220.1
This would mean all addresses from 160.82.1.1 to 160.82.254.254 would be routed via 160.82.220.1 and anything else via the RAS gateway.
When connected via RAS you will still be able to access resources outside of your local subnet on the LAN with no problems.
Q. How can I disable the "Save Password" option in dial-up networking?
A. When you connect via RAS you can cache the password. If you feel this is a security problem then you can disable the option to enable the password to be saved.
If you disable the "save password" make sure "redial on link failure" is not activated as one redial attempts as it does not save user information it will attempt to connect as Administrator which will not work (unless the ISP has very poor security :-) ).
Q. How can I set the number of Authentication Retries for Dial-Up connections?
A. By default after two unsuccessful authentication attempts the dial-up networking (DUN) component will hang up the line however this can be changed to between 0 and 10. 0 means the line will be hung up after the first attempt, 1 will allow one retry etc.
Q. How can I set the Authentication Time-out for Dial-Up connections?
A. As well as changing the number of Authentication Retries that are allowed, the amount of time between each attempt can also be configured and after that time has elapsed it will count as a logon failure. This can be between 20 and 600 seconds.
Q. Enabling 128-bit RAS Data Encryption.
A. Service Pack 3 (128 bit version) introduced the ability to use 128-bit RAS data encryption with a Windows NT 4.0 RAS server as opposed to the normal 40-bit encryption.
To enable this 128-bit encryption perform the following:
It is now necessary to enable the 128-bit setting:
After reboot is completed clients connecting via RAS or PPTP will have to authenticate using 128-bit key encryption. A number of event logs can be viewed using Event Viewer (Start - Programs - Administrative Tools - Event Viewer).
If a successful connection is made you will see the log:
Event ID: 20107
Source: RemoteAccess
Description: The user RAS connected to port COMx using strong encryption
If the connection was unsuccessful you will see entry
Event ID: 20077
Source: RemoteAccess
Description: An error occurred in the Point to Point Protocol module on
port COMx. The remote computer does not support the required encryption
type.
The client attempting connection would also receive a 629 error.
A. If you are viewing this page on the web then you are using TCP/IP now! TCP/IP is a suite of related protocols and utilities used for network communications. TCP/IP is actually two protocols, Internet Protocol (IP) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). There are many different implementations of TCP/IP however they all conform to a standard which means different implementations can communicate with each other.
Each machine that uses TCP/IP must have a unique TCP/IP address which is a 32 bit number, which is usually displayed in the dotted quad (or dotted decimal) format xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where xxx is a number from 0 to 255, for example the IP address 147.98.26.11 is shown in its 32 bit form, and how it breaks down into the dotted quad format
|
10010011 |
01100010 |
00011010 |
00001011 |
|
147 |
98 |
26 |
11 |
TCP/IP was originally used on ARPANET, a military network and grow to universities and is now used on virtually every computer system. Have a look at http://rs.internic.net/nic-support/15min/modules/arpanet/sld01.html for more information on Arpanet.
A. Below are the instructions on installing non-DHCP clients:
Q. Is there a way to trace TCP/IP traffic using NT?
A. As part of the Systems Management Server there is a Network Monitor module which enables the entire network to be monitored, also traffic over a modem. There is a limited version of this with NT 4.0 server, however only communications between the server and other computers can be monitored. The Network Monitor Service has to be installed (Control Panel - Network - Services - Add).
There are also 3rd party products available that are superior to Network Monitor, such as NetXRay from http://www.cti-llc.com/cinco.htm which retails for around $999.
Q. I do not have a network card, but would like to install TCP/IP.
A. Microsoft provide a Loopback adapter that can be used for the testing of TCP/IP. To install the Loopback adapter perform the following actions:
Q. I have installed TCP/IP, what steps should I use to verify the setup is correct?
A. Follow the steps below:
Q. How can I trace the route the TCP/IP packets take?
A. In general TCP/IP packets will not always take the same route to a destination, however the start of the journey is likely to be the same, i.e. to your gateway, to the firewall etc. The command to use is tracert and the syntax is as follows
c:\tracert <host name or IP address>,e.g.
c:\tracert news.savilltech.com
Tracing route to news.savilltech.com [200.200.8.55]
over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 <10 ms <10 ms <10 ms 200.200.24.1 200.200.200.24.1
is the gateway
2 <10 ms 10ms <10 ms 200.200.255.81
3 30 ms 10 ms 10 ms news.savilltech.com [200.200.8.55]
Trace complete
The first column is the hop count, the next 3 columns show the time taken for the cumulative round-trip times (in milliseconds), the 4th column is the hostname if the IP address was resolved, and the last column is the IP address of the host. It is really like a street map telling each turn to take. An important thing to note is to look for looping routes, so host a goes to b then c then back to a, as this indicates a problem usually.
Tracert will not always work with some FireWalls for hosts outside the FireWall.
A. As has been shown the IP address consists of 4 octets and is usually displayed in the format 200.200.200.5, however this address on its own does not mean much and a subnet mask is required to show which part of the IP address is the Network ID, and which part the Host ID. Imagine the Network ID as the road name, and Host ID as the house number, so with "54 Grove Street", 54 would be the Host ID, and Grove Street the Network ID. The subnet mask shows which part of the IP address is the Network ID, and which part is the Host ID.
For example, with an address of 200.200.200.5, and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, the Network ID is 200.200.200, and the Host ID is 5. This is calculated using the following:
| IP Address | 11001000 | 11001000 | 11001000 | 00000101 |
| Subnet Mask | 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111111 | 00000000 |
| Network ID | 11001000 | 11001000 | 11001000 | 00000000 |
| Host ID | 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000101 |
What happens is a bitwise AND operation between the IP address and the subnet mask, e.g.
1 AND 1 = 1
1 AND 0 = 0
0 AND 1 = 0
0 AND 0 = 0
There are default subnet masks depending on the class of the IP address as follows:
Class A : 001.xxx.xxx.xxx to 126.xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx uses subnet mask
255.0.0.0 as default
Class B : 128.xxx.xxx.xxx to 191.xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx uses subnet mask
255.255.0.0 as default
Class C : 192.xxx.xxx.xxx to 224.xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx uses subnet mask
255.255.255.0 as default
Where's 127.xxx.xxx.xxx ??? This is a reserved address that is used for testing purposes. If you ping 127.0.0.1 you will ping yourself :-)
The subnet mask is used when two hosts communicate. If the two hosts are on the same network then host a will talk directly to host b, however if host b is on a different network then host a will have to communicate via a gateway, and the way host a can tell if it is on the same network is using the subnet mask. For example
Host A 200.200.200.5
Host B 200.200.200.9
Host C 200.200.199.6
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
If Host A communicates with Host B, they are both have Network ID 200.200.200 so Host A communicates directly to Host B. If Host A communicates with Host C they are on different networks, 200.200.200 and 200.200.199 respectively so Host A would send via a gateway.
Q. What diagnostic utilities are there for TCP/IP?
A. We have already seen PING and TRACERT, and below is a full list
For more information on these commands just enter the command with a -?, e.g. netstat -?
Q. What is routing and how is it configured?
A. When host a wants to send to host b, if they are on the same local network then the IP protocol resolves the IP address to a physical address using ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), and the physical address (e.g. 00-05-f3-43-d3-3e) of the source and destination hosts are added to the IP datagram to form a frame, and using the frame, the two hosts can communicate directly with each other.
If the 2 hosts are not on the same local network, then they cannot communicate directly with each other, and instead have to go through a router. You have probably already come across a router when you install TCP/IP, as the default gateway is just a router that you have chosen to use as a means of communicating with hosts outside your local network if no specific route is known. A router can be a Windows NT computer with 2 or more network cards (one card for connection to each separate local network) or it can be a physical hardware device, such as Cisco routers.
Assuming our two hosts are not on the same local network, host A will check its routing table for a router that connects to the local network of host B. If it does not find a match then the data packets will be send to the "default gateway". In most cases, there will not be one router that connects straight to the intended recipient, rather the router will know of another route to pass on your packet, which will then goto another router etc.
For example:
Host A - 200.200.200.5
Host B - 200.200.199.6
Subnet Mask - 255.255.255.0
Router - 200.200.200.2 and 200.200.199.2
Host A's routing table - Network 200.200.199.0 use router 200.200.200.2
In this example, Host A would deduce that Host B is on a separate network, as its Network ID is 200.200.199. Host A would then check its routing table and see that it knows for network 200.200.199 (the zero means all) it should send to 200.200.200.2. The router would receive the packets and then forward them to network 200.200.199.
What actually happens is each router will have its own routing table that will point to other routes.
To actually configure a route, you use the route command, for example to configure a root for network 200.200.199 to use router 200.200.200.2 you would type
route -p add 200.200.199.0 mask 255.255.255.0 200.200.200.2
The -p makes the addition permanent, otherwise it will be lost with a reboot.
To view your existing information type route print.
A. ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol and was touched on in the previous question as a means of resolving a IP address to an actual physical network card address.
All network cards have a unique 48 bit address, that is written as six hexadecimal pairs, e.g. 00-A0-24-7A-01-48, and this address is hard coded into the network card. You can view your network cards hardware address by typing
ipconfig /all
.
Ethernet adapter Elnk31:
Description . . . . . . . . : ELNK3 Ethernet Adapter.
Physical Address. . . . . . : 00-A0-24-7A-01-48
DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . : No
IP Address. . . . . . . . . : 200.200.200.5
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . : 200.200.200.1
Primary WINS Server . . . . : 200.200.50.23
Secondary WINS Server . . . : 200.200.40.190
As discussed in the Subnet question, if a packets destination is on the same local network as the senders, then the sender needs to resolve the destinations IP address into a physical hardware address, otherwise the sender needs to resolve the routers IP address into a physical hardware address. When a NT machines TCP/IP component starts, it broadcasts an ARP message with its IP to hardware address pair. The basic order of events for sending to a host on the local network is as follows:
If you are sending to a destination not on your local network, then the process is similar except the sender will resolve the routes IP address instead.
To inspect your machines ARP cache, type:
arp -a
and a list of IP address to hardware address pairs will be shown. Try
pinging a host on your local network and then displaying the ARP cache
again and you will see an entry for the host, also try pinging a host
outside your local network and check the ARP cache and an entry for the
router will have been added. You will notice that the
word dynamic is listed with the records, and this is because they were
added as needed and are volatile, hence will be lost on reboot. In fact
the entries will be lost quicker than this! If an entry is not used again
within 2 minutes then it will be deleted from the cache. If it is used
within 2 minutes, it will not be deleted for a further 10 minutes, unless
used again and then it would be ten minutes from when used :-).
You may wish to add static entries for some hosts (to save time with the
ARP requests) and the format is
arp -s <IP address> <hardware address>, e.g.
arp -s 200.200.200.5 00-A0-24-7A-01-48
Q. My Network is not connected to the Internet, can I use any IP address?
A. The basic answer would be Yes, however it is advisable to use one of the following ranges which are reserved for use by private networks:
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 this is a single class A network
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 this is a group of 16
contiguous class B networks
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 this is a contiguous
group of 256 class C networks
The addresses above are detailed in RFC 1918 (Request for comment). The advantage of these addresses is that they are automatically filtered out by routers, thus protecting the internet. Obviously if you did one day want to part of your network on the internet you would need to apply for a range of IP addresses (from Internic or from your ISP).
Q. How can I increase the time entries are kept in the ARP cache?
A. The default 2 minutes can be changed by performing the following:
Q. What other registry entries are there for TCP/IP?
A. There is a whole knowledge base article on them that may be useful at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q120/6/42.asp .
Q. How can I configure more than 6 IP addresses?
A. Using the TCP/IP configuration GUI you are limited to 6 IP addresses however more can be added by directly editing the registry:
Q. What are the common TCP ports?
A. Below is a list of the most common TCP ports.
| Keyword | Port | Description |
| echo | 7 | Echo |
| systat | 11 | Active Users |
| qotd | 17 | Quote of the day |
| msp | 18 | Message Send Protocol |
| ftp-data | 20 | File Transfer (Data Channel) |
| ftp | 21 | File Transfer (Control) |
| telnet | 23 | Telnet |
| smtp | 25 | Simple Mail Transfer |
| name | 42 | TCP Nameserver |
| bootps | 67 | Bootstrap Protocol Servre |
| bootpc | 68 | Bootstrap Protocol Client |
| tftp | 69 | Trival File Transfer |
| gopher | 70 | Gopher |
| finger | 79 | Finger |
| www | 80 | World Wide Web |
| kerberos | 88 | Kerberos |
| pop | 109 | TCP post office |
| nntp | 119 | USENET |
| nfs | 2049 | Network File System |
Q. How can I perform a migration to DHCP?
A. There are only a few basic registry entries that define a client as a DHCP client so an easy way to migrate clients to DHCP is to create a registry script that sets the required values via logon script. You should obviously be careful that there is no overlap between the addresses in the DHCP address pool and those statically assigned.
TCPIP parameters are defined to each NIC (Network Interface Card).
The following is an example registry script you may consider using
REGEDIT4
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\<card
service>\Parameters\Tcpip]
"EnableDHCP"=dword:00000001
"IPInterfaceContext"=dword:00000001
"IPInterfaceContextMax"=dword:00000001
You should then add something into the logon script to detect the NIC installed into the computer, run the reg script and request an IP address, e.g.
if reg=elpc575 (for the 3com575tx) goto dhcp
..
..
..
:dhcp
regedit /s NIC_dhcp.reg
ipconfig /renew
net send %computername% Congrats Your computer has been configured for
DHCP!
endif
A quick way to find out which network card you are using is on you LAN you will have various types of NIC.
For instance you may have the 3c89d, netflx3,3c575tx for instance for the Neflx3 driver, when the install takes place on the NT 4.0 it adds a registry key in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\systems\Current control set\system\services\cpqNF31 with the parameters:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CpqNF31\Parameters\Tcpip]
"EnableDHCP"=dword:00000000.
You have to find out what the key name is because it is different for each NIC then you can run kix32.exe and use the arguement:
EXISTKEY (
"Key"
)
Checks for the existence of a registry key.
Parameters
Key - Identifies the key you want to check the existence of.
Returns
0 the key specified exists (Note : this is different from the way the
EXIST function works...)
>0 the key does not exist, returncode represents an errorcode
$ReturnCode = ExistKey(
"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CpqNF31"
)
If $ReturnCode = 0
? "Key exists...."
Endif
...to detemine if the key exist and then execute accordingly for that specific card.
A. DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol and is used to automatically configure a host during boot up on a TCP/IP network and also to change settings while the host is attached.
This means that you can store all the available IP addresses in a central database along with information such as the subnet mask, gateways, DNS servers etc.
The basics behind DHCP is the clients are configured to use DHCP instead of being given a static IP address. When the client boots up it sends out a BOOTP request for an IP address. A DHCP server then offers an IP address that has not been assigned from its database, which is then leased to the client for a pre-defined time period.
Q. How do I install the DHCP Server Service?
A. The DHCP server service can only be install on a NT Server.
Q. How do I configure DHCP Server Service?
A. The DHCP Server Service is configured using "DHCP Manager" that is installed after the installation of the DHCP Server Service.
Usually items such as DNS servers, WINS server etc will be configured on a global scale and this is also done using Server Manager
Q. How do I configure a client to use DHCP?
A. For NT workstation and Windows95 follow the instructions below:
Q. How can I compress my DHCP database?
A. NT Server ships with a utility called JETPACK.EXE which can be used to compact DHCP and WINS databases. To compact your DHCP database perform the following:
Note: While you stop the DHCP service, clients using DHCP to receive a TCP/IP address will not be able to start this protocol and may hang.
Jetpack actually compacts DHCP.MDB into TMP.MDB, then deletes DHCP.MDB and copies TMP.MDB to DHCP.MDB! Simple :-)
For more information, see Knowledge base article Q145881 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q145/8/81.asp
Q. How can a DHCP client find its IP address?
A. Depending on the client:
Windows NT machine - type ipconfig from the command
prompt
Windows 95 machine - run winipcfg.exe
Q. How can I move a DHCP database from one server to another?
A. Perform the steps below on the server that currently hosts the DHCP Server service. Be warned that while doing this no DHCP clients will be able to start TCP/IP so this should be done outside working hours.
Optionally if you want to remove DHCP from the source machine totally delete the DHCP directory (%systemroot%\system32\dhcp) and then delete the DHCP Service (Start - Settings - Network - Services - Microsoft DHCP Server - Remove)
On the new DHCP server perform the following
Q. How do I create a DHCP Relay Agent?
A. If you have routers separating some of your DHCP clients from the DHCP server you may have problems if they are not RFC compliant. This can be solved by placing a DHCP relay agent on the local network area which is not actually a DHCP server which communicates on behalf of the DHCP Server. The DHCP Relay Agent must be a Windows NT Server computer.
Q. How can I stop the DHCP Relay Agent?
A. All you have to do is stop the DHCP Relay Agent service:
Q. How can I backup the DHCP database?
A. The DHCP database backs itself up automatically every 60 minutes to the %SystemRoot%\System32\Dhcp\Backup\Jet directory. This interval can be changed:
You could backup the %SystemRoot%\System32\Dhcp\Backup\Jet directory if you wish.
Q. How can I restore the DHCP database?
A. Perform one of the following:
Q. How do I reserve a specific address for a particular machine?
A. Before performing this you will need to know the hardware address of the machine and this can be found by entering the command
ipconfig /all
Look for the line
Physical Address. . . . . . : 00-60-97-A4-20-86
Now at the DHCP server perform the following
Q. How do I install the DNS Service?
A. The DNS Service can only be installed on NT Server and is installed as follows:
Q. How do I configure a domain on the DNS Server?
A. A new application has been added to the Administrative Tools group, DNS Manager, to configure the domain follow the procedures below:
Q. How do I add a record to the DNS?
A. To add a record, for example TAZ with IP address 200.200.200.4 perform the following
Q. How do I configure a client to use the DNS?
A. For an NT machine (and Windows 95) perform the following:
To test, you can start a command prompt and enter
nslookup <host name>
e.g. nslookup taz
The IP address of Taz will be displayed. Also try the reverse translation by entering
nslookup <ipaddress>
e.g. nslookup 200.200.200.4
The name Taz will be displayed.
Q. How do I change the IP address of a DNS server?
A. The information below assumes you have already changed the IP address of the machine ( Start - Settings - Control Panel - Network - Protocols - TCP/IP - Properties) and have rebooted. The scenario below assumes the old IP address was 200.200.200.3 and the new is 200.200.200.8
Update all the clients to use the new DNS server IP address.
The above procedure is the most complete way, however it should still work if you only perform steps 2 and 3.
Q. How can I configure DNS to use a WINS server?
A. Is is possible to configure the DNS to use a WINS server to resolve the host name of a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN).
Q. Where in the registry are the entries for the DNS servers located?
A. The entries for the DNS servers are stored in the registry in the location HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters under the NameServer value, Each entry should be separated by a space. Using the Resource Kit utility REG.EXE the command to change would be as follows
reg update HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\NameServer="158.234.8.70 158.234.8.100" \\<machine name>
where 158.234.8.70 and 158.234.8.100 were the addresses of the DNS servers you wanted to configure. Note it sets the value, it does not append so ensure you enter in the existing DNS servers as well as the new ones.
This may be useful for granting users access to the internet by remotely updating their registry to know which DNS servers to use.
Q. I receive error message "No More Endpoints".
A. This can be caused by installing DNS on a machine that has previous settings contained in the %systemroot%\system32\dns directory. To correct perform the following.
Q. How do I configure DNS for an NT 5.0 domain? - NT 5.0 only
A. Windows NT 5.0 domains rely on DNS and require Dynamic DNS which is an update to the basic DNS specification and details can be found in RFC 2136 that can be viewed at ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/rfc2136.txt.
Another major update in DNS 5.0 is the addition of service (SRV) records and these have already been seen as a mechanism for publishing the ldap server, ldap.tcp.<domain> and it is through these records that domains can be looked up through the DNS service.
You could perform this on a separate NT 5.0 machine, the domain controller and the DNS server will probably not be the same machine, it just has to exist before upgrading the server to a domain controller. To install DNS 5.0 on the server perform the following:
You then need to configure the DNS service
Now the basic zone is configured the required entries for the domain need to be added
The final stage is to configure the zones to be dynamic update enabled which allows hosts to add records in the DNS server.
DNS is now configured for a domain and you can create the domain.
Q. How do I configure Active Directory integrated DNS? - NT 5.0 only
A. It is possible to configure DNS servers that are also domain controllers to store the contents of the DNS database in the Active Directory which will then be replicated to all domain controllers in the domain. The option to store the DNS database in the Active Directory is not available on DNS servers that are not domain controllers.
Q. Setting a secondary DNS server as primary results in errors.
A. If you have a secondary DNS server configured to duplicate all entries from another DNS server you may experience a problem if you try and set it as a primary DNS server, which results in the service not starting and an error to the effect of the data being wrong:
Event ID: 7023
The MS DNS Server service terminated with the following error:
The data is invalid.
Event ID: 130
DNS Server zone zone name has invalid or corrupted registry data.
Delete its registry data and recreate with DNSAdmin.
Event ID: 133 DNS
Server secondary zone zone name, had no master IP addresses in registry.
Secondary zones require masters.
The DNS Manager forgets to set the correct value for the DNS Type in the registry (secondary is remaining), but it is erasing the address of the primary DNS, where the data came from. To correct this perform the following:
You should now be able to successfully start the DNS service
C:\> net start dns
The TYPE value can have one of two values,
0x1 specifies Primary zone
0x2 specifies secondary zone
A fix for this can be downloaded from ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/fixes/usa/NT40/ hotfixes-postSP3/dns-fix
A. WINS stands for Windows Internet Name Service. WINS is a NetBIOS Name Server that registers your NetBIOS names and resolves into IP addresses.
If you're using NetBIOS over TCP/IP you will need to have WINS running so that each can find out the correct IP address of the other to communicate.
Need to browse over an interdomain network? WINS!
A. Once your machine is configured to point at a WINS server (and maybe a second backup WINS server);
A. WINS is a server service.
Go to Control Panel->Network->Services and install the Windows
Internet Name Service.
If you have any non-WINS clients, add them in as static name->IP
mappings.
Configure a WINS Proxy Agent if needed.
Configure WINS support on your DHCP server.
NT Workstation TCP/IP->Properties->WINS add the IP address of the WINS server (and your secondary if you have one).
Q. What is a WINS Proxy Agent?
A. If you have non-WINS machines on your subnet and
want them to be visible participants, you will want a Proxy Agent to be
active within this subnet.
A WINS Proxy Agent is a WINS client that allows non-WINS clients to
participate, by listening for broadcast name registrations and requests
and then forwards them to a WINS server. Use Registry Editor to open
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NetBT\Parameters and
set the EnableProxy parameter to 1.
Q. How do I configure WINS static entries for a non-WINS client?
A. Go into WINS Manager (under Admin Tools)
Mappings->Static Mappings->Add Mappings enter the NAME and IP
ADDRESS of the machine in question. Under TYPE usually you'll just enter
as Unique. Now click ADD.
Q. How do I configure WINS to work with DHCP?
A. If the computer is a DHCP client, then at the DHCP server, go into DHCP Administrator (Admin Tools) and add two new SCOPE options:
Q. How can I compress my WINS database?
A. NT Server ships with a utility called JETPACK.EXE which can be used to compact DHCP and WINS databases. To compact your WINS database perform the following:
Note: While you stop the WINS service, clients using WINS to resolve addresses will fail unless another mechanism of name resolution is in place.
Jetpack actually compacts WINS.MDB into TMP.MDB, then deletes WINS.MDB and copies TMP.MDB to WINS.MDB.
For more information, see Knowledge base article Q145881 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q145/8/81.asp
Q. WINS Automatic Backup does not run every 3 hours.
A. By default WINS backup will actually take place every 24 to 27 hours after the last backup completed.
To work around this perform the following:
Q. WINS Log files are created in incorrect locations.
A. The WINS service creates a number of log files, J50.log or J50.chk, in the %systemroot%\system32\WINS directory. This is normal.
If these files are being created in other directories then it may cause a problem and stop the WINS service from starting. The log files can be created in different directories from one of the following reasons:
If your system now has the log files in the wrong place and the WINS service will not start just copy the log files to the %systemroot%\system32\WINS directory and restart the service
C:\> net start wins
If the WINS service is running it will lock the file and you will not be able to delete them so you should perform the following:
Q. The Outlook/Exchange client takes a long time to start.
A. Sometimes the protocol binding for Exchange can be wrong if more than one protocol is installed, for example if you have NetBEUI and TCP/IP installed, and you connect to the Exchange server via TCP/IP, you need to ensure TCP/IP is first in the binding order, otherwise Exchange will attempt to communicate via NetBEUI initially. To check/set perform the following:
Q. How can I stop Outlook dialing my Internet Account on Startup?
A. Perform the following:
A. The following instructions are to install Exchange 5.0
It is a good idea to have a large pagefile.sys when running Exchange, a good size would be the amount of memory plus 100.
Q. How do I enable the Exchange Active Server Pages?
A. This functionality is new in 5.0, and enables a user to view their exchange mailbox from an Internet browser, such as Internet Explorer or Netscape. Before the Exchange Active Server Pages extension can be installed, there are two pre-requisites
NT Server 4.0 ships with IIS 2.0, therefore assuming you have not upgraded your system since then you will need to perform the following
Once this has finished, you will be able to connect to your Exchange mailbox by entering the URL
http://<Exchange server>/exchange
You then need to enter you Exchange alias and then click the "click here" text.
Q. How do I use the Exchange Optimizer utility?
A. After you install Exchange you are prompted to run the Exchange Optimizer utility, however it can also be run afterwards:
Q. How can I convert mail system X to Exchange?
A. Exchange is supplied with a migration wizard which can convert the following mail systems to Exchange
The wizard is in the Microsoft Exchange folder and below is an example of converting a MsMail Postoffice
Q. How can I create shortcut on the desktop with the "to" field completed?
A. As you may be aware, if you enter the command
exchng32 /n
This creates a blank new message, however it is not possible to
specify a qualifier containing information to the content. A workaround to
this is the following
If you now double click on the desktop message icon it will create a new message which you can edit and then send with information already filled in!
Q. NT Server hangs at shutdown if User Manager is running.
A. This is caused by an Exchange dll file which is used by User Manager, to fix this perform the following
Q. How can I send a mail message from the command line?
A. You need to use the MAPISEND.EXE utility that is supplied with the Exchange Resource kit. The resource kit can be downloaded from http://www.microsoft.com/msdownload/exchange/rkintel/rkintel.htm and you need to download the AdminNT part.
Once downloaded double click on the zip file and it will expand to a specified location. Copy the MAPISEND.EXE from the restored path (i386\admin\mapisend) to an area of your choice. The usage is simple as long as the exchange client is installed on the computer already (outlook is also OK).
mapisend -u "<profile>" -p <anything> -r <recipient>
-s "<subject>" -t <text file containing the message>
e.g. mapisend -u "john savill" -p anything -r
john@savilltech.com -s "Test message" -t c:\message\mail4.txt
This is just an example usage, and you may not be sure what you profile name is so instead of using -u and -p, use just -i and this allows interactive login and will also allow you to create a profile which you can then use in future. The full list of switches are
| -u | Profile name (user mailbox) of sender |
| -p | Login password |
| -i | Interactive login (prompts for profile and password) |
| -r | Recipient(s) (multiples must be separated by ';' and must not be ambiguous in default address book.) |
| -c | Specifies mail copy list (cc: list) |
| -s | Subject line |
| -m | Specifies contents of the mail message, this is ignored if -t is specified |
| -t | Specifies text file for contents of the mail message |
| -f | Path and file name(s) to attach to message |
| -v | Generates an 8 line summary of the sent message |
In all cases if the passing parameter is more than one word it should be enclosed in quotes.
Q. What files does Exchange use?
A. Below is a list of the more common files used by Exchange
| File | Directory | Use |
| Priv.pat Pub.pat | Mdbdata | Patch files, safe to delete if no backup is taking place and no startup recovery is in operation |
| Dir.pat | DsaData | Patch files, as above |
| Dlv.log Snd.log Dlvxxxxx.log Sndxxxxx.log | Mdbdata | These are created when Sending and Delivering diagnostics logging for either the private and public information stores are set. These can be deleted at any time. Dlv.log and Snd.log are the most recent logs created. |
| PUB.EDB PRIV.EDB | MDBdata | Information store |
| DIR.EDB | DSAdata | Directory information |
| EDB.LOG | Transaction Log | |
| EDB00nn.LOG | Previous Transaction Logs | |
| EDB.CHK | Check Point file | |
| RES1.LOG RES2.LOG | Emergency logs for when disk is full | |
| TEMP.EDB | In progress transaction |
Q. How can I change the location of my mail file in Outlook 98?
A. Your messages are stored in a .pst file, and by default this is kept in your personal profile space (%systemroot%/Profiles/<user name>/Application Data/Microsoft/Outlook). This is fine unless you use roaming files which mean you mail file is stored on a central server taking up space.
Fortunately moving you mail file is easy.
What this actually does is update one registry key, HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows Messaging Subsystem\Profiles\Microsoft Outlook Internet Settings\14780fd532f9d11181cc00600851c569\001e6700 and its value is the name and location of the .pst file.
Q. How can I reduce the size of my mail file?
A. When you delete files from your mail file the space is usually not cleared away and your mail file may actually grow! To reclaim the wasted space you can "compact" the mail database. The information below is for Outlook 98 but previous versions have similar functions.
If you find the mail file has not been substantially reduced in size it may be there is no redundant information or you may need to run the compaction a couple more times as sometimes the process does not work 100%.
Q. I have a bad message in my POP3 mail box , how can I remove it/read POP using TELNET?
A. It is possible to connect to a POP3 mailbox using Telnet so you should connect via telnet and delete the problem message.
This is obviously useful in a number of scerios and you could use it just to read you mail if you did not have access to a mail client.
Below is an example of the above in action.
Q. How can I send mail to a SMTP server using Telnet?
A. As with POP3, SMTP messages can also be sent using telnet by connecting to port 25 on the SMTP server, e.g.
C:\> telnet smtp.savilltech.com 25
Once connected you optionally announce to the server who you are (this is needed for some SMTP servers)
helo <domain>
e.g. helo savilltech.com
vrfy <user account>
e.g. vrfy john
Once you are verified you can commence to write an e-mail message. The first command is mail and you specify who it is from, e.g.
mail from:<billg@microsoft.com>
The address has to be in <>. Next you have to specify who will be receiving the message using rcpt, e.g.
rcpt to:<john@savilltech.com>
The from and to have been completed you can start the body of the message using the data command. You have to create the header information in the first lines of the message. Once you have completed the message enter a '.' on a blank link and the message will be sent. Below is an example creating a message.
As you can see I entered a from, date, to and a subject and then entered the body of the text. Make sure you don't make a mistake as if you backspace this is enterpreted as a bad character and will be rejected. If a message is rejected a rejection will be send to the address specified in the "mail from:<...>" and for this reason you should only ever put your e-mail address. Although I have used a different address as a joke you should NEVER do this.
Below is how the message looks when received in Outlook 98:
The above shows how easy it is to send a message and make it look from a different address but if you examined the header you would easily see it was sent from a different mail server and rumble its a fake (and a very bad one)!
I shall be adding future entries describing how to STOP people sending mail from your server (as they probably can at the moment).
For full information on SMTP and the commands you can use see Request For Comments 821.
Q. Is there a list of known Exchange Directory and Information store problems?
A. An excellent collection has been compiled and is located at http://support.microsoft.com/support/exchange/content/whitepapers/dsis.asp
Q. How do I install Exchange Server 5.5?
A. These instructions are to install the first Exchange Server in the Enterprise
Before you install Exchange Server 5.5, two accounts need to be decided on. The first account is the account that you log on as when you perform the installation of Exchange as this account will be automatically granted the Exchange Administrator permission.
The second account needs to be created and this will be used as the service account for running the Exchange Server services. Any name can be used, the most obvious would be "Exchange Service". To create this account perform the following:
Under Windows NT 5.0 this would be set using the Directory Management MMC, expand the domain, right click on Users and select New - Users. Enter Exchange Service, click Next and then select the options as in step 4 and click Finish.
Also before installing make sure you have a complete backup of your system.
Now you can start the installation.
Once Installation is complete you should run the Microsoft Exchange Performance Optimizer (Start - Programs - Microsoft Exchange - Microsoft Exchange Optimizer). You will be given the option to run this automatically if installation is successful.
Q. How do I run the Exchange Optimizer?
A. Exchange ships with a utility that allows the program to gather information about the computer and make changes to the Exchange configuration to enhance performance. These performance enhancements are primarily gained by moving the files that make up Exchange to different physical disk drives.
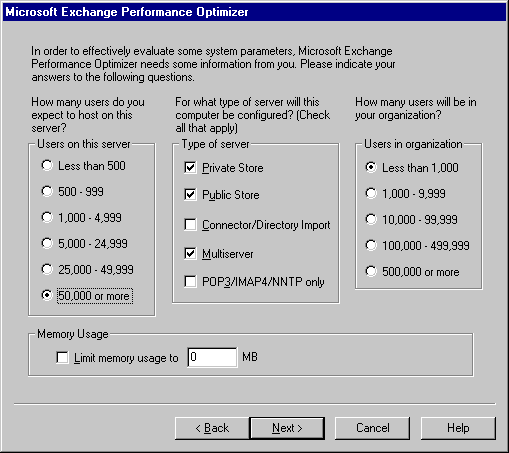
Q. What Service Packs are available for Exchange?
A. Below is a list of the service packs available:
Exchange 5.5
Service Pack 1 from ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/exchange/exchange-public/fixes/Eng/Exchg5.5/SP1/Server/
Files to download:
| SP1_550A.EXE | Server update for Alpha |
| SP1_550I.EXE | Server update for Intel |
| SP1_55CA.EXE | Chat server update for Alpha |
| SP1_55CI.EXE | Chat server update for Intel |
| SP1_55DC.EXE | Documentation |
| SP1_55FO.EXE | HTML Form Converter |
| SP1_55SS.EXE | Server support files (cluster,KMS,etc) |
| SP1_55XC.EXE | Exchange connector installation |
| SP1S550A.EXE | Server symbols for Alpha |
| SP1S550I.EXE | Server symbols for Intel |
| SP1S55CA.EXE | Chat server symbols for Alpha |
| SP1S55CI.EXE | Chat server symbols for Intel |
| SP1_55RE.EXE | Readme and HTML file |
Hotfixes post Service Pack 1
| PSP1STRI.EXE | Store Fix |
Exchange 5.0
Service Pack 1 from ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/exchange/exchange-public/fixes/Eng/Exchg5.0/Sp1/Server/
Files to download:
| SP1_500A.EXE | Server update for Alpha |
| SP1_500I.EXE | Server update for Inter |
| SP1S500A.EXE | Server symbols for Alpha |
| SP1S500I.EXE | Server symbols for Intel |
Service Pack 2 from ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/exchange/exchange-public/fixes/Eng/Exchg5.0/Sp2/Server/
Files to download:
| SP2_500A.EXE | Server update for Alpha |
| SP2_500I.EXE | Server update for Inter |
| SP2S500A.EXE | Server symbols for Alpha |
| SP2S500I.EXE | Server symbols for Intel |
Q. How can I retrieve mail from a POP3 mailbox and forward it to Exchange server?
A. If your ISP does not support ETRN, then you have to use a third party utility to retrieve the mail from a POP3 mailbox. One of these utilities is POP2exchange (http://www.gficomms.com). For one mailbox this is a freeware utility.
A more complete listing of utilities can be found on http://www.slipstick.com
Q. How do I upgrade from Exchange 5.0 to 5.5?
A. The Exchange 5.5 upgrade process actually performs a database upgrade before it actually copies any of the code of 5.5 to the server. This allows for a complete rollback in case the upgrade of the database fails. Below are the steps in performing the upgrade
Q. How do I uninstall Exchange?
A. To uninstall Exchange perform the following. Be aware you will lost all information.
Q. How do I install a duplicate Exchange server?
A. With the concepts of sites in Exchange, it is possible to install multiple Exchange services in a site which will replicate to one another. Duplicates servers in a site provide fault-tolerance and load balancing. To install a duplicate server in a site perform the following. Servers within a site don't have to be in the same domain but should be connected by a fast connection, 128KB is the normal definition of a fast link.
You now have a duplicate Exchange server in the specified site.
Q. How do I connect Exchange sites?
A. If you configure multiple sites by installing new servers and entering a different site name (but the same organizational name) you can connect the sites using Exchanges built-in site connector. To connect sites using the built-in connector they must be able to communicate via RPC calls and to test this see Q. How can I check if servers can communicate via RPC's?. Many routes actually filter out RPC's so it is important you perform this test.
To add a connector between sites perform the following:
The connection will now be visible under the Connections tab.
Q. Exchange Security Knowledge Base list.
A. Below is a list of useful Knowledge Base articles.
1) How to install Exchange 5.5 with support for V1 and V3 Certificates for SMIME and Public/ Private Key encryption (Signing and Sealing Mail Messages). This uses the CA version 1.0 (Certificate Authority) in IIS 4.0 that comes in the NT 4.0 Option Pack. This requires the Updated CA Server. See these KB's.
Q192044
Setting Up X509v3 Certs on Exch 5.5 SP1 KMS with Local CertSrv
Q184695
Readme Notes for Certificate Server Update
2) How to setup SSL/TLS between between Exchange Server 5.0 /5.5 and Internet Email Clients, POP3, IMAP4, NNTP, HTTP, SMTP.
Q175439 XFOR: Enabling SSL For Exchange Server
3) How to setup SSL/TLS between Exchange Server and other SMTP (non-exchange) host. This requires enabling SSL for the SMTP protocol first. See Q175439 for instructions, but select SMTP as the Protocol to be used in Key Manger.
Q174755 XFOR: Connecting IMS to IMS with SASL
4) When you use Microsoft Outlook Express to connect to Microsoft Exchange Server, version 5.0 with Service Pack 1 installed, the Information Store may stop responding (crash). Fixed in the Latest Service Pack.
Q166627 XCLN: Outlook Express Crashes Store When SSL Is Used
5) When trying to access a mailbox in Internet Explorer version 3.02 when the WWW Service for the Internet Information Server (IIS) computer is configured to use Windows (NTLM) authentication only, you may receive the following error message: The Login Request was Denied. Fix is to upgrade to IE 4.0 or use Registry Entry.
Q173307 XWEB: "The Login Request was Denied" Error Message
6) If you configure the Internet Mail Service on two Microsoft Exchange Server computers to use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) without authentication, you may receive a non-delivery report (NDR) when you attempt to send mail from one server to another through the Internet Mail Service. The text of the NDR includes a 505 error and indicates that authentication is required for the message to be delivered. Fixed in the Latest Service Pack for 5.5.
Q181481 XFOR: Non-Delivery Report When Using SSL Without Authentication
7) On July 17, 1998 Microsoft released an updated version of Schannel.dll. This latest version provides the following benefits: Updates the SChannel.dll used by IIS and Exchange Server for Encryption. See article for Details.
Q148427
Generic SSL (PCT/TLS) Updates for IIS and MS Internet Products
Q181937
Latest SGC-Enabled Schannel.dll Breaks IIS 3.0 Key Manager [iis]
8) Microsoft Proxy Server is designed to work well with other servers like Microsoft Exchange Server. Most Windows Sockets server applications are able to use the server proxy feature while installed on or behind the Proxy Server. Certain additional advanced settings may be required, based on your particular internal server configuration.
Q181420
How to Configure Exchange or Other SMTP with Proxy Server
Q187652
Accessing Data Published Behind MS Proxy Server 2.0
Q178532
Configuring Exchange Internet Protocols with Proxy Server
Q177153
Additional Proxy Server 2.0 Configurations [proxysvr]
9) This article discusses the known TCP/IP ports (TCP and/or UDP) that are used by services within Microsoft Windows NT version 4.0 and Microsoft Exchange Server version 5.0 and 5.5.
Q150543 WinNT, Terminal Server, & Exchange Services Use TCP/IP Ports [crossnet]
10) Microsoft Exchange Server versions 5.0 and 5.5 support a variety of Internet-focused protocols, including POP3, HTTP, LDAP, and NNTP. This article explains the different authentication forms for each protocol.
Q175440 Protocol Authentication on Exchange Server [exchange]
Q. How do I configure Exchange Directory Replication?
A. Once you have connected sites by a connector, be it Exchange, X.400 or Dynamic RAS, no data will be replicated until you configure the directory replication. You must have defined connections between the sites before Directory Replication can be configured.
To configure Directory Replication perform the following:
The Directory Replicator between the sites is now configured and can be modified by double clicking on the replicator as part of the Directory Replication folder.
Q. How do I monitor an Exchange link?
A. It is possible to install link connectors which can be configured to perform a number of actions in the event of a link failure.
Q. How do I delete a server from an Exchange site?
A. If you have multiple servers in a site and a server no longer exists you can delete it from the Exchange Administrator program by performing the following:
The server will now be removed.
Q. How do I setup an Exchange forward?
A. A forward can be configured in a number of places. The first place is at the Exchange server:
People will now be able to send mail to this person and it will be forwarded accordingly.
You could also in Exchange Administrator setup a Custom Recipient (as above), then in the Delivery Options for your mailbox set an Alternate Recipient which points to the Custom Recipient that you just created. Select the "Deliver messages to both recipient and alternate recipient" checkbox. In the properties for the custom recipient you can select the option to hide it from the address list.
Other options that can be done at the client end include
Q. How do I configure a X.400 Exchange connector?
A. Aside from the native Exchange Connector, the X.400 connector is the most common Exchange connector, allowing Exchange to connector to non-Exchange systems. While X.400 suffers a 20% drop in performance in comparison to the native Exchange connector it is still impressive.
X.400 is a common standard and Exchanges implementation is based on the 1988 standard. X.400 operates on the MTA stack and has to be installed before installing a X.400 connector. MTA stacks are available for TCP/IP, X.25 and TP4. It is available for RAS as well but that stack does not support X.400. In this walkthrough we will look at implementing X.400 over TCP/IP.
The first step is to install the MTA transport stack
If you find you don't have a number of MTA stacks check you installed the X.400 connector at installation time. Re-run setup and click Add/Remove. Select Exchange Server and click Change Options. Check the "X.400 Connector" box and click OK. Click Continue. You will now be able to install the TCP/IP MTA stack.
Now the MTA stack is installed you can install the actual X.400 connector and configure it accordingly.
You now have a functionality one-way X.400 link. You would now need to repeat the above for the opposite directory.
Q. How do I allow a user to administer Exchange?
A. When Exchange is installed the user who performs the installation is granted Exchange Administrator rights. To grant additional users the ability to administer Exchange perform the following:
The user (or group) will now have the granted rights to Exchange. You may want to create a group, e.g. Exchange Admins, grant this access in Exchange, then Add/Remove users to this group.
Q. How do I grant permission for people to create top level public folders?
A. By default all users can create top level folders however this can be changed if you would like to restrict this
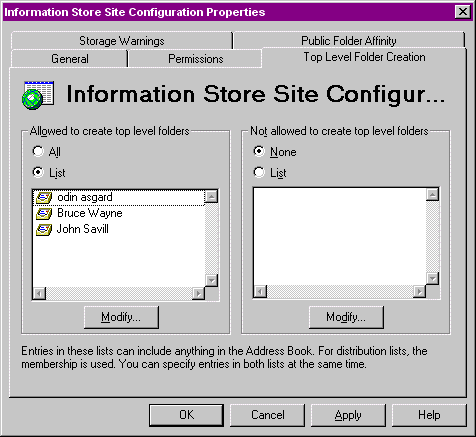
- Setting top level folder creation access
Alternatively you could have left is as All and modified the list of people who should not be able to create top-level folders.
If people are still logged in they will be able to continue to create top-level folders until they close Outlook/Exchange and restart it.
Q. How do I connect my Exchange server to a SMTP server?
A. Exchange Server 5.5 ships with the Internet Mail Service which allows Newsgroup feeds and, among other things, connections to a SMTP mailbox.
You will need a connection method to the SMTP mailbox, for example a RAS dial-up connection to an ISP. If you are connecting via a firewall make sure the ports used by POP and SMTP and not disallows (ports 25, 110 and 995).
Before doing any of this you should ensure DNS is correctly configured for you local domain (or this may be done by the ISP) by adding a MX record for the Exchange server in DNS (this is not needed if you are connecting via a RAS dial-up connection and just connecting to a specific host).
In this example we will connect to a SMTP mailbox at a ISP.
To configure items such as the dial-up account username and password double click on "Internet Mail Service" under Configuration\Connections, select the Dial-up Connections tab and click Logon Information. From this tab you can also configure time-out and how ofter to dial out.
If you have problems try applying Service Pack 1 which I found fixes a number of problems.
Q. How do I connect my Exchange server to a NEWS feed?
A. Exchange Server 5.5 has the ability to accept a news feed and publish to the Public Folders area. It can also be configured to post back any articles posted by your networks user to the appropriate news server.
It will now connect for the first time and get an initial feed for all newsgroups selected.
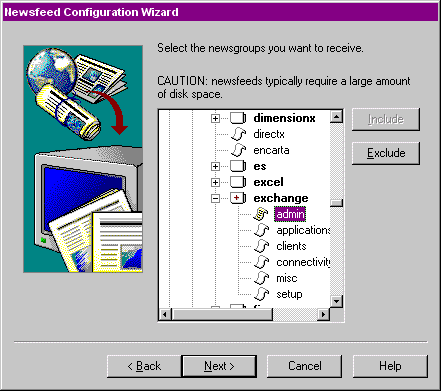
- Always download the Exchange Admin newsgroup :-), don't we all?
Clients will now be able to view via the Folders List in Outlook, Public Folders - All Public Folders - Internet Newsgroups - microsoft .....
You can change any details but double clicking on the appropriate Newsfeed entry under Connections. For example click Schedule allows you to specify how often to connect at certain times of the day/days of the week.
A. Internet Information Server (IIS) is a World Wide Web server, a Gopher server and an FTP server all rolled into one. IIS means that you can publish WWW pages and extend into the realm of ASP (Active Server Pages) whereby JAVA or VBscript (server side scripts) can generate the pages on the fly. IIS has fun things like application development environment (FrontPage), integrated full-text searching (Index Server), multimedia streaming (NetShow), and site management extensions.
Q. How do I install Internet Information Server?
A. IIS 2.0 is supplied with Windows NT Server 4.0. It can be installed at the time you installed NT 4.0 by checking the "Install Microsoft Internet Information Server" box, alternatively it can be installed at a later time by performing the following
Internet Information Server 3.0 is supplied on the Service Pack 2 CD-ROM and as part of Service Pack 3. It is supplied as an upgrade, so you must already have IIS 2.0 installed before applying the service pack.
Q. What is Internet Service Manager?
A. If you look under Programs->Microsoft Internet Server, you will find the Internet Service Manager. ISM is used to configure and monitor IIS. With ISM you can define user connections and user logon and authentication, the home directory location for each IIS service, logging and security.
A. It gives the ability to perform full-text searches and retrieve information from a Web browser. It can search HTML, text, and all Microsoft Office documents.
When started, it builds an index of the virtual roots and subdirectories on your Web server. You can select which directories and file types can be skipped.
The index is updated automatically whenever a file is added, deleted, or changed on the server.
Q. What are Active Server Pages?
A. ASP is server-side scripting. You can use ASP to create and run dynamic, interactive, Web applications. When your scripts run on the server, the SERVER does all the work involved in generating the HTML pages.
Q. How can I configure the Connection Limit?
A. This is configured using the Internet Service Manager and can be between 1 and 32,767
Q. How do I change the default file name?
A. The default file name is the file searched for if only a directory name is specified and can be changed by performing the following:
Q. How can I enable browsers to view the contents of directories on the server?
A. By default if you select a directory on a server and no default file name exists then an error is returned. It is possible to change this behavior to instead of an error a directory listing is displayed
You can only set this for the whole site, not on a per directory basis. If you want to set this on a directory basis enable the directory browsing and make sure the default file name exists in directories you do not want people to be able to browse.
Q. How can I configure the FTP welcome message?
A. Using the IIS admin utility a welcome, end and connect refused message can be displayed
Q. How do I configure a virtual server?
A. It is possible using Windows NT to bind multiple IP addresses to one network card and for each IP address it is possible to run a virtual domain server. The procedure below will add an IP address, add the new IP address as a domain and setup the new IIS virtual server.
To bind an additional IP address to your network card perform the following:
You now need to configure the DNS server to respond to the new name.com with the new IP address
Next update the IIS server to support the new domain
You will now be able to browse to this domain.
Q. How can I administer my IIS server using a web browser?
A. IIS comes with a built in HTML version of Internet Service Manager, with an address of <server name>/iisadmin/default.htm. It does have to be installed.
To check if its installed start the browser and move to the \iisadmin\default.htm and if you see the Internet Server Manager page but with no graphics, e.g.
To install perform the following:
If your default file name is not default.htm you may have a few navigation problems, if you do just enter default.htm after any directory name.
Once you connect using a browser to the iisadmin area you may have to enter a username and password depending on the browser you use, and you can then perform actions to administer the site.
Q. How can I configure FTP to use Directory Annotation?
A. Follow the procedure below:
You now need to create a file called ~ftpsvc~.ckm in each directory where you wish the annotation. The file is just a normal ASCII format file.
Q. Only the first line of the Directory Annotation is shown.
A. This is caused if you have no welcome message. Simply add a welcome message as described in Q. How can I configure the FTP welcome message?
Q. How can I configure the amount of IIS Cache?
A. By default InetInfo, the process responsible for WWW, FTP and Gopher uses a 3MB of cache for all of the services. This cache is used to store files in memory providing faster access than from disk. To change the amount of memory available for the cache perform the following:
If you wish to disable caching set the value to 0 however this could have a serious effect on performance.
Q. How do I create a virtual directory?
A. Before we describe how to create a virtual directory, it is first important to understand what a virtual directory is. For those who remember DOS, there was a command called join which allowed you to treat a different disk as a directory on the current drive. A Virtual directory is the same kind of thing, you can treat a directory or disk as a subdirectory of your web site.
For example your default web area may be c:\InetPub\wwwroot and this may be http://www.savilltech.com . If you had a subdirectory off of wwwroot called ntfaq, e.g. (c:\InetPub\wwwroot\ntfaq) you could access this as http://www.savilltech.com/ntfaq. What if I had run out of space on c: and wanted the FAQ to be on d:? You would create a virtual directory called ntfaq which would point to d:\pages\ntfaq and this procedure of creating a virtual directory is shown below.
Q. How to install FrontPage Extensions on Beta 2? - NT5 only
A. The FrontPage Extensions are not installed during the Beta 2 NT/IIS setup. To install the extensions, perform the following steps:
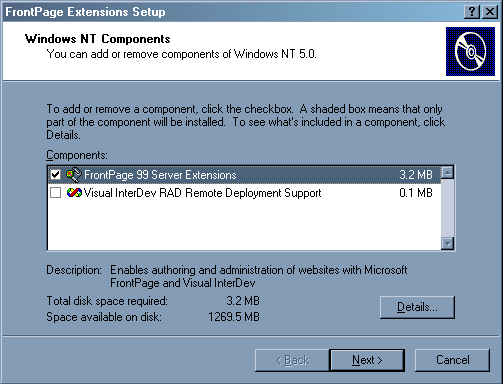
Contributed by Thomas Lee
Q. What fixes are available for IIS?
A. Microsoft have released the first NT Option Pack QFE (Quick Fix Engineering) Update but this actually only updates IIS 4.0 at this time.
The update includes every hotfix made to IIS from its release. This is a cumulative hotfix and you should only install this if you are experiencing specific problems with IIS. The new intent is about every month or so or when appropriate release a new fix pack. The value add here is not waiting for such a long period of time between service packs. Customers who are experiencing problems don't need to hunt down individual hotfixes any more they just download this update and get everything.
The uninstall is very clean, so if something goes wrong, remove the fix. Something new here is in letting customers know what DLL's are being replaced up front. Upon installation of the update, the file iis_hotfix.htm is dropped in the users \inetsrv directory. This file will contain all of the information about the fix and should make it very easy for PSS to determine what version of IIS the customer is using.
Download from : http://www.microsoft.com/windows/downloads/contents/updates/ntopqfe/default.asp
A. A Proxy Server is a system that sits between the client applications (such as Internet Explorer) and the connection to the Internet (Server) and intercepts the requests to the server to see if it can action them itself, this improves performance by filtering requests that go out to the Internet.
The Proxy Server can cache files it downloads from the Internet for a client, using this method if someone else asks for the same page the Proxy Server can send back the version its holding in its cache rather than sending a request out on the Internet. Proxy servers can also act as a fire wall by filtering IP traffic by port or IP address.
Proxy Server 2.0 performs the above but also has extra functions such as Winsock proxy for use by Winsock based clients such as Windows 95 etc. to enable IP type access even if the local network protocol used is, for example, IPX. It does this by replacing the winsock on the client machines. It can also be used to hide your networks TCP/IP configuration by allowing you to have any TCP/IP addresses on your Intranet as only the Proxy Servers IP address is used on the Internet.
Proxy Server 2.0 also has the Sock's proxy service for non-winsock type clients such as UNIX based machines.
Q. How do I install Proxy Server 2.0?
A. Before you install Proxy Server 2.0 make sure your system meets the following pre-requisites
Once your system meets the criteria above you can start the installation:
Q. How do I install the client for the WinSock Service?
A. There are two methods, the easiest is to use the Web based installation method. Before you start this, make sure the IIS server has default.htm as one of the default document types
Alternatively you can run the setup manually by connecting to the Mspclnt share on the server and running the Setup.exe. The installation is as above.
Once the machine has rebooted, confirm the installation is OK by performing the following:
Q. How do I remove the client WinSock Service?
A. Just run the Uninstall program from the Microsoft Proxy Client group.
Q. How can I bypass the client Winsock?
A. There may be a scenario where the machine is taken to different locations (such as a portable taken home) and in this situation you do not want to use the WinSock Proxy client. Rather then uninstalling every time you take the machine home, you can disable it:
Once the computer has restarted it will no longer use the Proxy WinSock. To re-enable perform the above but check the "Enable WinSock Proxy Client".
Q. How do I configure an Internet Browser to use the Web Proxy service?
A. This procedure is basically the same for all browsers:
Internet Explorer 4.0
Netscape Navigator 4.0
Mosaic 3.0
Q. How do I manage the Proxy Server?
A. Proxy Server uses the Microsoft Internet Service Manager (ISM) as its management interface, so to manage your proxy server just start the ISM (Start - Programs - Microsoft Proxy Service - Internet Service Manager). In the example below we will examine which clients are currently using the Web Proxy service
You use the Internet Service Manager to stop/start/pause/continue the Proxy services. If you select a service, for example the Web Proxy Service, if it was running the Stop and Pause buttons would become active and you could then stop or pause the service and its State would change.
Double clicking on the services brings up their options. You can also hide certain types of services from the display, as shown in the diagram I have hidden FTP and Gopher services by unclicking their icons.
Q. How can I configure the Proxy server to automatically dial out to the ISP when needed?
A. This is configured via the Internet Service Manager, however before Proxy Server is configured we need to ensure the correct RAS services are running.
You need to make sure before you proceed that you have a phonebook entry for your ISP, if not you should add one before you proceed.
The WINS client has to be disabled for the Remote Access WAN Wrappers
You can now configure the Proxy Services to autodial
You should now stop and start all services that will use autodial.
Any client request that cannot be locally handled will now cause the Proxy server to dial out to the internet.
Q. How can I stop and start the Proxy services?
A. There are several options available to you. The easiest is to use the Internet Service Manager, just select the service and click the stop/start button.
You can also stop the services from the command line using
| net stop/start w3svc | for the Web Proxy service |
| net stop/start wspsvc | for the WinSock Proxy service |
| net stop/start spsvc | for the Socks Proxy service |
Q. How can I use the Web based Proxy Server Administration software?
A. This can be downloaded from http://backoffice.microsoft.com/downtrial/moreinfo/proxyadmin.asp and on the Intel platform will download watx86r.exe to your machine. Before you download you really need IE4.0 to get the most from it.
To install follow the procedures below
To administer the Proxy server from a browser you would connect to http://<proxy server name>/PrxAdmin. You then click the large graphic and enter in an Admin username, password and domain.
You can then perform all the normal functions via the interface.
Q. Which port does WinSock use?
A. Proxy Server 2.0 uses UDP port 1745, Proxy Server 1.0 used 9321.
Q. How can I configure the RAS Autodisconnect?
A. You may have RAS Autodisconnect configured but it does not disconnect after the assigned time, the following may be to blame
To actually change the idle timeout perform the following:
Q. How can I remove the Active Desktop?
A. You can turn off the Active Desktop without removing it by performing the following:
To actually remove Active Desktop completely while leaving the browser intact:
Q. How can I get past the "Active Desktop Recovery" page?
A. This can usually be fixed by deleting the desktop.htt file:
Q. What keyboard commands can I use with Internet Explorer 4.0?
A. Below is a list of common keyboard commands:
| Alt + Left Arrow (or backspace) | Go Back |
| Alt + Right Arrow | Go Forward |
| Tab | Move to next Hyperlink |
| Shift - Tab | Move to previous Hyperlink |
| Enter | Move to page referenced by Hyperlink |
| Down Arrow | Scroll down |
| Page Down | Scroll down in greater jump |
| End | Move to bottom of document |
| Up Arrow | Scroll up |
| Page Up | Scroll up in greater jump |
| Home | Move to top of document |
| F5 | Refresh |
| Ctrl - F5 | Refresh not from cache |
| Esc | Stop download |
| F11 | Full screen/normal toggle |
Q. How can I create a keyboard shortcut to a web site?
A. It is possible to create your own keyboard shortcuts with a Ctrl + Alt + <letter> combination as follows:
You can also use the above to create a keyboard shortcut to a desktop item by right clicking on the shortcut and choosing properties.
Q. How can I customize folders with web view enabled?
A. If you have installed the Windows Desktop Update and have the view as web page enabled ( view - as web page) you can customize the folder (view - customize this folder) and then select the type (background picture or a whole HTML file) or you can change the default which is stored in a hidden HTML file (%systemroot%\web\folder.htt). You can then edit this file and change accordingly.
There is a line in folder.htt "HERE'S A GOOD PLACE TO ADD A FEW LINES OF YOUR OWN" which you can add your own links which will then appear on all folders.
There are 4 other templates you can edit:
As I said these are hidden so you will either need to remove the hidden attribute (attrib <file> -h) or just enter the name specifically in the edit utility you use to change these files. A word of warning, make a backup of these files before you break them :-).
Q. How can I change the icons in the Quick Launch toolbar?
A. The icons on the quick launch taskbar (Internet Explorer, Outlook Express, Show Desktop and Channels by default) are all stored in %systemroot%/profiles/<user>/Application Data/Microsoft/Internet Explorer/Quick Launch and to remove/add just add and remove the files from this directory using Explorer.
You can copy any shortcut to this directory and the update will be done straight away, no need to logoff/reboot. As you can see below I have added a shortcut for Word and Frontpage just by copying the shortcut to the Quick Launch directory, easy.
![]()
An alternative method is to just drag a shortcut over the Quick Launch bar and it will add the shortcut for you.
All the files in this folder are shortcuts except for Show Desktop and View Channels. See the next FAQ for their contents.
Q. I have lost Show Desktop/View Channels from the Quick Launch bar, help!
A. As was discussed in the previous FAQ these icons are just files in the %systemroot%/profiles/<user>/Application Data/Microsoft/Internet Explorer/Quick Launch directory. To get the Show Desktop/View Channels icons back create the following files in the Quick Launch directory (or copy from another user)
For Show Desktop, create "Show Desktop.SCF" with the
following content:
[Shell]
Command=2
IconFile=explorer.exe,3
[Taskbar]
Command=ToggleDesktop
For View Channels, create "View Channels.SCF" with
the following content:
[Shell]
Command=3
IconFile=shdocvw.dll,-118
[IE]
Command=Channels
Q. How do I change the default Search Engine?
A. The URL for the Search Engine used with the Go - Search the Web is stored in the registry so this can easily be changed:
Now when you select search you will be taken to this URL. If you want to change back to the default enter http://www.msn.com/access/allinone.htm
Q. How do I remove the Internet Explorer icon from the desktop?
A. This can be done from the advanced options of Internet Explorer:
A. As you may be aware when you connect to a site the information you view is cached locally to speed up future visits to the site (the cache size can be set View - Internet Options - General - Temporary Internet files - Settings). Its actually possible to view the web using only the cache when not connected, obviously you can only view sites that are stored in the cache. To work off line:
You can then enter URL's and link as normal but will receive an error if you attempt to link to a site that is not cached. To stop working Offline just deselect "Work Offline"
Q. How can I reclaim wasted space by Microsoft's Internet E-mail readers?
A. Microsoft's Internet E-mail clients (both Internet Mail under IE3 and Outlook Express under IE4) waste a large amount of disk space due to the method used to store mail. The reason behind this is to improve performance, however if you do want to reclaim some of the lost space perform the following:
Also set-up Outlook to automatically delete the "Deleted Items" folder contents
Q. I cannot specify a download directory when I download a file.
A. When you download a file you are asked what to do, "Open this file from its current location" or "Save this file to disk". If you take the latter option you are asked for a storage location and you then click Save. Also on the selection screen is a "Always ask before opening this type of file", if you clear this check in future any downloads of this type will be downloaded to the Temporary Internet Files folder and opened by the program associated with the file type. To undo this perform the following:
Q. Internet Explorer opens .EXE files instead of Downloading them.
A. As in the previous FAQ if you unselect "Always ask before opening this type of file" for an executable it updates the registry so you are not asked however this can be fixed:
For files such as WAV, MOV and AVI (ActiveMovie files) you would modify the entry HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\AMOVIE.ActiveMovieControl.2\EditFlags to be 00000000.
Q. How can I change the default start page?
A. When you first start Internet Explorer it loads a page, by default this is a Microsoft page (http://home.microsoft.com) however this can be changed:
The above just updates registry entry "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\Start Page". You could create a registry script that updates a machines registry to set your page up as the clients Homepage. The REG script would have the following:
REGEDIT4
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main]
"Start Page"="http://www.ntfaq.com/"
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main]
"Default_Page_URL"="http://www.ntfaq.com/"
You would then setup a link on your page to the script and people would select "Open from current location". The official Microsoft image for this is
(if you want it right click on it and select "Save Picture As").
I have set the above up so it sets http://www.ntfaq.com as your start page but I would advise against it ;-) If you wanted no start page, e.g. blank, set the value to "about:blank".
If you use Netscape use the following to change your default homepage
It does not store the start page location in the registry, rather in a javascript file prefs.js, which is located in the Program Files\Netscape\Users\<Netscape Profile Name> directory. The line in the file is
user_pref("browser.startup.homepage", "http://www.ntfaq.com/");
however you should not edit this file.
Q. I have forgotten the content advisor password.
A. The password for the content advisor is stored in an encrypted form and decryption it, while possible, is to complicated for our purposes so we will instead just "reset" the password as if it had never been set.
Q. How do I install NT Workstation 4.0?
A. The installation of NT is quite simple, and below is just a simple example of an installation of a Workstation using TCP/IP and NetBEUI connected to a Domain.
You now have NT Workstation installed :-).
Q. How do I install NT Server?
A. The installation of NT Server is the same as NT Workstation with a few exceptions
A. The best method is two create at least two partitions. The first around 200Mb and format to FAT, on this partition DOS will be installed. The reason 200Mb is suggested that this is enough space to later install Windows for Workgroups or Windows95 if needed. After installing DOS, install NT and install onto the second partition (and format FAT or NTFS). Once the installation is finished, on bootup of the machine you will have a choice of booting into DOS or NT. The advantage of having NT installed on a FAT partition is that if there is a problem then you can boot up in DOS mode and access the NT partition and possibly restore files, although that core NT startup files are located on the C partition anyway (boot.ini, ntdetect.com and ntldr).
Q. Installation hangs when detecting the hardware.
A. The program being called is NTDETECT.COM. The best course of action is to use the DEBUG version of NTDETECT.COM.
In the support area of the NT installation cd (/support) there is a file NTDETECT.CHK. Follow the instructions to use it:
Q. Is it possible to install NT without using boot disks or temp files?
A. This is not possible on the Intel platform. On Intel you can either have it not using disks (winnt(32) /b) or not using temp files but not both. On the Alpha platform, it is possible to boot from the retail or MSDN CD of NT 4.0 and install so no boot disks or temp files are used.
The Compaq servers allow you to boot off of the CD, by making the CD a bootable device. Other hardware may also be able to do this, it will depend on the motherboard.
Q. Does NT have to be installed on the C drive?
A. No, NT can be installed on any drive, however it does place a few files on the active partition in order for NT to boot.
Q. There is a file ROLLBACK.EXE. What is it?
A. It is used by developers to wipe the Registry completely. Do NOT use it!
Q. I have NT installed, how do I install DOS?
A. Follow the steps below
The procedure above will only work if the C drive is FAT.
Q. How do I convert NT Workstation to NT Server?
A. There are various discussions about the changing of 2 registry keys that turns a Workstation into Server, which in turn change a number of other keys, however this is against license agreements and should not be attempted.
Workstation can be upgraded to a Server, but it cannot become a PDC or BDC, to do this a fresh installation of NT server would be needed. To convert follow steps below
If you have your NT Workstation upgraded with Service Packs, it is necessary to upgrade the server with the same service pack best performed by an unattended installation described in your FAQ. Otherwise you get a lot of unpredictable problems up to an core dump.
Q. I have bought a new disk, how do I move NT to this new disk?
A. There are various methods, depending on your setup and needs. The best method is to:
If the tape drive is not an option and the partition is NTFS you still have a number of options, you could setup the new disk as a mirror of your existing disk, then break the mirror and remove the old disk setting the new disk as the boot disk. You can also use the utility scopy that is supplied with the NT resource kit by fitting the new hard disk, creating an NTFS partition on it and then performing
scopy <source drive>: <target drive>: /o /a /s
To use the scopy command you must have Backup and Restore User Rights. Once the copy is complete shutdown NT, remove the old drive, and set the new drive to master (if IDE) or SCSI 0/6 (if SCSI) and boot of the NT installation disks, and again repair everything except "Check System Files". If you have time it can be worth creating a temporary NT installation on the drive before performing the copy, booting off of this minimal installation and perform the scopy from there as this means no files will be locked, and then you would only need to repair the boot sector.
Other methods include ghost copy from http://www.ghostsoft.com and DriveCopy from http://www.powerquest.com which copy and entire disk which should eliminate the need for performing a repair. I have used the ghostsoft utility and it works well.
Make sure if you are moving NT to a different type of disk, i.e. one that needs a different driver, you install the new driver before you perform the copy so that when NT boots off of the new disk it has the needed drivers.
Another option would be to use Mirroring (if you have Server). Install the new disk and make it a mirror of the boot/system partitions. Once it is up-to-date remove the old disk and use the new.
Q. Can I upgrade from Windows95 to NT 4.0?
A. There is no upgrade path from Windows95 to NT4.0. The best option would be to have a dual boot if you have 150Mb of uncompressed space free. Just install NT4.0 into a DIFFERENT directory (if you install NT4.0 into the same directory as Windows95 it will corrupt the 95 registry) and when booting the machine you will have a choice of NT4.0 or Windows95.
Q. How do I remove NT from a FAT partition?
A. Boot MS-DOS with the deltree utility.
Q. How do I remove NT from a NTFS partition?
A. The best way is to delete the partition. Start the computer from the NT installation disks. When the option to create/choose partitions select the NTFS partition NT is installed on and press D to delete the partition, and then L to confirm.
Q. How do I install the Iomega Parallel Disk Drive?
A. Follow the steps below
Notes:
When you start up your pc, make sure there is no ZIP disk in the drive-
otherwise NT will run checkdisk on the drive, which can take an eternity.
If you do not have the ZIP drive attached when you boot up, you will get an error at bootup that a service did not start up.
Q. How do I install at tape drive on NT Server?
A. Follow instructions below
NT 4.0 will also detect and install certain tape drivers (such as 4mm DAT) which means there is no need for a reboot after the installation.
Q. How do I install the NEC 4x4 CD changer?
A. NEC does not currently have drivers for NT 4.0, so the CDROM must rely on Microsoft's generic drivers. I've been able to get all four slots to read data correctly without any special tweaking; however, there are some annoyances that still remain.
Create a shortcut that points to driveletter:\\ instead of using the run box and typing it in eases use of the drive.
Q. What are symbol files, and do I need them?
A. Symbol files are created when images are compiled and are used for debugging an image. They allow someone with the correct tools to view code as the software is running. You do not need symbol files unless you are a developer.
Q. How do I install NT and Linux?
A. Linux has a boot manager called LILO (which is a separate utility), and it will boot Linux on its native EXT2 partition, and any other DOS/WIN bootimages residing on a FAT16 partition. It doesn't really care whether it is dos/win95/NT, it will boot it. So as long as NT is installed on a FAT16 partition, there is no problem with LILO. Apparently the latest Linux kernel has FAT32 support, so that may also be an option as well. Actually Linux supports FAT16 and can mount the FAT16 partition under its filesystem and have all the DOS/WIN files visible if you want it to. An alternative to LILO is Grub which can be downloaded from http://www.uruk.org/~erich/grub .
There is something else called LOADIN, allowing linux to be installed as a MSDOS subdirectory in a DOS/WIN system. This allows Linux to be run as an application after you started DOS. This does not work with NT. This is as Linux needs to run in supervisor mode and not user mode. NT will not yield at all on this. Windows 95 is the same but you can set loadlin to run in Dos mode where it just sees Dos 7 and works fine.
Linux and NT will work even if Windows NT is on NTFS. You need to set in linux fdisk for the Linux drive to be flagged bootable, not NT. Then install lilo and select to boot the linux partition and NT (which will say OS/2 in lilo). This way you can use both NT and Linux and still have a NTFS partition. Lilo must reside on the Linux root sector and not the MBR.
Another method is as follows:
You can learn more about it from the Linux documentation project and the FAQ inside. It is mirrored in a large number of locations. This is one of the mirrors ftp://ftp.ox.ac.uk/pub/linux/LDP_WWW/linux.html
Q. How do I install NT over the network?
A. If you do not currently have any operating system installed on your machine, then you need to create a bootable floppy disk that contains a driver for your network card and network protocol. A tool is provided called "Network Client Administrator" which automatically creates a bootable disk used to install Windows95 or Network Client. It is possible to use this tool to also create a disk that can be used to install NT with a bit of tweaking :-)
If you plan to produce a large number of install disks you can configure the Network Client Administrator to also create Workstation and Server network installation disks. To do this you need to have the client directory on a hard disk and create 2 subdirectories under it (\\server\client).
When creating the network disk you will now also have options for "Windows NT Workstation" and "Windows NT Server".
Q. Is it possible to use Disk Duplication to Distribute Windows NT?
A. It is OK to use disk duplication to install NT, but not a complete NT installation. You should follow the steps below:
The traditional problems with cloning were that the SID would be duplicated, however there are now several third party products that enable you to change the SID of a duplicated machine, you would then add the machine a new Computer Account on the PDC and change its name.
| NT Internals | http://www.sysinternals.com |
| ImageCast | http://www.netversant.com |
| DiskClone | http://www.qdeck.com |
| DriveCopy | http://www.powerquest.com |
| ImageBlast | http://www.keylabs.com |
| Ghost | http://www.ghostsoft.com |
Q. How do I perform an unattended installation?
A. It is possible to specify a text file that can be passed to the Windows NT installation program that contains answers to the questions the installation procedure asks. This file is usually called unattend.txt and is passed to the Windows NT installation program using the /u:unattend.txt qualifier. The answer file has to adhere to a strict format which can be very complex, however there is a utility on the NT Server CD called SETUPMGR.EXE (in the Support/Deptools/I386) that allows the information to be filled into dialog boxes and it will then create the unattend.txt (or any other name) for you. Below is an example of how to use the SETUPMGR.EXE file:
Microsoft have a document on automated installations at http://www.microsoft.com/NTWorkstation called "Deployment Guide to Windows NT Setup"
Q. Is it possible to specify unique items during an unattended install?
A. The unattended installation file contains details for settings that will apply to all machines, however there are some settings that you may want to be different from machine to machine, such as user name, computer name, TCP/IP address etc. This can be accomplished by producing a text file in a certain format, with different sections for each computer. The UDF file is used by specifying the /UDF:ID[,<database file name>]. An example UDF file would be
[UniqueIds]
u1 = UserData,TCPIPParams
u2 = UserData,TCPIPParams
[u1:UserData]
FullName = "John Savill"
ComputerName = SavillComp
ProductID = xxx-xxxxxx
[u1:TCPIPParams]
IPAddress = 200.200.153.45
[u2:UserData]
FullName = "Kevin Savill"
ComputerName = KevinComp
ProductID = xxx-xxxxxx
[u2:TCPIPParams]
IPAddress = 200.200.153.46
The ID specified would be (in the case above) u1 or u2. If the above
file was saved as udf.txt to perform an unattended
installation for machine one you would use
winnt /b /s:z: /u:unattend.txt /UDF:u1,udf.txt
which would set the installation as user John Savill, computer name
SavillComp and IP address 200.200.153.45. If a parameter is specified in
both the unattend answer file and the UDF the value in the UDF will be
used. (The /b means its a floppyless installation and the /s specifies the
source for the installation files and UDF etc. You would needed to have
created the connection to z: already (net use z: //savillcomp/dist))
The structure of the UDF uses a subset of the sections available in the unattended answer file.
Q. How do I automatically install applications as part of the unattended installation?
A. A utility is supplied on the NT distribution CD called SYSDIFF.EXE which is used to create a file containing files and registry changes needed for an application or set of applications to be installed. To use SYSDIFF just copy it from the CD to your hard disk
Alternativly there is a newer version available as a fix from ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/fixes/usa/NT40/utilities/Sysdiff-fix/, download sysdiffa.exe for Alpha, sysdiffi.exe for Intel.
The basics behind SYSDIFF is it creates a snapshot of the system before the application is installed, the application is installed and SYSDIFF is run again which compares the current system to the snapshot taken, and any changes to the registry and files are saved. An example usage need to include the following
Note: Using the /apply method the %systemroot% has to be the same on all machines, i.e. if the diff file was created on a machine with a %systemroot% of d:\winnt\ all machines must be installed to d:\winnt\ ([Unattended] TargetPath)
Q. Install detects the wrong video card and locks the installation.
A. When NT detects a video card it insists that you click the "Test" button. If the NT installation procedure incorrectly detects the hardware then it can cause the NT installation to hang and the only way to continue is to press the Reset button (e.g. the Number 9FX Reality card). To solve this problem when it detects the card just click the CANCEL button and it will leave the default VGA driver.
After the installation has finished manually install the new driver supplied with the graphics card, or download it from the makers web site.
Q. How do I upgrade from NT 3.51 to NT 4.0?
A. The scenario below is for upgrade an NT Workstation 3.51 machine to a NT Workstation 4.0 machine. It is the same to upgrade a NT Server 3.51 to a NT Server 4.0, except that if you upgrade a server you will also be given the option to install IIS (Internet Information Server).
The only problem with the upgrade is it does not remove old applications that were part of 3.51, such as cardfile.exe.
Q. When I use an unattended installation, how do I avoid the click "Yes" at the license agreement?
A. In the [unattended] section of your unattended answer file insert the line
OemSkipEula = yes
Q. I have NT installed, how do I install Windows95?
A. If you already have DOS installed, then boot to DOS and install Windows95. The instructions below are if you only have Windows NT installed.
For this procedure to work the system partition (c:) must be FAT.
Q. How do I remove Windows95/Dos from my NT system?
A. The procedure below should be used on systems with Windows95 and/or DOS installed, however be aware it is sometimes good idea to have a small DOS installation for use with hardware setup etc. Before you start this make sure you have an up-to date ERD (rdisk -s) and the 3 NT installation disk (winnt32 /ox) just in case :-)
Q. I can't create a NTFS partition over 4GB during installation.
A. During the text based portion of the NT installation, it is possible to create and format partitions. The maximum size for an NTFS partition is very large (16 exabytes), however the maximum size for a FAT partition under NT is 4GB (2GB under DOS). If you format a partition as NTFS during NT installation, it originally formats it as FAT and then converts it in the final stages of the NT installation, and this you are limited to a maximum partition size of 4GB during the NT installation.
To get round this problem there are several paths of action open to you
If you are performing an unattended installation it is possible to create a greater than 4GB partition using the ExtendOEMPartition flag in the unattended file. This key causes text-mode setup to extend the partition on which the temporary Windows NT sources are located into any available unpartitioned space that physically follows it on the disk. Under the [unattended] section include the lines:
FileSystem = convertNTFS
ExtendOemPartition = 1, NoWait
The NoWait is only availble from Service Pack 1 and above.
Also if you are installing from a distribution kit you can copy the Service Pack 3 version of setupdd.sys and replace the version in i386 folder of the NT distribution set.
For more information see knowledge base articles:
Q. I cannot upgrade my 4.0 NT installation with the NT 4.0 upgrade CD.
A. Microsoft have confirmed this to be a problem with the software, and more information can be found in knowledge base article q154538 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q154/5/38.asp .
A workaround is available, as the setup procedure checks the registry entry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\CurrentVersion for the version number, and only upgrades if the version is 3.1 ,3.5 or 3.51. You can therefore edit this entry and change the current version number
You should now be able to upgrade.
Q. How do I create the NT installation disks?
A. Follow the procedure below:
Q. How can I use a Network card that is not one of those shown with Network Client Administrator?
A. The Network Client Administrator tool located in the Administrative Tools section is a very useful tool, but lacks the seemingly obvious function of "Have disk" to use a NDIS 2.0 compatible driver supplied with the network card. You can get round this though with a minimum of hassle.
The Network Client Administrator disk is now configured to use your network card. A known problem is with Irmatrac/Microdyne token ring adapters, and will not work unless the net sub-directory on the disk is renamed to dev.
This solution is fine for one off disk creations, however you may want to have the network card displayed as an option by the Network Card Administrator program, to do this perform the following
Network Client Administrator will now list the new card as an option as a Network card.
A. The easiest way to do this is to use the net localgroup command, however before you can use the command you have to have connected to the PDC and start the netlogon service. The following commands can be used in the unattended installation using the CMDLINES.TXT file:
net use \\<machine name of the PDC> /user:<domain name>\<username>
<password>
net start netlogon
net localgroup Administrators "<domain name>\<user>"
/add
Q. I have problems running a program as part of the unattended installation?
A. You can use the /e switch during the unattended installation to specify a program to run, e.g.
winnt.exe /u:unattend.txt /s:w: /e:"w:\servpack\update -u -z"
The above would be used to install a service pack after the NT installation (-u for unattended, -z for no reboot), however you may get an error and in setuplog.txt the following error:
"Warning:
Setup was unable to invoke external program
<drive>:\<directory>\<program> because of the following
error:
CreateProcess returned error 3."
This is because after the installation network drives are no longer mapped and w: no longer exists. Any source files need to be locally stored to be able to be run and then with the /e use a local drive letter.
Q. I have Windows NT installed, how do I install Windows 98?
A. As with the installation of Windows 95, the system partition (the active partition, c:) must be FAT and not NTFS as Windows 98 cannot read or write to an NTFS partition. Windows 98 places COMMAND.COM on the active partition (along with a blank autoexec.bat).
If you system partition is not FAT then you should back up your data, reformat the partition as FAT and restore the backup.
Windows 98 is NT boot menu friendly which means it will not replace the boot loader code of the disk and instead automatically adds an option to the boot menu (boot.ini) of the format
C:\="Microsoft Windows 98"
This means upon booting the machine Windows 98 or NT can be chosen.
Windows 98 cannot be installed from within Windows NT so if you have DOS also installed, boot from DOS (its boot menu item will be replaced after the Windows 98 installation with the Windows 98 name) and run the setup.exe on the Windows 98 installation disk.
If you do not have DOS installed you should boot off of a DOS boot disk with a driver for your CD-ROM and again run SETUP.EXE.
Once installation has started you will be able to choose the installation drive and directory (only FAT partitions will be allowed). If there are NTFS partitions on the system a warning will be given that the contents will not be viewable under Windows 98.
Once installation has completed no user action is needed and you may boot off of either installation.
Ensure once you have completed the Windows 98 installation you do NOT upgrade the active partition to FAT32. Windows NT 4.0 cannot read FAT32 and converting the active partition to FAT32 will render the NT boot menu unusable and unbootable.
Q. I have Windows 98 installed, how do I install NT?
A. The only requirement for installing Windows NT after Windows 98 is that the system partition (C:) is not FAT32 as Windows NT cannot read FAT32 (at least until version 5.0 of NT which has full FAT32 support).
If the active partition is FAT32 you will need to convert it back to FAT16. There are a number of 3rd party applications that can do this, e.g. Partition It from QuarterDeck (http://www.quarterdeck.com). I have never used it but other people have recommended it.
To begin the installation of NT just boot into Windows 98 and run WINNT32.EXE from the Windows NT installation and proceed as normal (select install not upgrade). The Windows NT installation procedure will automatically detect the Windows 98 installation and add it to the NT boot menu.
Do NOT upgrade the system partition to NTFS using the CONVERT.EXE command as Windows 98 will no longer be able to boot.
Q. I have Windows NT 5.0 installed but when I try to install Windows NT 4.0 the installation fails.
A. Windows NT 5.0 has changed the boot loader and so trying to install Windows NT 4.0 afterwards Setup may continuously restart each time the computer is started without ever finishing.
Service Pack 4 provides an updated winnt32.exe that allows Windows NT 4.0 to be installed after NT 5.0 so you will need to perform the following:
Q. I want to install Windows 98 and NT, what file system should I use?
A. Windows 98 supports 2 file systems, FAT and FAT32. Windows NT 4.0 supports 2 main file systems FAT and NTFS. The only common file system is FAT which means the active partition, C:, must be FAT.
If you then partition the harddisk into one partition for the active partition, one for 98 (d:) and one for NT (e:) you could have FAT32 on D: and NTFS on E: but you should be aware that the 2 operating systems will not be able to see the partition of the other. If you ever want a partition that can be seen by both you will need FAT.
Windows NT 5.0 introduces support for FAT32 so in this case the active partition could be FAT32 and you would only need one separate partition for NT if you wanted NTFS.
There are tools that enable Windows 9x to read NTFS, e.g. NTFSDOS from http://www.sysinternals.com however these are mainly readonly and I may lead to corruption if not used correctly. Also bear in mind Windows NT 5.0 introduces NTFS 5.0 which these utilities will not be able to read.
Q. How do I manually install SCSI drivers before the autodetect of installation?
A. When you put the first Boot disk in to install NT. There is a brief moment when at the top of the screen in white lettering is "Setup is inspecting your Hardware....". Press the F6 key there. Once the NT Kernel is loaded it will ask you to select which drivers to install at the end of reading disk 2 but before selecting the installation type.
Q. During installation of Windows NT Server 5.0 the type of server cannot be set. - NT 5.0 only
A. Unlike earlier versions of Windows NT, the role of a server can be changed at any time in its life, e.g. from a member server to a domain controller, and from a domain controller back to a member server. This means that when initially installed, ALL servers are installed as stand-alone/member servers (even upgraded PDC/BDC's) which then have to be promoted to domain servers.
For information on promoting a server to a domain controller see Q. How do I promote a server to a domain controller?
Q. How do I delete the recycle bin as part of an unattended installation.
A. The recycle bin is just a registry entry so if we delete the registry entry it will remove the recycle bin.
Create the following in a file remreycl.inf
[Version]
Signature = "$Windows NT$"
Provider=%Provider%
[Strings]
Provider="SavillTech Ltd"
[DefaultInstall]
AddReg = AddReg
DelReg = DelReg
UpdateInis = UpdateInis
[AddReg]
[DelReg]
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Desktop\NameSpace\{645FF040-5081-101B-9F08-00AA002F954E}
[UpdateInis]
You should then create a $OEM$ folder in your I386 installation directory and copy the file remreycl.reg into the directory.
If the file cmdlines.txt exists edit it otherwise create it (in the $OEM$ directory) and add the following:
[Commands]
"rundll32 setupapi,InstallHinfSection DefaultInstall 128
.\remreycl.inf"
Q. During an unattended installation I am prompted for an IP address if 0 is in the given address.
A. If you have an unattended install file with information such as
[TCPIPParameters]
DHCP=NO
IPAddress=200.200.0.200
Subnet=255.255.0.0
You will receive an error dialog during the installation:
"The IPAddress key has an invalid IP address. Please correct the problem after the property sheet is displayed"
If you then click OK the installation will continue.
The bug only applies if there is a 0 in the second or third octet, e.g. xxx.here.orhere.xxx.
Service Pack 2 or later corrected this problem and so to avoid the message replace the tcpcfg.dl_ on your distribution server (the i386 directory) with the tcpcfg.dll from the latest service pack.
Q. How do I map a network drive during an unattended installation?
A. This may be useful if you want to install software, such as a service pack, during installation.
Using the Cmdlines.txt file it is easy to map to a network share. Cmdlines.txt must be stored in the $OEM$ directory under your NT installation area, e.g. i386\$OEM$. A very basic cmdlines.txt would consist of
[Unattended]
OemPreinstall = yes
The map command should be under the [Commands] section of your unattended installs file, e.g.
[Commands]
".\net use <drive letter>: \\<server>\<share>
/user:<domain>\<user> [<password>] /persistent:no"
It is important to add the /user otherwise the system will attempt to use the System account which does not have an actual user account thus the command would fail. The /persistent:no is used as the connection should not be remade at each logon.
One option would be to enable the Guest account and give it access to the share which would mean you could connect at /user:<domain>\Guest which would allow a connection to be made to the share even if the domain controller cannot be contacted.
A. The basic idea behind Windows NT licensing is that you purchase NT Server and license which allows you to install the software on one machine, however you cannot use the software unless you have a client license. A client license is just a piece of paper, no codes, no passwords, just a piece of paper saying you can use one more client. A client license is around US$40, which means you have to buy the NT server software (around US$650) and then US$40 times the number of clients to the machine, plus the cost of the client software and licenses!
There are two methods of licensing, per seat and per server. Per seat licensing is where each network user has a license, and allows the user to access as many/all of the servers in the enterprise. This is the most popular and cost effective method if you have two or more NT servers.
The second method, per server, also known as concurrent licensing is where licenses are purchased and "installed" on the server. For example, if you purchased 50 client licenses and installed them on the server, up-to 50 connections at a time would be allowed. If you then purchased another server, you would need to buy another 50 client licenses for connections to that server.
From the above you can see that if you have more than 2 NT Servers you will want per seat, with the exception of a machine such as an Internet service server, which would have different people connecting to the site all the time, so you would need x client licenses, where x is the maximum number of people you expect to connect at any one time.
It is possible to perform a once only conversation of per server licenses to per seat licenses.
Q. How can I view what licenses I have installed/used?
A. NT Server has a utility called License Manager that enables you to inspect the licenses and their use:
Q. How do I install extra licenses?
A. This method is only for Per Server
For Per Seat
Q. How do I convert from Per Server to Per Seat?
A. This is legally a one way conversion process:
Q. How can I reset the License Information?
A. More information can be found in Knowledge Base article Q153140:
Q. How can I run the License Manager software on a NT Workstation?
A. The NT Workstation server tools do not include this software, however since Server and Workstation share much of the same code then you can just copy the following files from the %systemroot%/system32 directory on the server to the %systemroot%/system32 directory on the workstation
Q. How do I communicate with a Windows 95 client?
A. Enable the winpopup utility on all Windows 95 machines. The best way is to place winpopup in the Startup group under Program Files.
Other options include using Microsoft's System Management Server product and Hewlett Packards Desktop Administrator (DTA) (http://www.openview.hp.com/dta/).
Q. How can I administer my domain from a Windows95 client?
A. Install the server tools that are part of the Windows NT installation CD. Right click on the file <CD ROM>:\clients\srvtools\win95\srvtools.inf.
Other options are the Hyena product, http://www.adkins-resource.com/index.html, which I have not used but have been advised is very good.
Q. How do I force a 95 machine to logon to a domain?
A. Using the Policy editor, create a new profile, or edit your existing profile
Q. How do I enable Windows 9x machines to use Group policies?
A. Copy the file grouppol.dll from the windows9x installation CD to the system folder of each Windows 9x machine, e.g. c:\windows\system. You also need to apply the changes as supplied in the grouppol.reg file (in the same directory as grouppol.dll). This needs to be run by entering
C:\> regedit grouppol.reg
This adds the following entries (if you have problems check they exist)
- Registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Network\Logon
Value name (STRING): PolicyHandler
Value data: GROUPPOL.DLL, ProcessPolicies
- Registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\
MSNP32\NetworkProvider
Value name (STRING): GroupFcn
Value data: GROUPPOL.DLL, NTGetUserGroups
- Registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\
NWNP32\NetworkProvider
Value name (STRING): GroupFcn
Value data: GROUPPOL.DLL, NWGetUserGroups
This could be automated by adding the copy and the registry update to a logon script. A grouppol.inf is also supplied which enables you to install copletely by right clicking on it and selecting install.
All of the above is performed if you install the Windows 9x system policy editor on a machine.
Q. How do I enable Load Balancing on a Windows 95 machine?
A. Follow procedures below:
This will enable a Windows 95 machine to look for the script from the logon server.
Q. How can I stop a Windows 95 machine acting as a browse master or backup browser?
A. To stop a Windows 95 machine acting as a browse master perform the following:
Q. Some of the Windows 95/98 clients do not show up in Network Neighborhood.
A. This is usually caused by the machines not having "File and Print Sharing" installed
A. In the old Windows for Workgroups days the admincfg.exe utility was used to disable password caching and a similar functionality exists in Windows 95 and Windows 98.
Upon reboot clients will no longer have to enter a local password, just the domain.
When clients use the Password control panel applet the "Change Windows Password" button under "Windows password" will be grayed out and only "Other passwords can be set". Clients would then select "Microsoft Networking" as per normal
Q. How do I enable profiles on a Windows 9x machine?
A. By default all users of a Windows 9x machine share the same profile, however machines can be configured so that each logon name can have individual settings such as background, colours etc. To enable multiple profiles perform the following:
Once restarted when you logon for the first time as a user on the machine you will be given the option to retain options. Click Yes.
The profiles are stored in the C:\windows\profiles\<username> directory (or wherever windows is installed).
If you wanted to automate this process you could create a system policy using the Windows 9x policy editor
Q. How do I enable roaming profiles for Windows 9x machines?
A. Once you have enabled individual profiles on the Windows 9x machines a copy of the profile is automatically stored in the users home directory (which is normally on a network server) and will consist of a number of files and a user.dat which is the Windows 9x equivalent of ntuser.dat.
Therefore to enable roaming profiles for Windows 9x machines nothing needs doing except the following:
Q. Can Windows NT and Windows 9x share a roaming profile?
A. No. The main problem is that Windows 9x clients store the profile in the root of their home directory whereas Windows NT clients store the profile in the "profile path" location. Even if you made these the same it would still not work as there are differences in the registry structure and Windows NT stores the user portion of the registry in the file NTUSER.DAT, Windows 9x stores in USER.DAT.
Sorry!
Q. How do I install the Windows 9x Policy Editor?
A. To install the Windows 9x Policy Editor on a Windows 9x machine perform the following:
The System Policy Editor will now be available under Start - Programs - Accessories - System Tools - System Policy Editor.
To install the Windows 9x policy editor under an NT machine just copy the Netadmin\Poledit directory to a folder on the Windows NT machine, e.g. 98poledt and create a shortcut on your desktop or Start menu to poledit.exe. When you first run it, it will load the NT .adm files. Remove these using Options - Policy Template and then re-add those located in the 98poledt folder (normally common.adm and windows.adm). Be aware - Profiles created under NT, even with the Windows 9x version of the policy editor will not be read correctly from a Windows 9x machine so the config.pol file needed for Windows 9x machines should be created under a Windows 9x machine and then copied to the netlogon share of the domain controller.
Installing under NT is only useful for experimenting and it will not be able to load profiles created by a Windows 9x machine.
Q. How can I stop Windows 9x profiles being copied to the home directory?
A. By default if individual profiles are configured on a Windows 9x machine the profile is also copied to the users home directory (usually a network share) which means the user has the same desktop settings on any 9x machine. If you don't want this behaviour but still want individual settings perform the following on each machine:
Once the reboot is complete the users profile will no longer be copied to the network share.
Q. I am getting a message 'dbprocess dead or not enabled' running my query.
A. If you receive the above error and/or are seeing an 'Exception Access Violation' message in the SQL errorlog there are a number of possible explanations.
Basically SQL is internally global page faulting or Access Violating (same thing) and you should see messages to this effect in the SQL errorlog. There are only three reasons for this :-
Assuming it's not a database corruption, then follow the following diagnostic process :-
MS will need :-
With SQL 7 there is a new utility that will garner most of this information for you automatically. It is called sqldiag -
C:\> sqldiag -U<login> -P<password> -O<output filename>
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. How can I add/amend/delete columns?
A. Under SQL 7.0 all the above are easily done with the gui or supplied stored-procedures.
With SQL 6.5 and below it is only possible to ADD a nullable column. For any other change a new table must be created, the data copied across, and the tables renamed around.
Certain 3rd party tools provide a gui interface to do this, that makes it look transparent, however they are really doing all the work described above, so if you make the change to a large table it will take a long time to do the work.
Examples of tools are Microsoft's Visual Database Tools (part of Visual Interdev) and SFI's SQL Programmer.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. I am getting a blue screen / completely hung machine / server restart on my SQL Server/client.
A. All the above can ONLY be caused by a problem with something in NT running in Kernel Mode. e.g. bits of NT, scsi drivers, network drivers, video drivers etc.
All SQL Server code runs in user mode, just like any normal program. Therefore it is no more capable of causing a blue-screen than Word is. It can only "cause" the problem in as much as it might hit the disk subsystem hard and expose a bug in a scsi driver.
If you are getting one of these problems then it needs to be investigated like any other NT blue-screen problem. i.e. check the driver/program in control at the time, use dumpexam, apply a newer service pack, contact MS.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. Where are the cascade update/delete functions in SQL Server?
A. There aren't any I'm afraid. These were initially thought to be going into SQL 7 but won't be there now. They will be in a "future" SQL release.
You need to implement your own cascade functionality with triggers. See Q142480 (http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q142/4/80.asp)in the MS Knolwdge Base for more information on this and the ways to work with foreign keys which cause problems due to the way that triggers work/fire.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. How can I issue a SQL command that uses a variable for the tablename, columns etc?
A. Look up the EXEC command information in the SQL built in help. Basically it is used to run a defined procedure.
A short example that selects a column from a table :-
USE pubs
go
DECLARE @str varchar(255)
DECLARE @columnname varchar(30)
SELECT @columnname='au_lname'
SELECT @str = 'SELECT ' + @columnname + ' FROM authors'
EXEC (@str)
-------------------------------
Another example from the books-online. This example shows how EXECUTE handles dynamically built strings with variables. This example creates a cursor (tables_cursor) to hold a list of all user-defined tables (type = 'U').
DECLARE tables_cursor CURSOR
FOR
SELECT name FROM sysobjects WHERE type = 'U'
OPEN tables_cursor
DECLARE @tablename varchar(30)
FETCH NEXT FROM tables_cursor INTO @tablename
WHILE (@@fetch_status -1)
BEGIN
/*
A @@fetch_status of -2 means that the row has been deleted.
No need to test for this as the result of this loop is to
drop all user-defined tables.
*/
EXEC ("DROP TABLE " @tablename)
FETCH NEXT FROM tables_cursor INTO @tablename
END
PRINT "All user-defined tables have been dropped from the database."
DEALLOCATE tables_cursor
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. Why does my transaction-log fill up when I use fast-bcp?
A. You may think that fast-bcp does not log anything, and indeed Fast BCP does not log record updates, however it does log extent allocations. It needs to do this so that if the bcp is terminated unexpectedly (maybe the power goes out), SQL can recover the space.
Therefore with large bcp's when a lot of extents need allocating the log can still fill. In which case it needs to be made larger.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. Why can't I backup/restore my SQL Server database to the network?
A. The reason is that the MSSQLSERVER service is running under a separate set of NT credentials. It doesn't matter who YOU are logged on as (after all SQL runs quite happily when no-one is logged on to the console doesn't it). Therefore your logon account and any mapped drives are irrelevant. It is SQL Server doing the backup, not you.
The default set of NT credentials used by MSSQLSERVER is the Local system account. You can check what user-id that MSSQLSERVER is running under by looking at control panel/services highlighting MSSQLSERVER and choosing the start-up option.
The Local system account has no access to shares on the network as it isn't an authenticated network account.
So, if you want to backup to a network share you have two choices :-
1, Change the account the MSSQLSERVER service runs under to a user account with the relevant network rights.
or
2, Amend the following registry value on the TARGET server and add the sharename you want to dump to - the share does not then authenticate who is coming in and so a Local system account will work. The server service on the target server must be re-started before the change takes effect. Note that this effectively removes security on that share, so you need to be careful about what is in the share. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters\NullSessionShares
Whichever method you use, you MUST also use a UNC name to reference the file required and not a drive letter.
e.g. DUMP DATABASE pubs to DISK='\\server01\share\backupdir\backup.dmp'
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. Can I do a SQL backup to a tape drive on another server?
A. No, not with built-in SQL tools. SQL will only dump to local tape devices. If you could find an NT driver that would make a remote tape drive look local then this would work as SQL just uses standard i/o calls. I don't know of such a driver at the moment.
You can always dump the SQL database to disk locally (or across the network with some provisos) and then back that up to tape.
Finally, you CAN do what you want with a 3rd party backup tool that has a SQL agent. Examples are BEI Ultrabac, Cheyenne Arcserve, Seagate BackupExec, Legato Networker and IBM ADSM - I'm sure there are others. These put SQL dumps (via a standard named-pipe interface) onto a standard dump tape, potentially as part of a complete server backup and not just SQL. Obviously if the named-pipe connection is made across the network then the dump will usually be a lot slower than doing it locally.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. I have a query that seems to lock other users out of the system.
A. This can happen especially when using tempdb. In situations like this the usual problem is with locks. Check with sp_lock or sp_lock2 what the offending query is doing.
One common occurrence that people fell foul of was introduced in SQL 6.5 when MS decided to let table creation be allowed in transactions by making it an ATOMIC transaction. A by product of this is that when a SELECT INTO is done it locks out system tables in the database concerned and prevents other users from accessing them. With a long-running select into this can cause real problems.
MS recognised this and as long as you have service pack 1 applied you can set traceflag -T5302 to remove this behaviour. Check out Q153441 (http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q153/4/41.asp) for more info.
Contributed by Neil Pike
A. All service-packs come with problems, however in most cases they fix a lot more problems than they cause. 99% of bugs you may find in SP4 will be present in the gold release and all subsequent service packs - they are un-fixed/unknown bugs that are present in every release.
SP4, as SQL service packs go, is a very stable one. For a list of bugs fixed in SP4, download it and check the fixlist.txt file.
There are a couple of known problems with SP4 that don't occur with other service packs.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. How do I transfer data from another DBMS/format to SQL Server?
A. For example if you wanted to transfer from FoxPro, Access, AS/400, DB/2, Oracle.
There are a variety of methods :-
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. Why can't I get at a network file when I run a program from xp_cmdshell?
A. The reason is that the MSSQLSERVER service is running under a separate set of NT credentials. It doesn't matter who YOU are logged on as (after all SQL runs quite happily when no-one is logged on to the console doesn't it). Therefore your logon account and any mapped drives are irrelevant. It is SQL Server running the program (e.g. bcp) not you.
The default set of NT credentials used by MSSQLSERVER is the Localsystem account. You can check what userid that MSSQLSERVER is running under by looking at control panel/services highlighting MSSQLSERVER and choosing the start-up option.
The Localsystem account has no access to shares on the network as it isn't an authenticated network account.
So, if you want a program running under xp_cmdshell to access a network resource you have two choices :-
1, Change the account the MSSQLSERVER service runs under to a user account with the relevant network rights.
or
2, Amend the following registry value on the TARGET server and add the sharename you want to access - the share does not then authenticate who is coming in and so a Localsystem account will work. The server service on the target server must be re-started before the change takes effect. Note that this effectively removes security on that share, so you need to be careful about what is in the share. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters\NullSessionShares
Whichever method you use, you MUST use a UNC name to reference the
resources required and not a drive letter.
e.g. xp_cmdshell 'dir \\server01\share'
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. Is MS SQL Server Y2K compliant?
A. That depends on what you mean. If you mean the base SQL functionality then yes, as long as you are using "proper" datetime formats then SQL is compliant - if you are holding dates in char/numeric format, then it totally depends on how you are processing them, it is not an MS SQL Server issue. It does date-windowing for two digit dates. If you specify only the last two digits of the year, values less than 50 are interpreted as 20yy, and values greater than or equal to 50 are interpreted as 19yy. For example, if you specify 3, the result is 2003. If you specify 82, the result is 1982. You must type the century when the day is omitted or when you need a century other than the default.
However, if you mean the whole of the MS SQL Server product including all the tools, then there are a few non-showstopper problems that have been found. These can be found documented at www.microsoft.com/y2k along with MS's stance and technical info on all Y2K issues.
These problems have been found, fixed and tested in SQL 6.5 and will be in Service Pack 5 when it is released. Before that a Y2K fix (build 339) can be obtained from MS PSS - however I would recommend waiting for SP5.
SQL 7.0 will be Y2K compliant at release.
SQL 1.x, 4.x and 6.0 are NOT being tested or certified by MS. They are unlikely to have other problems than those found in the 6.5 product though, so if you can live with those (and most people can), then they should be ok. Vendor's certification should only be one part of Y2K testing anyway - the most important part is that YOU test your clients, servers, apps, databases, networks etc. in a real-world test.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. How can I change the owner of an object?
A. With SQL 7.0 there is a stored-procedure to do this, however under SQL 6.5 and earlier there is no supported method to do this.
It can be achieved by directly addressing and updating the system table concerned though.
(The last step is necessary as portions of system tables are kept in memory by SQL Server, and the only way to force these to update is to recycle SQL Server)
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. I've just changed NT domain for my SQL Server/clients and am unable to connect.
A. This isn't a SQL issue, it's an NT one. If you are using a net-lib that requires NT authentication - e.g. named-pipes or multi-protocol - then you MUST be able to authenticate to the copy of NT running SQL Server. You can test whether you can do this by doing a:
C:\> net view \\<servername>
from a command prompt on the client. If you get an access denied message, or get prompted for a password, then you aren't being authenticated.
If this happens then you need to setup a trust between the domains. Or, you could use a net-lib that does not need authentication - e.g. TCP/IP sockets.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. Are there any "easter eggs" in SQL Server?
A. The only one I'm aware of is in SQL Enterprise Manager under 6.5. (It may be there in 6.0 but I've never tried it).
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. How do I encrypt fields in SQL Server?
A. There is no supported, documented way of doing this, and because you can't write user-defined functions then your choices are :-
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. What tools are available to produce entity relationship diagrams for SQL Server?
A. There are several on the market, including (in no particular order)
Also there are some tools built-in to MS products. Note that these just do diagrams, whereas the 3rd party tools above have a wide-range of project lifecycle, reverse engineering etc. abilities.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. Where is the SQL Server FAQ?
A. There isn't one all encompassing FAQ like there is for some non-MS newsgroups, but there are a few smaller faq's worth a look.
Though it isn't a faq in the strictest sense, the best source of info on SQL problems, bugs etc. is www.microsoft.com/support - where the MS knowledgebase is.
Finally, you should always have a subscription to Technet as this gives you the knowledgebase on CD, as well as hundreds of articles, white-papers, resource-kits, service packs etc.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. Which SQL net-lib is the fastest?
A. On normal LAN and fast WAN links you are unlikely to see a real-world difference in responses times between any of the net-libs - this is due to the fact that network response/number of packets is not significant in these environments compared to application/database/server responses.
However, on slow network connections - anything from 64Kbit/sec and below can be considered slow - then you will see a performance improvement if you use the tcp-ip sockets net-lib.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. I'm having trouble installing SQL Server.
A. Try the following check-list of things that could go wrong.
Once installed, if you have trouble registering your SQL Server by name in SQL EM, then just register it with a name of just a period. i.e. "." without the quotes. This again bypasses the network layer and ensures that a local named-pipe is used.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. I am missing the whole of MSDB, or just some tables - how do I create them?
A. In the <sql>\INSTALL directory are the scripts that SQL runs itself to create the MSDB database and it's tables. If you need to re-create it, then make sure the devices are already there and then run :-
via ISQL/W or ISQL.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. Why do my device sizes appear as negative values in SQL EM?
A. You may also find that because of this error it will not let you make any changes.
This is caused by a known bug in Enterprise Manager when there is greater than 2Gb of free space on a disk. It was fixed in 6.5 SP3 and above. If you are running SQL EM from a client then you will need to apply SP3 to that as well.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. How do I do row-level locking on SQL Server?
A. Only SQL 7.0 has full built-in row-level locking.
SQL 6.5 has limited row-level locking that only occurs for inserts to the end of the last page of a table, if "sp_tableoption 'table_name', 'Insert row lock', true" is set. See the books-online for 6.5 for more information.
SQL 6.0 and previous have no row-level locking capabilities.
You can however effectively do row level locking with version 6.5 and earlier as long as each row takes up a whole page - thus locking 1 page is the same as 1 row. You can do this by padding a row with CHAR NOT NULL fields until the row length is forced to be greater than 1024 bytes. (Rows cannot span pages so this forces one row per page).
However, you should note that although the rows on this last data page are being row-level locked, any non-clustered index pages involved are not. These can be a source of contention and even deadlock - when two logically distinct transactions need to lock one or more index pages, and pessimistically in different orders.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. How many bytes can I fit on a page in SQL Server and why?
A. Rows can never cross page boundaries - page size in 6.5 and earlier is 2K, in SQL 7.0 it is 8K.
For 6.5 and earlier :-
Each 2048 byte page has a 32 byte header leaving 2016 bytes for data. You can have 2 rows of 1008 bytes or 10 rows of 201 bytes. The row size also includes a few bytes of overhead in addition to the data itself; there is more overhead if there are variable length columns.
One row cannot be 2016 bytes - this is because when you insert/update/delete a row, the entire row must be written to the transaction log in a log record. Log pages also have 2016 available bytes per page, and need 50 bytes for transaction log specific information, so this gives a maximum size for a single row of 1962 bytes.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. I am getting a gpf/registry error installing SQL Server - what is happening?
A. This could well be a known issue with SNMP caused when SNMP managers that come with some server management tools (especially with HP servers) register a lot of SNMP extensions. Specifically when HKLM\System\CCS\Services\SNMP\Paramaters\ExtensionAgents got to around 1K or more.
Either remove the SNMP service before installing SQL Server, or try the following workaround.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. How do I change the sort-order or character set for a SQL Server database?
A. Basically you can't. You have to get these parameters correct when you install SQL. You will have to :-
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. What SQL servicepack am I running?
A. Do a select @@version and check the build number against the following table. If it isn't listed here, then it is a "hot-fix" build that MS has given you to fix a specific problem. Hot-fix releases are NOT regression tested, so they should be applied to production systems with extreme caution.
Note that you can't apply 6.5 SP4 to either SBS or EE versions of SQL Server. You can wait for SP5, or get a hot-fix interim build from MS PSS.
| 6.50.201 | SQL Server 6.5 "gold" release. |
| 6.50.213 | SQL Server 6.5 with Service Pack 1 |
| 6.50.240 | SQL Server 6.5 with Service Pack 2 |
| 6.50.252 | SQL Server 6.5 with "bad" Service Pack 3 - SP3 was pulled and re-issued. Do not use this version. |
| 6.50.258 | SQL Server 6.5 with Service Pack 3 |
| 6.50.259 | SQL Server 6.5 on SBS only |
| 6.50.281 | SQL Server 6.5 with Service Pack 4 |
| 6.50.339 | SQL Server 6.5 "Y2K" Hot-fix |
| 6.00.121 | SQL Server 6.0 "gold" release. |
| 6.00.124 | SQL Server 6.0 with Service Pack 1 |
| 6.00.139 | SQL Server 6.0 with Service Pack 2 |
| 6.00.151 | SQL Server 6.0 with Service Pack 3 |
| 7.00.517 | SQL Server 7.0 Beta 3 |
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. My SQL Server database has been marked "suspect" - what can I do?
A. Firstly look in <sql>\LOG and look at all recent errorlog(s). There WILL be an indication here as to why the database has been marked suspect. You need to fix whatever the problem is first (i.e. missing file, permissions problem, hardware error etc.)
Then, when the problem has been fixed and you're either sure that the data is going to be ok, or you have no backup anyway, so you've nothing to lose, then change the database status to normal and restart SQL Server. To change the database status, and to get more information on recovery, look up the sp_resetstatus sp in the Books Online.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. How do I remove the tempdb database from master?
A. Do the following.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. What are the changes/differences between vX and vY of SQL Server?
A. Changes in functionality are typically documented in incremental steps from the previous release. The following sources are available :-
There is currently no Kb article for SQL 6.5 to SQL 7.0, so just look in the Books Online.
There are also occasionally changes introduced in service packs. These changes are documented in the readme.txt for the servicepack, which is cumulative. So SP4's readme contains all changes from SP1, 2 and 3 as well.
Contributed by Neil Pike
Q. How can I speed up SQL Server applications running over slow links?
A. First we need to define what a "slow" link is. Typically this is anything from 64Kbit/sec and down. On links of this speed the size of a resultset and the number of network packets that are exchanged can make a significant difference to overall response times.
First, either do a network trace, or use SQL Trace to see what exactly is being transferred during a typical client session. Then try the following :-
Q. How can I fix a corruption in a system table?
A. If the problem can be fixed with an index re-create, then there is a system stored-procedure to do this.
sp_fixindex <db_name>,<system_table_name>,<index-id>
e.g. sp_fixindex pubs,sysindexes,2
You can also issue the relevant dbcc command directly if sp_fixindex refuses to attempt the fix - e.g. for a non-clustered index on sysobjects
DBCC DBREPAIR(dbid, REPAIRINDEX, sysobjects, 2)
It is not possible to rebuild the clustered index on sysindexes or sysobjects.
If the above do not work, then the only choice is to create a new database and then use the transfer tools in SQL EM to copy the good data and objects across.
Q. Why can't I connect Enterprise Manager to my local copy of SQL Server?
A. This is down to the way that SQL interfaces with the NT networking code. The easiest way around this is to register the local server with a name of "." or "(local)" - ignore the double quotes in either case. Both of these names should force SQL to use a local-named pipe to connect which should work no matter what the default SQL connection parameters are set to.
Q. What is the limit on the number of tables in a query in SQL Server?
A. With SQL 6.5 and earlier the limit is 16. With SQL 7.0 the limit is 256. These figures are hard-coded into the SQL kernel and are arbitrarily chosen by the MS developers - but with good reason. The more tables there are, the longer it takes to optimise a query properly. There has to be a trade-off between the speed of running a query and the speed of optimising it.
It is possible to up the limit of 16 in SQL 6.5 by setting traceflag -T105. This is an undocumented and unsupported trace flag, so MS may not support you with any problems on a system that is running this. However, it was allegedly put into the product to allow some of the more complex Peoplesoft queries to run, and so it must have had some testing/QA done on it.
Normally, if a query needs more than 16 tables then you have a very bad query and/or database design. The best practice would be to break the query down into smaller parts and use temporary tables to hold interim resultsets. This will also make the query more understandable and may even speed it up as the optimiser has more of a chance to choose correct access plans and indices.
A. If you find objects are being dropped from the source this is a known bug that is caused when the server you are connecting to has a period in the name. Typically this is because you are referring to it by tcp-ip address.
What happens is that SQL sees the period and does a local named-pipe connect - which it should do if the name consists of just a period, but not when it contains a period - this means that SQL connects to the local machine as the target. As most people have checked the "drop objects first" box it then proceeds to drop all the objects concerned from what it thinks is the target machine - which is unfortunately the local (source) machine.
To prevent this problem do not refer to your SQL Server's by IP address. Either :-
Q. What registry entries does SQL Server use?
A. SQL Server uses the following registry keys. (If you delete all these then the SQL setup routine shouldn't spot the old version)
Q. How can I view the SQL Server log?
A. The SQL log is not accessible via standard SQL commands. The ways of accessing this information are :-
---------------------------------------
dbcc log [ (@dbid, @objid, @pagenum, @rownum, @nrecords, @type [, @printopt]) ]
dbcc log (5, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 1) // Show the last begin transaction record in the log
Parameters:
@dbid Database ID
@objid Object ID
A negative value indicates that @pagenum & @rownum represent a row
in the log to use as a starting pointin the scan of the log.
A value of zero indicates that log records for changes to @pagenum will
be included in the commands output.
A positive value followed by a non-zero value for @pagenum indicates that
@pagenum and @rownum represent a transaction ID. Log reccords for that
transaction will be included in the output.
A positive value followed by zero values for @pagenum and @rownum
indicates an object ID. Log records for changes to that object will be
included in the output.
@pagenum page number
@rownum row number in the log
Together with @pagenum, this is either a starting point in a scan of the
log or a transaction id.
@nrecords number of records to examine. If positive, the first
@type
@printopt
Q. How can I upgrade the 120-day evaluation version to the full SQL version?
A. It should be as simple as re-running SQL Setup from the full version CD, but unfortunately it isn't. (At least with 6.5 and earlier versions anyway)
One method would be to backup the databases, un-install SQL, re-install SQL and then load the databases again.
A faster method is :-
Q. I'm not seeing anything in the current activity screen in SQL EM.
A. This is usually caused by the "select into/bulkcopy" database attribute for tempdb being unchecked.
Set the option on again using SQL EM or sp_dboption and that should fix it.
A. SQL Server doesn't have a handy SPOOL command like Oracle does, but there are a number of ways of doing what you want.
A. Netware connectivity is available!
NT-based systems can integrate with existing Netware servers. The IPX/SPX
network protocol is supported on NT by using the NWLink IPX/SPX Compatible
Transport. So, on top of this protocol, you need some tools to provide the
integration.
Q. What are Client Services for Netware?
A. CSNW provides an NT workstation with basic file and printer connectivity to Netware. It supports both Bindery and NDS.
Q. What are Gateway Services for Netware?
A. GSNW is available only for NT servers. It includes the CSNW service to provide basic file and printer connectivity. In addition, GSNW allows an NT Server to act as a non-dedicated gateway. This means that your NT Server can connect to a Netware box and share the Netware drives as NT shares for all of your Microsoft network clients to access seamlessly (including those coming in via RAS).
While it works well, it's likely that it would be a bottleneck if you were going to link large networks using this single gateway!
The Netware server will need a special GROUP created called NTGATEWAY and a user account on Netware must be assigned to this group and to the gateway service on the NT Server.
Q. How do I install Gateway Services for Netware?
A. Perform the following:
Q. How do I attach to a NetWare 3.12 Server?
A. Perform the following:
Q. How do I attach to a NetWare 4.1 Server?
A. NetWare 4.1 connections is more complex than 3.12 connection as NetWare 4.1 has the complexity of NetWare Directory Services:
Q. What are File and Print Services for Netware?
A. CSNW and GSNW provide the ability to connect to Netware for file, printing and applications from your Microsoft network based clients.
FPNW does the reverse - it allows Netware clients to see the NT Server as if IT was a Netware box! FPNW allows you to appear as a Netware 3.12-compatible server.
Q. What is Directory Service Manager?
A. DSMN copies Netware user/group accounts to NT Server and will then propagate any changes BACK to the Netware box. This sharing of user/group information happens without you adding any software to the Netware side at all.
So, what does DSMN give you?
Q. What is Migration Tool for Netware?
A. This is a tool to allow you to migrate user and group accounts as well as login scripts, files and directories from Netware servers to a PDC or BDC.
This tool is located under the Administrative Tools program group and is called "Migration tool for NetWare". When run you have to select the NetWare server to convert and the NT service to convert the information into. Also you have to select a prefix for the NetWare users and groups, nw_, is the norm. Once the migration starts it may take a long time depending on the number of records.
Q. What are the NT equivalents of NetWare Rights?
A. The table below outlines the NetWare rights and the NT equivalents:
| NetWare | Windows NT |
| Supervisor (S) | Full Control (All) |
| Read (R) | Read (RX) |
| Write (W) | Change (RWXD) |
| Erase (E) | Change (RWXD) |
| Modify (M) | Change (RWXD) |
| Create (C) | Add (WX) |
| File Scan (F) | List (RX) |
| Access Control (A) | Change Permissions (P) |
Q. NWCONVE.EXE is not migrating your users and groups.
A. The Netware migration tool (nwconve.exe) does not support the NetWare Directory Services (NDS) service type of logon on Windows NT 4.0, and therefore you will need bindery emulation configured on the NetWare server for the migration to successfully migrate.
To configure bindery emulation perform the following on the NetWare Server
To set it perform the following (still on the NetWare Server)
You should then log off and back on to the NT Server. Rerunning NWCONVE.EXE should then run.
Q. I have very slow performance saving documents to a FPNW server.
A. File and Print services for NetWare allows an NT Server to be viewed by Novell clients. Problems can occur when trying to save a file to a FPNW volume, especially in Word.
The performance problem is caused by the save operation retrying every 3 seconds if a sharing violation is encounted caused by the optimization of both the Server service and the FPNW service.
To correct this problem perform the following
Q. How can I disable the print separator page when printing to a NetWare print server?
A. If you are using the client services for NetWare, CSNW, then upon installation a new control panel applet would have been created which allows the configuration of all things NetWare.
Banners will no longer be printed. You will also notice that options such as notifies and form feeds can also be configured.
Q. How can I stop my machine complaining about NWLNKRIP service not starting?
A. This service relies on NWLNKIPX and if this is not running the service cannot start. NWLNKRIP is installed if the machine is running NetWare protocol but if you don't want the service perform the following to stop it trying to start.
Q. NetWare migration tool cannot find the domain controller.
A. When the NetWare migration tool (nwconv.exe) is run it tries to establish a connection to the domain controller, or specifically the ADMIN$ share. If it fails the error:
Cannot connect to server: <servername>
The Network name cannot be found
The Admin$ share can be disabled by setting AutoShareServer to 0 on the domain controller. To fix this perform the following:
You should now reboot however if that is not convenient just type
C:\> net share admin$
which will create the share now and thanks to the registry change it will also be created at reboot time.
If AutoShareServer was already 1 or did not exist the it may be just admin$ has been corrupted so again type the command
C:\> net share admin$
to recreate.
Q. How can I assign NetWare variables to NT variables?
A. If an NT Workstation computer is running the Client Service for NetWare (CSNW) or an NT Server is running the Gateway Services for NetWare (GSNW), the login variables used by NetWare can be assigned to relevant Windows NT environment variables.
These mappings are performed using the NetWare login scripts on the NetWare server and can be a personal, system or container login script. The basic syntax is
SET <NT variable name>="%<NetWare variable name>
For example
SET LOGIN_NAME="%LOGIN_NAME"
SET FULL_NAME="%FULL_NAME"
SET MAC_ADDRESS="%P_STATION"
Q. How do I add the services for Macintosh?
A. Follow the instructions below:
Q. How can I read a Macintosh disk from Windows NT?
A. Mac Opener 2 by DataViz (http://www.dataviz.com/) allows Macintosh disks to be accessed by NT.
Another option is to ask the Mac user to format a floppy disk as a PC disk. Every MacOS 7.5 or above is shipped with "PC Exchange" Control Panel which gives you ability to read, write and format PC disks.
Q. Does NT RAS support AppleTalk?
A. No, however NBT (NetBIOS over TCP/IP) protocol is available for Macintosh from http://www.thursby.com (allowing Macintosh access to NT shares over RAS or LAN connections)
Q. Can NT act as an AppleTalk client?
A. No, however the AppleTalk protocol is available for NT from http://www.miramarsys.com
Q. How can I make a Macintosh PPP connection to Windows NT RAS?
A. There are full instructions at http://valleynet.on.ca/~aa158/mac-ras.html
Q. I am unable to write to the Microsoft UAM folder from the Macintosh?
A. The UAM (User Authentification Module) volume that shows up by default with SFM is set to read-only for the macs (except for Administrators). To change this start File Manager (winfile.exe) or Server Manager (under NT 4.0), from the MacFile menu choose View/Modify volumes. Select the volume, and clear the "This volume is read-only". You may also change permissions by clicking properties, then permissions. Permissions for Mac Users are set separately from standard NT file permissions.
Q. Is there an Outlook (Exchange Server) client for Macintosh?
A. The latest version of Outlook for the Macintosh includes support for Mac OS 8, and was released as part of the Exchange Server 5.5 SP1 update. It runs on Macintosh 68k and PPC platforms. The full Macintosh client can be downloaded from ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/exchange/exchange-public/fixes/Eng/Exchg5.5/ Sp1/Mac/
Q. Does NT Workstation support RAID?
A. Workstation does not support fault tolerant RAID, e.g. RAID 1 or RAID 5, however it does support RAID 0 (stripe set without parity). Obviously hardware RAID will work as it is transparent to the Operating System.
There is much talk about changing the ProductType registry key to enable fault tolerance on NT Workstation and while it can be done this is against Microsoft licensing and would also be unsupported by Microsoft. Do NOT mail me asking for the method as I will not distribute it and will just delete the mail message without replying.
Q. What RAID levels does NT Server Support?
A. NT Server supports RAID 1 (disk mirroring) and RAID 5 (strip sets with parity check). NT also support RAID 0, which is Striping without Parity, however this offers no data redundancy.
Q. How do I create a Stripe Set with Parity?
A. Follow instructions below
Note - A stripe set will only use the lowest common disk space on each physical drive, i.e. with 3 disks of 100MB, 50MB and 40MB free, each part of the stripe set would only be 40MB with a maximum of 120MB partition in total.
Q. How do I recreate a broken Stripe Set?
A. When a member of a Stripe Set with Parity fails, you do not get a warning, and everything continues to work. Indications include when you start Disk Administrator and on the Event Log. Follow instructions below
Q. How do I remove a Stripe Set?
A. Follow instructions below
Note - You will lose ALL data on the stripe set
A. If NT is providing software RAID 0 or RAID 5 (stripe set or stripe set with parity) then neither the NT boot or system partition may be on a RAID 0 or RAID 5 volume. This is because using this type of volume requires the fault tolerant driver and that is loaded during NT's bootup. If you require NT to be on a stripped set then you will need to purchase hardware RAID.
Q. How do I create a Mirror Set (RAID 1)?
A. To create a mirror you should first create what the prime will be, and then you can create a mirror of it:
Q. How do I break a Mirror Set?
A. If part a Fault Tolerant is lost (by hardware failure etc.) then a message will be displayed "A disk that is part of a fault-tolerant volume can no longer be accessed". The drive will still be usable, but the Mirroring will have been suspended. To break the mirror set:
Q. How do I repair a broken Mirror Set?
A. Make sure you have an area of unpartitioned space that is at least the size of the Primary partition:
Q. Can I install NT on a stripe set?
A. No. See Q. Can NT be on a Stripe Set? for more information.
Q. I am unable to boot using on the Mirror disk.
A. When you create a mirror disk the partition is automatically created for you but the Master Boot Record of the disk is not updated with the NT boot loader.
To install the NT boot loader you should first partition and format the drive with disk administrator which will write the MBR to the shadow (to be) disk. You should then delete this partition and continue creating the mirror as normal.
If you already have a mirror disk which you need to boot off and do not wish to use a modified NT boot disk (see Q. How do I create an NT Boot Disk? for details) you can write the MBR record to the shadow disk using the repair process.
Q. I have reinstalled NT now I have lost all RAID/volume sets.
A. Windows NT stores information about volume/mirror/stripe sets in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\Disk registry key so if you reinstall Windows NT it will lose this information and not recognize the volumes as fault tolerant sets.
The best way to avoid this problem is before you reinstall perform the following:
A single file, SYSTEM, will be created on the disk. Keep the disk safe and you should label it with the system name and the date taken.
When you reinstall NT you can then start Disk Administrator and select Configuration - Restore from the Partition menu, insert the disk and your original volume/RAID sets will be restored along with any drive letter assignments.
If you are simply installing another installation of NT on the machine and keeping the original you can just perform a Configuration - Search from the Partition menu and it will attempt to find any other copies of Windows NT and then give you the option to duplicate its configuration.
If none of the above is possible and you have already lost your configuration the only option is to use the FTEDIT.EXE resource kit utility which enables the editing of fault tolerant sets. Full help is given with the utility but use it carefully or you may actually lose the data.
A. Follow procedures below:
Q. How big and where should my Pagefile be?
A. Below are things to consider.
To enhance performance, one can create a second pagefile on another physical disk. MOVING, however, is never advised, since it disables the option to create a Memory dump file at a crash (System Properties, Startup-tab). In order to be able to dump the RAM content to the pagefile (saved i.e. as MEMORY.DMP), the pagefile MUST be located (as well) on the boot partition.
Q. Users complain server response is slow, but when I use the server everything is fine.
A. It could be the server Screen Saver! The Open GL screen savers (especially the pipes) can use every CPU cycle off the Server. In general you should always use the blank screen saver on a server.
Q. Is there a RAM disk in NT4.0?
A. No. However there is a piece of software which creates a RAM disk. In general the NT cache does a very good job. Microsoft also produced a RAM disk which still works on NT 4.0 called NTRamdsk.
A commercial package SuperDisk-NT is now available from EEC Systems (http://www.eecsys.com/)
Q. How can I monitor disk performance?
A. NT's built in Performance monitor can be used to
monitor disk activity, however this is not active by default, and needs to
be activated by typing
diskperf -y
from the command prompt. You will then need to reboot, and then disk
activity can be viewed using Performance Monitor.
Q. How can I tell if I need a faster CPU?
A. You use Performance Monitor (Start - Programs - Administrative Tools - Performance Monitor) to see how much time the computer is waiting to use the CPU:
Q. I need to run a number of 16 bit apps, what is the best way to do this?
A. The best way is to create a shortcut to the 16 bit application, then right click on the shortcut and select properties. Click on the shortcut tab and check the box "Run in separate memory space". This will make the app run in its own VDM (Virtual Dos Machine) with its own memory space. This improves performance and system stability as one 16 bit app can no longer effect another's.
An application can also be forced to run in its own memory space using:
start /separate <application name>
Q. How can I run an Application at a higher priority?
A. It is possible to start an application at a priority other than normal, however if you run applications at high priority THEY may slow performance. Priorities range from 0 to 31, 0 - 15 are used by Dynamic applications, such as user applications and most of the operating system parts, 16-31 are used by real time applications like the kernel which cannot be written to the page file. Normal priority is level 8 (NT 3.51 normal was 7). The full list is
To start an application at a priority other than the default use the start command, e.g.
start /<priority> <application>, e.g. start /high winword
Be warned that if you run applications at high priority may slow performance as other application get less I/O time. To use the /realtime option you have to be logged on as a user with Administrator privileges.
To modify the privilege of a currently running application use Task Manager
It is also possible to increase the priority of whichever application is currently in the foreground, as opposed to the background processes.
Q. How can I monitor processes that start after I start the Performance monitor?
A. If you are running performance monitor in log mode, after the log is closed and you wish to view certain processes in the drop down list you only see processes that were running at the time you started the log. This is not true :-)
What this means is the instances shown are only those running at the start of the time window, so to add other processes running at other times, you may need to continue moving the start of the time window.
Q. How can I view information in the Event Log from the command line?
A. A utility called DUMPEL.EXE is supplied with the Windows NT Resource Kit which outputs a comma or tab separated file. It allows the events from all 3 logs to be dumped on the local or remote computer. For full information see the NT Resource Kit Tools help however below is the basic syntax.
dumpel -f <filename for output> [-s \\<servername>]
[-l <which log, e.g. system, application,security>] -c
e.g., dumpel -f applog.txt -l application -c
This would dump out the application log as a comma separated file (alternatively use -t instead of -c for a tab separated file).
Another useful switch is -e <event> which allows you to only output a given event, e.g.
dumpel -f winlogon.txt -l application -c -m "winlogon"
Would display all information re winlogon (you don't need the quotes if the event is one word).
Another application is NTLast which can be downloaded from http://www.ntobjectives.com. This utility does two major things that event viewer does not. It can distinguish remote/interactive logons and it matches logon times with logoff times. Example uses:
ntlast - gets a default list of last 10 successful logons
against local machine
ntlast /f - gets last 10 failed logon attempts
ntlast /f /i - gets last 10 failed interactive logon
attempts
ntlast /f /r - gets last 10 failed remote logon attempts
ntlast /i - gets last 10 successful logons
ntlast /r - gets last 10 successful remote logons
ntlast /n 6 - gets last 6 logons
And most useful
ntlast /m machinename /f /r - gets last 10 failed remote
attempts against machinename
Q. Is there anything to help diagnose performance problems?
A. You can use the Excel Macro Perfmon.xla. Perfmon.xla can be downloaded from http://www.ntfaq.com/ntfaq/download/perfmon.zip. Use the macro as follows:
This macro is only basic, but it may give you some starting points to investigate and automates the line of thinking you should be following.
Q. Is there anyway to output performance logs directly to a comma separated file?
A. The Windows NT Resource Kit ships with the PerfLog service which can output data directly to a file in with comma or tab separated format. To install perform the following:
To start the service select from the Services control panel applet and click start. You can also start from the command prompt using
C:\>net start "performance data log"
To change the config at a later time just rerun the PDLCNFIG.EXE image.
Q. How can I control the amount of memory NT uses for file caching?
A. Windows NT does not allow much tuning of caching except for one registry entry.
If you start the Network control panel applet and select the Services tab you can select Server and click Properties. Select "Maximize Throughput for Network Applications" to use less memory (this actually sets LargeSystemCache to 0).
System internals have released CacheSet (http://www.sysinternals.com) which allows you to more specifically set memory used for caching.
Q. How can I stop Windows NT System Code and Drivers being paged?
A. Normally User-mode & kernel-mode drivers and kernel-mode system code is written to either pageable or non-pageable memory. It is possible to configure NT never to page out drivers and system code to the pagefile that are in the pageable memory area however this should only be done on systems with large amounts of RAM or severe performance problems could develop.
Q. How can I change the size of the pagefile?
A. We have previously discussed moving the pagefile (see Q. How do I move my pagefile? ), however it may be you just need to modify the size of an existing pagefile or add a new one as an addition to your existing one. Remember the more disk heads, the better performance so moving your page file to a RAID 0 disk arrangement would give excellent performance (RAID 0 is a stripe set without parity), while writing to a RAID 5 disk may adversely affect performance due to the extra parity information that needs to be written (RAID 5 is a stripe set with parity). There is little point adding a second pagefile to another partition if it is on the same physical disk, it would be better to just increase the size of the existing file, however 2 smaller pagefiles on different physical disks will give better results.
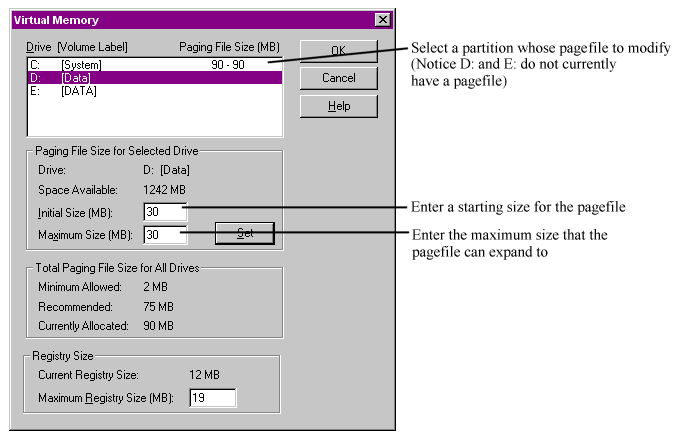
Q. How can I tell the role of my NT machine?
A. There are several ways to do this, however the
easiest is to type the command
net accounts
And at the bottom of the output, the Computer Role will be shown as one
of the following:
WORKSTATION - A normal NT Workstation machine
SERVER - A standalone NT Server machine
PRIMARY - A Primary Domain Controller (PDC)
BACKUP - A Backup Domain Controller (BDC)
Q. How can I tell who has which files open on a machine?
A. To view which files are currently open, and which
user has them open use the
net file
command which displays information in the form of
ID Path Username # Locks, e.g.
ID Path User name # Locks ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9 D:\index.lnk savillj 0 11 D:\john.lnk savillj 0 23 D:\www.savilltech.com\images\me.gif savillj 0 27 D:\www.savilltech.com\images\mcse.gif savillj 0 31 D:\www.savilltech.com\images\mvp.gif savillj 0 35 D:\www.savilltech.com\images\40179.JPG savillj 0 39 D:\www.savilltech...\goldeneye.gif savillj 0 43 D:\www.savilltech...\Rita1sml.jpg savillj 0 47 D:\www.savilltech...\Rita2sml.jpg savillj 0 49 D:\www.savilltech.com\me.html savillj 0 The command completed successfully.
Also using net file, it is possible to delete a file lock using
net file 47 /close
which would remove this lock.
To use Net File you must have the server service running on the machine (check Start - Settings - Control Panel - Services)
You can also use the Server Control Panel Applet on the domain controller (In Use).
There is a freeware utility called OFL (Open File List) from http://www.merxsoft.com/ which provides more information.
The best 3rd party applications I have found are NTHandle (a command line file use utility), and NTHandleEx (a GUI version of NTHandle). Both these utilities are available from http://www.sysinternals.com.
Q. How do I view all the applications/processes on the system?
A. You can use Task Manager that is standard part of NT (Right click on the Task Bar, and select Task Manager). There is also the PVIEW program that comes with Visual C++. For command line viewing there is TLIST that comes with the resource kit
Q. Where can I get information about my machine?
A. There are several utilities available, however winmsd is good, and can produce a full printed report about your computer including IRP,DMA settings for devices. A command line version of winmsd is called winmsdp which is good to run regularly, this utility is part of the Windows NT Resource Kit.
Q. How can I tell when NT was last started?
A. From the command prompt, enter the command net statistics workstation and at the top it says "statistics since ...". You will need to be quick with the Ctrl-S (to pause the output, Ctrl-Q starts it again). This will give the time since the workstation service was started, so if someone has performed a
net stop workstation
net start workstation
the time up will be incorrect.
The time NT has been up is also displayed from the PVIEW utility, and also there is a set of applications that display this information called 3UPTIMES.ZIP (there is a command line and a windows version included). These apps are from http://barnyard.syr.edu/~vefatica/. Be aware this gives incorrect information if the system has been up more than 50 days.
The last line of output from the Windows NT Resource Kit utility SRVINFO.EXE displays the total uptime as well in the format:
System Up Time: 24 Hr 3 Min 29 Sec
ElWiz from http://www.heysoft.de/nt/eventlog/ep-elwiz.htm will always give the right uptime (among lots of other usefull information) and it is free, too.
Q. I have lost my NT Installation CD-ROM case that had the Key number, how can I find it out?
A. The easiest way is to run WINMSD (Start - Run - Winmsd) and look at the Version tab. On the line above the register info you will see a number in the form of 50036-xxx-yyyyyyy-71345. The xxx-yyyyyyy is the number on the back of the CD case. This is also the same as the registry entry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProductId.
Q. How can I tell if my NT installation was upgraded?
A. Upgrades from Windows 95 etc are not possible, but if you system was upgraded from a Windows 3.x system the registry entry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Update\UpdateMode would be set to 1.
Q. How can I get detailed system information from the command prompt?
A. The Windows NT Server Resource Kit supplies SRVINFO.EXE which is an excellent tool for gaining a picture of your system with including details about:
C:\>srvinfo
Server Name: GARFIELD
Security: Users
NT Type: WinNT WorkStation
Version: 4.0, Build = 1381, CSD = Service Pack 4, RC 1.99
Domain: SVILLUK
PDC: \\SVLON1
IP Address: 160.82.220.19
CPU[0]: x86 Family 6 Model 3 Stepping 3
Hotfixes: [Q147222]:
Drive: [FileSys] [ Size ] [ Free ]
Services:
[Stopped] Alerter
..
..
System Up Time: 23 Hr 51 Min 43 Sec
The utility has a number of switches to give extra/less information:
SRVINFO [[|-ns|-d|-v|-s] \\computer_name]
-ns: Do NOT show any service information
-d: Show service drivers and service
-v: Get version info for Exchange and SQL
-s: Show shares
Q. How do I disable CD AutoPlay?
A. You can use the TweakUI utility and goto the paranoia tab, or edit the registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Cdrom and change Autorun 0x1 to 0x0 to disable autorun. If you use TWEAKUI it will only affect the current user, where as the registry entry will set it for all users. To achieve the same as TWEAKUI change HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer and set the value NoDriveTypeAutoRun from 0x95 to 0xff.
Q. How do I install a Joystick in NT?
A. On the NT CD goto directory drvlib\multimed\joystick\x86 and right click oemsetup.inf and select install.
Q. How do I change my Soundcards Settings (IRQ)?
A. From Control Panel, double click MultiMedia. Select the "devices" tab and expand the Audio Devices. Click on the soundcard and click properties. Click settings, and scroll to the setting you wish to change and click "change setting". Change the setting and click OK, then reboot.
Q. Does NT 4.0 support Direct X?
A. Direct X is built into NT 4.0, although limited. There is no way to upgrade the Direct X part of NT, however Service Pack 3 has complete Direct X 3.0 support. NT 4.0 pre Service Pack 3 supports the DirectDraw, DirectSound and DirectPlay components of DirectX.
Q. Does NT have a speaker driver?
A. There is no NT speaker driver like there was in DOS, however this used to hammer performance and it is better to buy a cheap soundcard.
The very nature of this driver prohibits its use. A preemptive multitasking operating system will not allow enough CPU cycles to generate the sound. The sound is generated by pulse with modulation which requires 100% of CPU time while the sound is being played. Sound cards offload this to their DAC chips
Q. How do I install my SoundBlaster Sound Card?
A. If you have one of the newer Plug and Play Sound Blaster cards then the install is simple.
If you have one of the older non-PNP sound cards download the file awent40.exe and follow the instructions that come with the file once expanded.
Q. How do I install a WaveBlaster card?
A. Follow the instructions below:
Q. I have lost the speaker icon from my task bar.
A. You can easily recreate this by running systray.exe. To ensure that you have the speaker icon every time you start windows you can place it in your startup group.
Alternativly start the Multimedia control panel applet (start - settings - control panel - multimedia) and check that "Show volume control on the taskbar" is checked.
Q. How do I create a captive account?
A. It is not possible to create a captive account, however you can force a user to run a program, and if they close that program they can be logged out:
The file Logout.exe just logs out the user. It is also possible to restrict a Users applications using the Policy Editor. From the Policy Editor you can select which applications a User can run (make sure you give them Explorer!).
Microsoft have also created the zero administration kit which allows a user to be confined to a single application or a set of applications.
Q. Where should Login Scripts go?
A. Login scripts should be in the WINNT\SYSTEM32\REPL\IMPORT\SCRIPTS directory
Q. What should be in the Login Script?
A. This will vary from site to site, however generally
a login script will synchronize the time of the workstations with the
server (providing the servers time is accurate!), and perhaps connect a
home area (this is set using User Manager). Net use x: /home will ask the
domain server for your home area location and connect to it. A login
script may be
@echo off
net time \\johnserver /set /yes
net use p: /home
Q. Are there any utilities that help with login scripts?
A. With the NT resource kit you get KIX that enables you to write more advanced login scripts. There is also a freeware utility call KixTart.
Microsoft has released the Windows Scripting Host which is bound to be the next standard in all cases where scripting is necessary, including login scripts.WSH will be included in NT5 and can be downloaded at http://www.microsoft.com/management/wsh.htm.
Q. Is there a way of performing operations depending on a users group membership?
A. On the resource kit for NT you'll find a program called IFMEMBER, this is what you'll have to base your login script upon. Important safety tip, IFMEMBER works by checking for membership in a group and returning an ERRORLEVEL hence you'll have a bunch of IF THENS..
Q. How do I limit the disk space for a User?
A. NT server has no way to do this, however there is 3rd party software such as
Q. What variables are available for use with a User?
A. Below is a list of variables you can use in login scripts and other batch files. These may only be used on NT client/servers.
| %COMPUTERNAME% | Name of computer |
| %HOMEDRIVE% | Users local drive letter |
| %HOMEPATH% | The full path of the users home area |
| %HOMESHARE% | The share that contains the users home area |
| %LOGONSERVER% | This is the name of the machine that validates the user logon |
| %OS% | The operating the User is connected to |
| %PROCESSOR% | e.g. 486 (useful to put in a login script and ridicule if a 386 or below) |
| %USERDOMAIN% | Domain containing the Users Account |
| %USERNAME% | The name of the user |
Q. Can I add user accounts from a database?
A. There is a utility with the resource kit, ADDUSERS.EXE, that as an input excepts a database file (e.g. and Excel spreadsheet) and will add users and groups.
Q. Is there a utility that shows who is currently logged on?
A. The resource kit has a utility called WHOAMI.EXE. It displays the domain/workgroup and username.
Alternativly you could just display the %userdomain% and %username% variables, e.g.
C:\> echo %userdomain%\%username%
Q. How can I change environment variables from the command line?
A. The resource kit has a utility called SETX.EXE. It
enables the user to change environment settings, e.g.
setx johnvariable 1
setx johnvariable -k HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\...\DefaultDomainName
Q. How can I hide drive x from users?
A. This can be done using the TWEAKUI utility from the
"My Computer" tab, and just deselect the tick next to drives you
want to hide. All this does is change the registry value
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies
\Explorer\NODRIVES which is a 32-bit word. The lower 26 bits of the
32-bit word correspond to drive letters A through Z. Drives are visible
when set to 0 and hidden when set to 1.
Drive A is represented by the rightmost position of the bitmask when viewed in binary mode.
e.g. A bitmask of 00000000000000000000010101(0x7h)
The bitmask above hides local drives A, C, and E
Drives hidden using the NODRIVES setting are not available through Windows Explorer, under the My Computer icon, or in the File Open\Save dialog boxes of 32bit Windows applications. File Manager and the Windows NT command prompt are not affected by this registry setting.
Q. How do I make the shell start before the logon script finishes?
A. Change the registry value HKEY_CURRENT_USER\software\microsoft\windows nt\currentversion\winlogon\RunLogonScriptSync to 0, which means the shell starts before the logon script has finished. A value of 1 means the shell will not start until the logon script finished.
Q. How can I find out which groups a user is in?
A. NT provides a means of getting information about
your domain account using the
net user <username> /domain
which includes information about group membership, however there is a
utility that ships with the NT resource kit called SHOWGRPS.EXE that
only shows the groups and the usage is:
showgrps <domain>\<user>
e.g. showgrps savilltech\john
Q. I can no longer see items in the common groups from the Start Menu.
A. There is a registry flag that sets whether or not the common groups are displayed on the Start Menu. To disable this setting, set HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer\NoCommonGroups to 0 using the registry editor (regedit.exe). By default this value will not exist.
Q. How do I configure a user so they can change the system time?
A. The ability to change the time on an NT system is a Right that has to be granted through the User Rights Policy in User Manager.
Also see Q. Can I synchronize the time of a NT Workstation with a NT Server?
A. To add a new user to a domain you need to logon to the Server as an Administrator and run the User Manager for Domains Utility. Before adding a new user however, you should consider the different naming conventions that can be used, and there are really 4 main standards
It is important to stick to a standard, however unless this is a new installation, there will already be a standard to follow at your company. To add a user:
Q. How do I configure roaming profiles?
A. When you sit at a computer and change its attributes, such as the wallpaper, when someone else logs on they still have the environment that they last had when they logged on, and this is achieved using a profile for the user which is stored locally in the %systemroot%/profiles/<username>, e.g. d:\winnt\profiles\savillj.
If the user then sat at a different computer they would not have their setup, to achieve a profile that follows the user to different NT machines (a roaming profile) you need to store the users profile on a network share, that can be downloaded each time the user logs on. When the user logs off the network profile is updated, and a copy of the profile is saved locally. To configure roaming profiles perform the following
To make the profile mandatory, i.e. the user cannot change it, rename the file ntuser.dat to ntuser.man which is located at the base of the profile location.
As mentioned earlier, profiles are cached locally to machines, however this can be disabled by performing the following
Q. How can I configure each user to have a different screen resolution?
A. You cannot, the screen resolution is stored in the registry, in a non-user specific area and is therefore not configurable for individual users. The resolution would have to manually changed when the user logs on.
Q. How can I create a list of all User Accounts?
A. There a number of ways to produce a list of all user accounts in a domain (or accounts just on a machine):
It may be that none of these suit your exact needs, or you need to access the user list from within a program, you can use the NetUserEnum(), NetGroupEnum() and NetLocalGroupEnum() functions to get the required information. For each of these, the first argument is the computer name to perform the operation on, a null pointer will make it use the current system, or use NetGetDCName() to get the computer name of the Domain Controller. That's enough code for me, I'm starting to sweat :-)
Q. How can I add a user from the command line?
A. The simple answer is to use the net user <username> <password> /add (/domain) , however it is possable to automate not only the addition of the user, but also his/her addition to groups and the creation of a template user account directory structure. Many organisations have a basic structure with word, excel directories and some template files. This can be automated with a basic script. For example
addnew.bat
net user %1 password /add /homedir:\\<server>\users\%1
/scriptpath:login.bat /domain
net localgroup "<local group>" %1 /add
repeat for local groups
net group "<groups>" %1 /add /domain
repeat for global groups
xcopy \\<server>\users\template \\<server>\users\%1\
/e
cacls \\<server>\users\%1 /e /r Everyone
remove the everyone permission to the directory
cacls \\<server>\users\%1 /g %1:F /e
cacls \\<server>\users\%1 /g Administrators:F /e
Q. How can I move users from one machine to another?
A. If you just want to replace the PDC of a domain with a new machine, the easiest way is to install the new machine as a BDC and then promote to the PDC which removes the need of adding/removing users.
If you actually want to merge two domains or just move some accounts the procedure below should help. You will need the resource kit utility addusers.exe
Q. How can I configure a user to logoff at a certain time?
A. Basic user manager functionality allows the setting of working hours for a user, and using user account policies you can force NT to logout users who are logged on past their hours.
Q. How can I grant User Rights from the command line?
A. Usually user rights, such as Logon Locally, are grant by starting User Manager and selecting User Rights from the Policies menu. If you want to grant rights from the command line, for use with account generation scripts etc., the Windows NT Resource Kit Supplement Two includes a new utility called NTRIGHTS.EXE which grants user rights from the command line.
The program uses a series of codewords for each user right:
| Code Word | User Right |
| SeNetworkLogonRight | Access this computer from the network. |
| SeTcbPrivilege | Act as part of the operating system. |
| SeMachineAccountPrivilege | Add workstations to domain. |
| SeBackupPrivilege | Back up files and directories. |
| SeChangeNotifyPrivilege | Bypass traverse checking. |
| SeSystemtimePrivilege | Change the system time. |
| SeCreatePagefilePrivilege | Create a pagefile. |
| SeCreateTokenPrivilege | Create a token object. |
| SeCreatePermanentPrivilege | Create permanent shared objects. |
| SeDebugPrivilege | Debug programs. |
| SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege | Force shutdown from a remote system. |
| SeAuditPrivilege | Generate security audits. |
| SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege | Increase quotas. |
| SeIncreaseBasePriorityPrivilege | Increase scheduling priority. |
| SeLoadDriverPrivilege | Load and unload device drivers. |
| SeLockMemoryPrivilege | Lock pages in memory. |
| SeBatchLogonRight | Logon as a batch job. |
| SeServiceLogonRight | Log on as a service. |
| SeInteractiveLogonRight | Log on locally. |
| SeSecurityPrivilege | Manage auditing and security log. |
| SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege | Modify firmware environment values. |
| SeProfileSingleProcessPrivilege | Profile single process. |
| SeSystemProfilePrivilege | Profile system performance. |
| SeUnsolicitedInputPrivilege | Read unsolicited input from a terminal device. |
| SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege | Replace a process level token. |
| SeRestorePrivilege | Restore files and directories. |
| SeShutdownPrivilege | Shut down the system. |
| SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege | Take ownership of files or other objects. |
To grant a user right perform the following
ntrights +r SeInteractiveLogonRight -u SavillTech\savillj
This would grant savillj of the SavillTech domain the right to log on locally. To grant the right on a remote machine use the -m switch
ntrights +r SeInteractiveLogonRight -u SavillTech\savillj -m \\<machine name>
Q. How can I configure the system so all users share a common favourites folder?
A. It is possible to explicitly define the UNC for the favourites folder for each user by editing the registry. The steps would be as follows
Q. How can I change the local Administrator passwords on machines without going to them?
A. As you may be aware it is possible to change your password from the command line using the net user command, and if you combine this with the at command you can run the command on different machines, e.g.
at \\<machine name> <time> cmd /c net user
Administrator anythingyouwant
e.g. at \\savilljohn 18:00 cmd /c net user Administrator password
The /c after cmd causes the command window to close after the command has been executed. An alternative to the at command would be the soon command
soon \\<machine name> cmd /c net user Administrator password
Q. How do I change my password?
A. Perform the following:
To change your password from the command line use the net user command, e.g.
net user <username> <password> (/domain)
To change from a program use the NetUserChangePassword() call.
Q. How can I configure default settings for new users?
A. When a new user logs in for the first time a copy of the default user profile (ntuser.dat) is copied into the users profile. To set default settings for a user you can edit the default ntuser.dat file. Anything you define under HKEY_CURRENT_USER can be changed by editing ntuser.dat.
To change default settings for a new user on a workstation perform the following:
Anyone logging onto the machine will now pick up these default settings.
To configure a default NTUSER.DAT for a domain perform the above and logon as a user to take these settings. You now need to export these out to the PDC.
If you have trouble exporting a profile see Q. I get an error when I try to export a profile other than Administrator. (I did :-) )
Q. How can I tell which User has which SID?
A. Perform the following:
If you knew the SID and just wanted to know the user name you could use the REG.EXE command (with Resource Kit Supplement 2), e.g.
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList\<SID>\ProfileImagePath"
e.g. reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList\S-1-5-21-1843332746-572796286-2118856591-1000\ProfileImagePath"
And again this will show the ProfileImagePath giving you the user.
A. This was the standard behavior under NT 3.51, but for this to work under NT 4.0 as well as the user profile being ntuser.man instead of ntuser.dat the users profile folder also has to be .man so rename the users profile folder to <name>.man.
Q. How do I automatically logoff clients after n minutes of inactivity?
A. The registry entry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters. Add a new variable (Edit - New - Dword value) and call it Disc. Set the value to the number of minutes inactivity wanted. Some network programs constantly communicate with the server (such as mail) so this will not always work. This will only terminate remote connections, to actually logoff from a session use the winexit.scr that comes with the resource kit.
Q. How can I modify the size of icons on the desktop?
A. As you may be aware you can change the size of icons in Explorer by selecting the Large icon/Small icon from the view menu. You can actually make the icons even bigger!
If large icons are selected in Explorer you will now see the new size, you don't need to logoff, just change folders.
It's also possible to change the icons for the small icon/start menu
Logoff and on again for the change to take effect.
To change the number of colours the icons use perform the following:
Again you need to logoff for the change to take effect.
A. This can be disabled via the registry:
You need to restart the computer for this to take effect.
Q. How can I configure the Alt-Tab display?
A. Again you can configure this through the registry:
Restart the computer for the change to take effect
Q. How can I edit the list of connections listed in Explorer when I map a connection?
A. When you select "Map Network Drive" from Tools menu in Explorer and click the drop down box for the path, Explorer checks the HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Network\Persistent Connections area of the registry for a list of old/current drive mappings. To remove items from the list (or add) perform the following:
Q. How can I exclude the Temporary Internet Files folder from the user profile?
A. By default the storage area for temporary internet files is "%systemroot%\Profiles\<user>\Temporary Internet Files", and if you implemented roaming profiles then these files would count as part of your profile taking up valuable server space. To change the location from the browser perform the following:
You will need to restart the machine for the new location to take effect
Alternatively you could create a reg file to manually update the following registry values and include it as part of a logon script
An example .reg file would be
REGEDIT4
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet
Settings\Cache\Paths\path1]
"CachePath"="E:\TEMP\Cache1"
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet
Settings\Cache\Paths\path2]
"CachePath"="E:\TEMP\Cache2"
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet
Settings\Cache\Paths\path3]
"CachePath"="E:\TEMP\Cache3"
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet
Settings\Cache\Paths\path4]
"CachePath"="E:\TEMP\Cache4"
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Shell
Folders]
"Cache"="E:\TEMP"
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\User
Shell Folders]
"Cache"="E:\TEMP"
This would set the cache area to e:\temp however you could change this to anything you want. Save the above as cache.reg and run as
regedit /s cache.reg
Netscape does not store temp files under the user profile (if you are interested it is stored in the registry location HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Netscape\Netscape Navigator\Users\<user>\DirRoot ;-) ).
Q. How can I stop the programs in my start-up folders running when I log on?
A. Hold down Shift during your logon and any programs in the startup folders will not run.
If Administrators wish to disable this behavior add IgnoreShiftOveride of type String to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon and set the value to 1.
A. This can be caused by a number of things. You can try deleting the user from the command line:
net user <username> /delete [/domain]
If this does not work try renaming the account and then deleting it
The above solution would work if you had an invalid username (like AAAAAAAAAAA)
Q. How can I stop users from being able to map/disconnect network drives?
A. This is accomplished using the Policy Editor under normal conditions however it can also be performed by directly editing the registry.
Q. How can I disable a whole group of users?
A. There is no built in mechanism to do this but can be accomplished with 2 commands:
The first command users the resource kit utility SHOWMBRS.EXE outputing to a file:
C:\>showmbrs <domain>\<group> > users.txt
e.g. C:\>showmbrs savilltech\sales > users.txt
The second command iterates through the file and performs a net user <username> /active:no /domain
C:\>for /f "skip=2" %I in (users.txt) do net user %I /active:no /domain
An example output is as follows
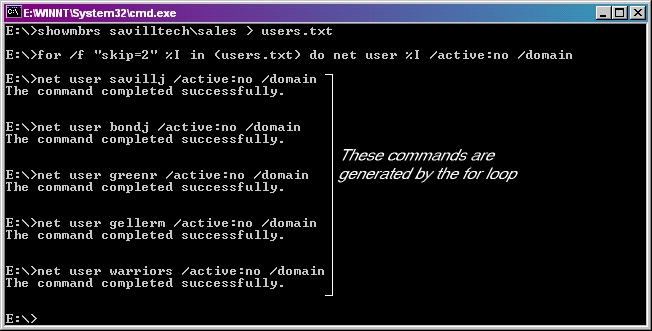
If you wanted to create a script enter the following into file dsblgrp.bat. The usage is
dsblgrp <group name>
e.g. dsblgrp savilltech\sales
REM
REM dsblgrp <group name>
REM by John Savill, 20th July 1998
REM
showmbrs %1 > users.txt
for /f "skip=2" %%I in (users.txt) do net user %%I
/active:no /domain
Make sure you use two %% before the I or it won't work.
There is a problem with showmbrs.exe that only view groups with less than 7 members. To fix this download the fixed version from ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/reskit/nt40/i386/Shombrs.exe
Q. How can I remove a user from a group from the command prompt?
A. If the group is a local group perform the following:
C:\> net localgroup <group name> <user> /delete
e.g. C:\> net localgroup Administrators savillj /delete
If the group is part of a domain user
C:\> net group <group name> <user> /delete /domain
Q. How can I remove the : from the time?
A. This can be accomplished by editing the registry
To see the change logoff and on again.
Q. How can I rename a user from the command prompt?
A. A utility, RENUSER.EXE exists which can be downloaded from http://www.ntfaq.com/ntfaq/download/renuser.zip which has the following usage:
C:\> renuser <old username> <new username> [<domain
name>]
e.g. C:\> renuser savillj johns savilltech
Q. Roaming profiles are not saved to the server.
A. If a user is a member of the Domain Guests group then no changes to profiles are stored, therefore you should check the members of the Domain Guests group do not include those users that are having the problem.
Q. I have made user shares hidden now connection fails.
A. To hide a share all you need to do is add the $ sign to the end, for example, \\server\share$.
If previously in your logon scripts you had the command
net use f: \\<server>\%username%
it will no longer work as the share is hidden with the $ and to connect you will need to specifically specify the $ so change the command to
net use f: \\<server>\%username%$
Q. How can I disable the Display control panel applet?
A. Using policies it is possible to disable the display control panel applet, however it can also be accomplished using the registry editor
The change takes immediate effect and if you try and run the display control panel applet either by right clicking on the desktop and selecting properties or starting from the control panel applet you will receive the message
"Your system administrator disable the Display control panel"
Q. How can I disable elements of the Display control panel applet?
A. Again using policies it is possible to disable elements of the display control panel applet, however it can also be accomplished using the registry editor
| NoDispAppearancePage | Removes the Appearance tab which means users cannot change the colours or colour scheme |
| NoDispBackgroundPage | Removes the Background tab meaning no more Pamela Anderson background (damn!) |
| NoDispScrSavPage | Removes the Screen Save tab |
| NoDispSettingsPage | Removes the Settings and the Plus tab |
These change takes immediate effect and any disabled tab will not be displayed.
Of course the user can go into the registry and change these back which is why it is better to implement these as policies (which is what I do), however as they take immediate effect there is nothing to stop someone creating a reg script to run as part of the start-up group, which sets it to how they want to get round the policy, but I would never condone this :-)
Q. How do I debug roaming profiles?
A. It is possible to create a log file of all roaming profile transactions using the checked version of userenv.dll. The checked version of the UserEnv.dll is the same dynamic link library (.dll) as the retail version, except that it contains debug flags that you can set and use with the kernel debugger. This file, which is included in both the Windows NT Device Driver Kit (DDK) and the Windows NT Software Development Kit (SDK)
A log file of the roaming profile transactions will be written to userenv.log to the root of the C: drive. Below is an profile log.
=========================================================
LoadUserProfile: Entering, hToken = <0xb0>, lpProfileInfo = 0x12f4e8
LoadUserProfile: lpProfileInfo->dwFlags = <0x2>
LoadUserProfile: lpProfileInfo->lpUserName = <savillj>
LoadUserProfile: lpProfileInfo->lpProfilePath = <\\titanic\Profiles\savillj>
LoadUserProfile: lpProfileInfo->lpDefaultPath = <\\TITANIC\netlogon\Default
User>
LoadUserProfile: lpProfileInfo->lpServerName = <\\TITANIC>
LoadUserProfile: lpProfileInfo->lpPolicyPath = <\\TITANIC\netlogon\ntconfig.pol>
ParseProfilePath: Entering, lpProfilePath = <\\titanic\Profiles\savillj>
ParseProfilePath: Tick Count = 20
ParseProfilePath: FindFirstFile found something with attributes <0x10>
ParseProfilePath: Found a directory
LoadUserProfile: ParseProfilePath returned a directory of <\\titanic\Profiles\savillj>
RestoreUserProfile: Entering
RestoreUserProfile: Profile path = <\\titanic\Profiles\savillj>
RestoreUserProfile: User is a Admin
IsCentralProfileReachable: Entering
IsCentralProfileReachable: Testing <\\titanic\Profiles\savillj\ntuser.man>
IsCentralProfileReachable: Profile is not reachable, error = 2
IsCentralProfileReachable: Testing <\\titanic\Profiles\savillj\ntuser.dat>
IsCentralProfileReachable: Found a user profile.
RestoreUserProfile: Central Profile is reachable
RestoreUserProfile: Central Profile is floating
GetLocalProfileImage: Found entry in profile list for existing local
profile
GetLocalProfileImage: Local profile image filename = <%SystemRoot%\Profiles\savillj>
GetLocalProfileImage: Expanded local profile image filename = <E:\WINNT\Profiles\savillj>
GetLocalProfileImage: No local mandatory profile. Error = 2
GetLocalProfileImage: Found local profile image file ok <E:\WINNT\Profiles\savillj\ntuser.dat>
Local profile is reachable
Local profile name is <E:\WINNT\Profiles\savillj>
RestoreUserProfile: About to call UpdateToLatestProfile
UpdateToLatestProfile: Entering. Central = <\\titanic\Profiles\savillj>
Local = <E:\WINNT\Profiles\savillj>
UpdateToLatestProfile: Central and local profile times match.
RestoreUserProfile: About to Leave. Final Information follows:
Profile was successfully loaded.
lpProfile->szCentralProfile = <\\titanic\Profiles\savillj>
lpProfile->szLocalProfile = <E:\WINNT\Profiles\savillj>
lpProfile->dwInternalFlags = 0x112
RestoreUserProfile: Leaving.
UpgradeProfile: Entering
UpgradeProfile: Build numbers match
UpgradeProfile: Leaving Successfully
ApplyPolicy: Entering
ApplyPolicy: PolicyPath is: <\\TITANIC\netlogon\ntconfig.pol>.
ApplyPolicy: Local PolicyPath is: <E:\WINNT\Profiles\savillj\prf1.tmp>.
ApplyPolicy: Looking for user specific policy. OpenUserKey: No entry for
savillj, using .Default instead.
CopyKeyValues: EnableProfileQuota => 1 <OK>
CopyKeyValues: ProfileQuotaMessage => You have exceeded your profile
storage space. Before you can log off, you need to move some items from
your profile to network or local storage. <OK>
CopyKeyValues: MaxProfileSize => 48 <OK>
CopyKeyValues: WarnUserTimeout => 15 <OK>
ApplyPolicy: Processing group(s) policy.
ApplyPolicy: Failed to get group processing order.
ApplyPolicy: Looking for machine specific policy.
OpenUserKey: No entry for ODIN, using .Default instead.
ApplyPolicy: Leaving with 1
LoadUserProfile: Leaving with a value of 1. hProfile = <0x90>
=========================================================
Q. How can I copy a user profile?
A. User profiles are stored under the %systemroot%\profiles directory, but if you just try to copy this to someone else the new user will not have permission to use the profile. Instead the following procedure must be used.
You should then check that the file ntuser.dat has been created where you selected.
If you have trouble exporting a profile see Q. I get an error when I try to export a profile other than Administrator.
Q. What are the differences between NT and 9x profiles?
A. The first differences is that difference files are used:
| Windows NT | Windows 9x |
| NTuser.dat | User.dat |
| NTuser.dat.LOG | User.da0 |
| NTuser.man | User.man |
The Windows 9x User.da0 and the NT NTuser.dat.Log files work in a different way. Everytime you log off in Windows 9x a copy of User.dat is copied to to User.da0. Windows NT uses NTuser.dat.LOG as a transaction log file to provide fault tolerance. This allows Windows NT to recover the user profile if a problem occurs while Windows NT is updating NTuser.dat.
This obviously means you can't share a profile between the two OS's. Other differences include:
Q. When I log off all my home directory files are deleted.
A. The most common cause is if your roaming profile path and your home directory path are the same. It seems that part of the update makes sure the contents of the directories (and subdirectories) are the same, and as the local profile directory does not contain your home directory files they are deleted!
You should therefore change the location of the roaming profile so it is different from the users home directory. It may be a subdirectory if you wish. This can be changed by using the User Manager application, click the Profiles button and change the locations.
Q. How can I delete a local profile?
A. Using the System Control panel applet any locally stored profile can be deleted.
Please note you can't delete a profile if you are currently logged on as that user, an area that the profile is in use will be displayed.
If you want to remotely delete a locally stored profile you can use the DELPROF.EXE utility which is supplied with the Windows NT Server Resource Kit. The tool deletes all profiles that have not been used for a given number of days, for example
C:\>delprof /p /q /i /c:\\garfield /d:3
Would delete any profiles that have not been used for 3 days. The /p prompts for confirmation before deleting each profile, the /q suppresses the starting:
Delete profiles on \\garfield that have not been used in the last 1 days? (Yes /No)
prompt. The /i ignores errors, /c is the computer name and /d: is the number of days the profile needs to be older than.
Q. Copy profile locally problems.
A. If you are not using roaming profiles but are instead just copying a profile for another domain user on the local machine you may just create a directory under profiles for the user and copy it there as per the instructions in Q. How can I copy a user profile?
If you do this you will find that when the user logs in for the first time for whom you copied the profile, they will not use the directory you created for them, but instead a <username>.000 will be created instead. This is because a mapping is used for the user to the Profile area and if the user logs in for the first time and a directory of its user name already exists it won't use it and will instead create a new area of the format <username>.nnn where nnn starts at 000.
The workaround to this is to logon as the domain user first, logout and then copy the profile as this will setup the correct mapping of the user to profile area.
If this has already happened perform the instructions in Q. Defining the profile area to use for a user.
Q. Defining the profile area to use for a user.
A. By default when a user logs on for the first time at a machine a directory under %systemroot%\profiles is created under the name of the user to hold the users profile, e.g. for user saviljo the area created would be %systemroot%\profiles\saviljo.
Problems arise if the directory already exists and so an alternate directory <user name>.nnn will be created, starting with 000. This mapping is stored in the registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList. You can therefore force a user to use a specific profile area by performing the following:
The user should now login using the profile you originally copied for them. Once you are sure it works you can delete the <username>.nnn directory under %systemroot%\profiles. You should make sure the user has the right to user the original profile, for example if you have copied it to that location and granted rights accordingly.
Q. How can I view which local groups on a trusting domain a user belongs to?
A. The normal method for checking which local groups a user belongs to on a machine would be to start User Manager and double click on the user in question and click the Groups button.
If however you wanted to see which local groups on a server a member of another domain belonged to there is no way to do this. Fortunately a utility from http://www.fidutec.com has been released as FreeWare which does exactly this. The diagram below best illustrates how it works.
Download from http://www.ntfaq.com/ntfaq/download/gestgrp.exe
Q. How do I delete/rename the Recycle Bin?
A. When you right click on the Recycle Bin it's context menu does not display a rename or delete option as on other desktop shortcuts/components. To add the rename option perform the following:
If you right click on Recycle Bin you now have a rename option.
If you want to be able to delete the icon change the Attributes value to 60010020 by following the procedure above. To have the rename and delete option change the Attributes value to 70010020. You can now delete by right clicking on the icon and select Delete. Click Yes to the confirmation.
You may want to avoid manually updating the registry and you can delete the icon by using the TweakUI utility. If you have TweakUI installed perform the following:
Q. How do I disable Task Manager?
A. This can be done using the registry as follows
This can also be done using the policy editor
To remove Task Manager for all users just rename taskmgr.exe to something else, or if it is on a NTFS partition you can set the permissions so normal users cannot access it.
Q. How do I disable Window animation?
A. Using TWEAKUI on the General tab, you can unselect "Window Animation" which will stop the animation when a window is minimized/restored. This can also be accomplished using the registry:
Q. How do I reduce/increase the delay for cascading menus?
A. You can use TWEAKUI - Mouse tab and decrease/increase the menu time, however this can also be accomplished using the registry editor and changing the value HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Desktop\MenuShowDelay.
Q. How do I change the My Computer icon?
A. This can be changed using Themes for NT or the Plus Tab of Display settings, however it can also be changed using the registry editor
Q. How do I hide the "Network Neighborhood" icon?
A. You can use TWEAKUI and on the "Desktop" tab unselect "Network Neighborhood". This can also be done using the registry:
Q. Why can't I move any icons?
A. It is possible to configure NT to autoarrange the icons, which means you cannot manually move them. To turn off this feature, right click on the desktop (anywhere where there is not a window), Arrange Icons, and unselect auto-arrange.
Q. How can I disable the Right mouse button?
A. For those systems running with Service Pack 2 or above, it is possible to disable the context menu as follows:
To remove this, just delete the value NoViewContextMenu and logout and login again (or set it to 0)
Q. How do I change the colour used to display compressed files/directories?
A. The colour used is stored in the registry in hexadecimal format, therefore before you try and change the colour you need to work out what the value is in hex. Usually you know a colour as an RGB value like 255,0,0 for red and to convert this to Hex use the calculator supplied with Windows NT (calc.exe)
You will now have a hex value for the colour, e.g. 255,128,0 would be ff, 80, 0
If you would prefer to avoid the registry, you can make the same change using the TweakUI utility
Q. How can I configure the wallpaper to be displayed somewhere other than the center of the screen?
A. It is possible to configure NT to display a wallpaper anywhere on the screen, however you have to manually update the registry
Q. How can I stop the "Click here to begin" message?
A. There are 2 ways to accomplish this. If you have the TweakUI utility perform the following
If you don't have TweakUI you will need to edit the registry directly
Q. How can I get more room on the Task Bar?
A. If you move the cursor over the top of the task bar it will turn into a double headed arrow. When the cursor is the double arrow hold down the left hand button and drag upwards and the task bar's area will be increased one row at a time. Likewise you can shrink it by dragging downwards.
Q. How do I add the Control Panel to the Start Menu?
A. Create a New folder under the start menu you wish to have it on. (administrator or All users) Name the New folder
Control Panel.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}
Complete with the period, brackets and dashes. Once entered it will automatically be renamed to Control Panel and unlike the Settings Control Panel it will be cascading meaning all control panel applets will be shown as sub-objects.
If you have a problem, try pressing F5 to refresh the screen, or log off and on again.
Q. How can I remove a program from the Open With when right clicking?
A. Each entry in the "Open With" has an entry in the registry HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT called <extension>_auto_file, e.g. doc_auto_file for work. To remove the entry just delete the base <extension>_auto_file tree in the registry. If you were unsure you could use the following:
Q. How do I change the Internet Explorer icon?
A. For Internet Explorer version prior to 4.0 follow the procedure below:
There is a program called MicroAngelo available from http://www.iconstructions.com which automates this procedure.
The solution above does not work for Internet Explorer 4.0 and above, the method is as follows:
There are some really nice IE icons at http://www.blably.com/iconstructions/ .
Q. How do I add an item to the Right Click menu?
A. Follow the procedures below:
When you right click on a file the new entry will be displayed.
Q. Is it possible to move the Task bar?
A. The Task bar can be moved any of the 4 sides, left, right, top and bottom. To move just single click on the task bar and drag to the side you wish the task bar to reside on.
If you have lost the task bar just press Ctrl-Esc to redisplay.
Q. How can I configure NT to display a thumbnail of bitmaps as the icon instead of the Paint icon?
A. Perform the following, for best effect make explorer use large icons
Q. Can I remove one of the startup folders on the Start Menu?
A. Unfortunately no, one is your own user startup folder (%systemroot%\Profiles\<Username>\Start Menu\Programs\Startup) and the other is the All Users (%system root%\Profiles\All Users\Start Menu\Programs\Startup). Both are system files and therefore undeletable.
It is possible to hide one or both of the startup folders by setting the hidden attribute on the folder:
attrib +h %system root%\Profiles\<Username>\Start Menu\Programs\Startup
A trick has been found to remove one of the startup menus by copying the All Users Startup group over the Administrator Startup group which then deletes the All Users startup group.
Q. How can I clear the Run history?
A. The Run history is stored in the registry in location HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\RunMRU as a series of values a-z. To delete an entry from the run menu perform the following:
If you want to clear the whole Run list you can use the TweakUI utility
Q. How can I remove the Documents menu?
A. There is no way to remove the Documents menu from the Start button, however it is possible to empty it at the start of each session.
The documents menu is actually the contents of %systemroot%\Profiles\<username>\Recent, e.g. d:\winnt\Profiles\savillj\Recent, and if you delete the contents of this folder then nothing will be shown in the documents menu. The easiest way to do this would be to create a batch file and place it in you startup group
When you login from now on the batch file will be run and delete your Documents menu.
The same effect can be gained if you have TweakUI installed by clicking the Paranoia tab and checking "Clear Document history at logon"
Q. How do I disable the context menu for the Start button?
A. The context menu if displayed when you right click on an object. If you right click on the Start button you get options to start explorer, find etc. To disable this perform the following:
Right clicking on Start will now have removed these options.
To disable the context menu entirely perform the following
To re-enable the Context menu you would set to 0. Logout and in again for this to take effect.
Q. How do I change the Network Neighborhood icon?
A. This can be changed using Themes for NT or the Plus Tab of Display settings, however it can also be changed using the registry editor
Q. How do I change the Recycle Bin icons?
A. There are two icons for the Recycle bin, an empty and a full. To change them use the following
You can also change the icons using the Plus tab of Display properties.
Q. How do I change the Briefcase icon?
A. To change this icon perform the same as in Q. How do I change the Network Neighborhood icon? but use HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{85BBD920-42A0-1069-A2E4-08002B30309D}\DefaultIcon in step 2.
Q. How can I get rid of the arrow over the shortcuts?
A. You can remove the overlay by using TweakUI
You can also remove the arrow by editing the registry
Q. I have deleted the Recycle bin how can I recreate it?
A. If you have TweakUI click the Desktop tab and check the "Recycle Bin" and click Apply then OK. If you do not have TweakUI you can re-add by directly updating the Registry:
Q. I have deleted Internet Explorer from the desktop how can I recreate it?
A. Again you can use TweakUI, select Desktop and check the "The Internet" box, click Apply then OK. Alternatively you can directly edit the registry:
Q. How can I add a shortcut to launch a screensaver on the desktop?
A. Screensavers are just programs with a .scr extension. To create a shortcut of a screensaver perform the following:
Q. How do I delete/rename the Inbox icon?
A. When you right click on the Inbox icon it's context menu does not display a rename or delete option as on other desktop shortcuts/components. To add the rename option perform the following:
If you right click on the Inbox icon you now have a rename option.
If you want to be able to delete the icon change the Attributes value to 60000000 by following the procedure above. You can now delete by right clicking on the icon and select Delete. Click Yes to the confirmation.
You may want to avoid manually updating the registry and you can delete the icon by using the TweakUI utility. If you have TweakUI installed perform the following:
Q. I have deleted the Inbox icon, how can I recreate it?
A. If you have TweakUI click the Desktop tab and check the "Inbox" and click Apply then OK. If you do not have TweakUI you can re-add by directly updating the Registry:
Q. How can I stop and start Explorer (the shell)?
A. Explorer is just a process so you can stop the Explorer process and then start a new one. You should use caution with this though and you will also lose the service type icons on the taskbar when Explorer restarts.
Q. How do I enable the mouse snap-to?
A. Is it possible to configure windows to move the mouse to the default button to speed up general operations. To enable this perform the following:
This can also be accomplished using the Mouse control panel applet, select the "StepSavers" tab and check the SnapTo box if you have the IntelliMouse software installed or select the Motion tab and check the "Snap Mouse to the default button in dialog" box if you don't. Click Apply then OK and you won't have to reboot.
Q. How do I enable X Windows-Style auto-raise?
A. Is it possible to configure windows so when you move the mouse over a window it will come into focus:
Q. How do I remove a template from the New menu?
A. If you select New within, for example, Explorer you will be given a large list of document templates that have registered themselves on your machine.
If you would like to trim away some of these perform the following:
It will now be removed from the new menu (you will have to restart Explorer if it is running so it reloads in the registry information).
Q. I don't have the new item on my desktop context menu.
A. If when you right click on the desktop there is no "New" item perform the following:
You should now have a New item on the desktop context menu. A reboot is not needed.
Q. How can I configure the command prompt?
A. When you are in a cmd.exe session, it is possible to change the prompt to display other information, such as time, date, OS version etc. To change the prompt just use
prompt <text>
e.g. prompt johns prompt
While basic text will work it is not very helpful, and below is a list of all the codes you can use
| $A | & Ampersand |
| $B | | Pipe |
| $C | ( Open parenthesis |
| $D | Current date |
| $E | Escape code (ASCII code 27) |
| $F | ) Close parenthesis |
| $G | > greater-than sign |
| $H | Backspace (erases previous character) |
| $L | < Less-than sig |
| $N | Current drive |
| $P | Current drive with path |
| $Q | = Equal sign |
| $S | Space |
| $T | Current time |
| $V | Windows NT version number |
| $_ | Carriage return and linefeed |
| $$ | $ sign |
If you have command extensions, you can also use
$+ Zero or more + characters depending on the depth of the PUSHD
directory stack
$M Displays the remote name associated with the current drive letter
Q. How do I enable/disable command extensions?
A. When you use CMD.EXE, there are various extensions which are enabled by default. To enable/disable perform the following
You can also enable/disable them for a specific command session by using the appropriate qualifier to cmd.exe
cmd /y disables command extensions for this cmd session
cmd /x enables command extensions for this cmd session
Q. What commands can be used to configure the command window?
A. The commands below may be useful:
mode con lines=n - Where n is the number of lines to
keep (if n is larger than can fit on the screen a scroll bar will be
added)
mode con cols=n - Where n is the number of columns to
show (again a scroll bar will be added)
Q. How can I configure a scroll bar on my command window?
A. It is possible to increase the line buffer for the command windows above the normal 25. To change the "history" perform the following:
You will now see a scroll bar on side of your command window. You would also have seen under the properties you can change the default starting location for command windows.
What the above actually does is create HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Console\E:_WINNT_System32_cmd.exe key with a value ScreenBufferSize where the first part is the buffer height in hexadecimal.
Q. How do I cut/paste information in a command box?
A. To copy the entire contents of a command window, you can maximize the window (Alt - Enter) and press the Print Scrn button. Alternatively:
Alternatively you can enable QuickEdit mode by right clicking on the title bar and selecting properties. Select the options tab and check the "QuickEdit Mode" box. Now you can select text with the left mouse button and just press Enter to copy into the clipboard.
Q. How do I enable Tab to complete file names?
A. NT has this functionality built in, however by default it is disabled. To enable perform the following
Q. How do I create a shortcut from the command prompt?
A. There is a utility supplied with the Windows NT Server Resource Kit Version 4.0 Supplement One (phew) called shortcut.exe which can be used to create .lnk files. The application is quite powerful, and allows you to specify not only the resource to link to, but also an icon etc. An example is shown below
shortcut -t "d:\program files\johnsapp\test.exe" -n "Johns App.lnk" -i "d:\program files\johnicon\icon1.ico" -x 0 -d "e:\johns\data"
What does it mean?
-t this is the location of the resource to be
linked to
-n the name of the link file to be created
-i the icon file
-x the icon index to use in the icon file
-d the starting directory for the application
once started
You can copy shortcut.exe off of the CD with the resource kit, and it is located in <processor>\desktop (e.g. i386\desktop). There are no other files needed, just shortcut.exe.
Q. How can I redirect the output from a command to a file?
A. The most basic use is as follows:
<command> ><file name>
e.g., dir/s >list.txt
However with this errors still get output to the screen, to rectify this use the 2> for the errors, e.g.
<command> ><file name> 2><error file>
e.g. dir/s >list.txt 2>error.txt
If you want the errors and output to goto the same file use the following
<command> ><file name> 2>&1
Q. How can I get a list of commands I have entered in a command session?
A. You can press the up and down arrow keys when in a command session to display your old commands (same as the old DOSKEY software), however if you press the F7 key a list of all the commands entered will be displayed and you can then select the command and press enter to run it.
You can configure the history by right clicking on the title bar and selecting the Options tab. Update the "Command History" section.
Other keys you can use are as follows:
| F2 | Searchs for a character in the previous command and will display up to that character |
| F3 | Recalls the last command issued |
| F8 | Moves backwards through the command history |
| F9 | Lets yuo return to a command but its number given by F7 |
Q. How can I start explorer from the command prompt?
A. Enter the command
explorer /e
to start explorer in your current directory, or
explorer .
to bring up the single pane version of explorer.
Q. How can I change the title of the CMD window?
A. By default the title display name is the location of CMD.EXE, however this can be changed using two methods depending on the situation.
If you currently have a command session and you wish to change its title use the title command,
title <title>
e.g. title John Savill's Command Window
Alternativly if you want to start a new command session from an existing command prompt use the start command
start "<title>"
e.g. start "John Savill's Command Window"
Q. What keyboard actions can I take to navigate the command line?
A. Rather than just using the left and right arrows to move one character at a time through the command you can also use the following
| Home | Start of the line |
| End | End of the line |
| Ctrl+left arrow | Move back one wor |
| Ctrl+right arrow | Move forward one word |
| Insert | Toggle between insert and overstrike mode |
| Esc | Delete current line |
You can also use the Tab key to complete filenames for you as described in Q. How do I enable Tab to complete file names?
If you enable QuickEdit on command windows (Right click on the title bar, select properties, Options, QuickEdit Mode) you can select an area of text with the left mouse button, right click on it to copy it to the clipboard and then click the right mouse button again to paste it the current cursor location (reminds me of the good old VT keyboards with the hold key ;-) )
Q. How can I change the default Dir output format?
A. The DIR command has many switches and you can configure your own default behavior for the command instead of the normal format. For example you may want to view the output one page at a time (/p), in lowercase (/l), with files time as their creation rather that last write (/tc) and sorted by extension then name (/oen). Normally you would type
dir /p /l /tc /oen
however this is slightly tedious so to set this as your default perform the following
Any new command session will now use the new dir output format.
Q. How do I pause output from a command to one screen at a time?
A. Just add |more to the end of the command, e.g.
findstr /? |more
would display the help one screen at a time.
Q. How can I increase the environment space for a single command session?
A. While you can update the config.nt with a larger shell= to effect all command sessions, to set the environment space just for a single session, call the command with the /e switch, e.g.
COMMAND /E:2048 MYAPP.EXE
where /e:nnnnn is sets the initial environment size to nnnnn bytes.
Q. How can I stop a process from the command line?
A. Usually to stop a process, you start task manager, select the Processes tab, select the process and click "End Process" however you can also accomplish the same from the command prompt using 2 Resource Kit utilities.
Firstly you need to get a list of all processes on the system and this is accomplished using the tlist.exe utility.
C:\>tlist
0 System Process
2 System
20 smss.exe
26 csrss.exe
34 WINLOGON.EXE
42 SERVICES.EXE
45 LSASS.EXE
72 SPOOLSS.EXE
91 Nettime.exe
64 navapsvc.exe
...
198 notepad.exe Untitled - Notepad
214 TLIST.EXE
The first part, the number, is the process ID, for example, 198 is the process ID of the notepad.exe process that is running. Once we know the Process ID (or PID) we can stop it using the kill.exe utility.
C:\>kill 198
process #198 killed
You can optionally use the -f switch which forces the process kill.
You may, if you wish, kill a process on its name instead, e.g.
c:\>kill notepad.exe
will also work.
Q. How can I open a command prompt at my current directory in Explorer?
A. It may be a normal situation you are browsing directories in Explorer and want to open a command prompt at the current location without having to type a long cd .... to get to the correct directory. It is possible to add a context menu option to folders to bring up a "Command prompt here" which will open a command prompt at your current explorer location.
A Powertoy, Command Prompt Here, can be downloaded from Microsoft (and is also included with the resource kit, cmdhere.inf), however all this does is update a couple of registry entries and can be accomplished manually allowing greater flexibility
There is no need to reboot the machine and the new option will be available when you right click on a folder
Q. How can I open a command prompt at my current drive in Explorer?
A. Exactly the same as the previous tip but this time a command prompt for a base drive (which has a separate context menu)
Below is an inf file that incorporates the creation of the Command Here for drives and directories of you don't have cmdhere.inf that comes with the resource kit. Save it with a .inf extension and then right click on it and select install.
; Command Here
[Version]
Signature = "$Windows NT$"
Provider=%Provider%
[Strings]
Provider="SavillTech Ltd"
[DefaultInstall]
AddReg = AddReg
[AddReg]
HKCR,Directory\Shell\CmdHere,,,"Command Here"
HKCR,Directory\Shell\CmdHere\command,,,"%11%\cmd.exe /k cd ""%1"""
HKCR,Drive\Shell\CmdHere,,,"Command Here"
HKCR,Drive\Shell\CmdHere\command,,,"%11%\cmd.exe /k cd ""%1"""
Q. How can I change the editor used to edit batch/command files?
A. If you right click on a .bat or .cmd file and select edit the file will be opened in Notepad however you may want to use a different editor as the default.
This can be accomplished by making two small registry modifications
No reboot is required and any changes take immediate effect
You could also perform the above via a GUI front end by selecting View - Folder options - File Types from Explorer. You could then select the file type, e.g. "MS-DOS Batch file" and click Edit. The context menu options available are listed and you can modify them. All this does is update the registry values we have looked at.
If you wanted to leave the existing option and add a new Edit option, e.g. "Edit with MSDEV" perform the following (in this example we will only update .bat with a second edit option but the same could be performed on cmd):
You will now have two options when you right click on a batch file, edit and edit with MSDEV.
You can use this on any type of file, e.g. txt files by editing HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\txtfile\shell\open\command. Just look through HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\xxxfile where xxx is the extension (actually to find the correct file type use the assoc command, e.g. assoc .txt, it will then return the file type, txtfile).
Q. The AT command works differently under NT 4.0 than NT 3.51.
A. To better support long file names the parsing algorithm was changed in NT 4.0 so that only the target file should be surrounded by quotes, for example
Under Windows NT 3.51
C:\> at 20:00 "notepad d:\documents\bonde\maxfactor.txt"
Where as under Windows NT 4.0
C:\> at 20:00 notepad "d:\documents\bonde\maxfactor.txt"
This causing a problem as if you surround the whole command in double quotes, for example a batch file, it will not run correctly.
Support for a registry key has been improved in Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 4 which allows you to force the parse of the AT command to behavior in the same manner as 3.51 and to achieve this perform the following:
Q. How can I append the date and time to a file?
A. You can use the batch file below which will rename a file to filename_YYYYMMDDHHMM.
@Echo OFF
TITLE DateName
REM DateName.CMD
REM takes a filename as %1 and renames as %1_YYMMDDHHMM
REM
REM -------------------------------------------------------------
IF %1.==. GoTo USAGE
Set CURRDATE=%TEMP%\CURRDATE.TMP
Set CURRTIME=%TEMP%\CURRTIME.TMP
DATE /T > %CURRDATE%
TIME /T > %CURRTIME%
Set PARSEARG="eol=; tokens=1,2,3,4* delims=/, "
For /F %PARSEARG% %%i in (%CURRDATE%) Do SET YYYYMMDD=%%l%%k%%j
Set PARSEARG="eol=; tokens=1,2,3* delims=:, "
For /F %PARSEARG% %%i in (%CURRTIME%) Do Set HHMM=%%i%%j%%k
Echo RENAME %1 %1_%YYYYMMDD%%HHMM%
RENAME %1 %1_%YYYYMMDD%%HHMM%
GoTo END
:USAGE
Echo Usage: DateName filename
Echo Renames filename to filename_YYYYMMDDHHMM
GoTo END
:END
REM
TITLE Command Prompt
Example:
D:\Exchange> datetype logfile.log
RENAME logfile.log logfile.log_199809281630
Other date options include LOGTIME.EXE which enables you to specify a string and then writes the time followed by the string to the file logtime.log at the current default directory.
The other option is NOW.EXE which just replaces itself with the date and time, e.g.
D:\temp>now Batch complete
Mon Sep 28 15:54:19 1998 -- Batch complete
Both of the above utilities are part of the resource kit.
Q. How do I decrease the boot delay?
A. There are two ways of performing this change, the first method just automates the second method.
Method 1
Method 2
Method 1 just updates the timeout value in the [boot loader] section of boot.ini so we can do this manually:
A. There is a file in your system32 directory,
CONFIG.NT, that tells NT how to run DOS 5 sessions. Add the line
device=c:\winnt\system32\ansi.sys
or
device=%systemroot%\system32\ansi.sys.
You will then have to start a command line using the COMMAND.COM that came with DOS 5.0 (dig out those old disks!).
Q. How can I configure the local machine to perform a task at a set time?
A. Use the at command, e.g. for a job to run every
weekday (like a backup)
c:\ at 20:00 /every:M,T,W,Th,F "<command string e.g.
backup>"
Q. How do I change the Organization name on NT?
A. Your company changed names again? To change the company name in NT is easy,
Q. How do I change the default location NT expects to find NT software for installation(i.e. CD)
A. Start the Registry editor, and change HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SourcePath and HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Setup\SourcePath to the desired path (double click on the value to change it then press OK)
Q. How can I remove the Shut Down button from the login screen?
A. To remove the Shut Down button, start the registry editor, and change KHEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon and change ShutdownWithoutLogon from 1 to 0.
This can also be accomplished using the policy editor (poledit.exe). Expand the Windows NT System - Logon tree and blank out "Enable shutdown from Authentication dialog box".
Q. How can I Parse/Not Parse autoexec.bat?
A. The value HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\ParseAutoexec should be set to 1 for autoexec.bat to be parsed, or 0 for autoexec.bat not to be parsed.
Q. How do I add a path statement in NT?
A. Start Control Panel, double click the System icon, and goto the Environment Tab. Choose if it should be a user or system path defined, and click on the path variable, and then add the statement to the end of the current string (including a ;), then click set.
Q. Can I change the default Windows Background?
A. Using the Registry Editor (regedt32), edit the key HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Control Panel\Desktop and double click the Wallpaper Key, and enter the value including directory (e.g. c:\winnt\savlogo.bmp).You can also change the background colour HKEY_USERS\DEFAULT\Control Panel\Colors, double click Background, and change value (e.g. 0 0 0 for black).
Q. How do I change the Start menu items under the line?
A. Items above the line are part of the logged in users profile (winnt/profiles/<user name>/Start Menu/Programs). Items under the line are part of the all user group (winnt/profiles/All Users/Start Menu/Programs). To change these click on Start - Settings - Taskbar & Start Menu - Start Menu - Advanced and then move directory to the All Users and then make changes. You can only set the All Users Folder if you are logged on as a member with Administrative Privs.
Q. How can I restore the old Program Manager?
A. NT 4.0 by default uses the "Explorer" shell (explorer.exe), however the old Program Manager (progman.exe) is still delivered with NT 4.0, and be configured to be the default shell using the registry:
Q. Is there a way to start NT in Dos mode?
A. The command shell is command.com, and NT can be started in this mode with command.com as the default shell. Just perform the steps in previous FAQ, but instead of changing the shell value to progman.exe, change it to command.com or cmd.exe.
Q. How can I disable "Lock Workstation" when I press Ctrl-Alt-Del?
A. This cannot be done with a setting in the registry, however it is possible if you don't mind hacking one of the system dll files. The file that the ctrl-alt-del dialog is stored in is msgina.dll. Using any 32bit resource editor (such as one with a Win32 C++ compiler, Visual C++, Borland C++) you can edit this dll and remove the "Lock Workstation" button. Below are instructions for performing this with Visual C++ however for another resource editor find dialog #1650 and edit the attributes of the "Lock Workstation" to "inactive" or "invisible".
There is now a utility written by Alaxander Frink which automates the above process available at http://wwwthep.physik.uni-mainz.de/~frink/nt.html .
Q. How can I make NT powerdown on shutdown?
A. Follow the procedures below:
You will need an ATX power supply in order for this to work, otherwise the machine will just reboot.
Q. How do I enable Ctrl-Esc to start Task Manager?
A. This was removed in release 4.0 of NT, however it can be restored by editing the registry:
Q. How can I allow non-Administrators to issue AT commands?
A. By default only Administrators can issue AT commands (which use the schedule service). It is possible to allow Server Operators to also submit AT commands:
You may want to recreate your emergency repair disk after making this change.
Q. How do I control Access to Floppy Drives/CD-ROM drives?
A. By default Windows NT allows any program to access the floppy and CD-ROM drives. In a secure environment you may only want the interactive user to be able to access the drives and this is accomplished using the registry:
Q. I have DOS, Windows95 and NT installed, and want them all to show on the boot menu.
A. You need a handy utility called bootpart, which creates multiple operating .sys files enabling DOS and Windows 95 to be shown on the boot menu:
Be aware that using Bootpart may cause problems if you select "Previous Windows version" from Windows 95.
Q. How do I remove an App from Control Panel?
A. Each item in the Control Panel corresponds to a .cpl file. When Control Panel starts it search's %systemroot%/system32 for all .cpl files. To remove an item from Control Panel rename the .cpl file (e.g. to .nocpl).
An alternative to this if you only want certain users not to be able run a particular applet is to have the boot partition on NTFS, and remove the READ permission for these users/groups.
Have a look at Q. What are the .cpl files in the system32 directory? for more information on the .CPL files.
Q. How do I assign a drive letter to a removable drive?
A. It is not possible to assign a drive letter to a removable device using Disk Administrator, however you can assign drive letters to the other partitions leaving the letter unused that you want the removable drive to use. NT assigns drive letters to physical devices first (first partition) then to removable drives and then to other partitions (e.g. secondary partitions). For example if you had one harddisk with two partitions and a removable drive the letter assignments would be
To ensure that a removable drive receives a certain drive letter follow the instructions below:
A fix is now available which allows you to actually set the letter for a removable drive, http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q142/6/35.asp.
Q. How do I configure a default Screen Saver if no one logs on?
A. This is accomplished using the registry editor:
Q. How do I configure the default screen saver to be the Open GL Text Saver?
A. Follow the procedure below:
A word of caution, the Open GL screen savers use a lot of system resources, so I would not advise to use this, however I was asked :-)
Q. How can I create a new hardware profile?
A. If you are about to change hardware, you may want to create a copy of your current hardware config before starting which will enable you to revert to your old configuration:
Q. I have entries on the Remove software list that don't work, how can I remove them?
A. Each entry on this list (Start - Settings - Control Panel - Add/Remove Programs) is an entry in the regisry under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall. Just remove the key for any entries you don't want.
Q. How can I disable Dr. Watson?
A. Dr. Watson can be disabled using the registry editor:
Alternativly just set HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\AeDebug\AUTO to 0
To re-enable Dr. Watson type drwtsn32 -i
Q. How do I create a network share?
A. It is possible to create a share from the command prompt by typing:
net share <share name>=<drive>:<dir> /remark="<description>"
e.g. net share john=c:\data\johndrv /remark="Johns drive"
A share can also be created using explorer:
It is possible to add a $ to the end of the share so it will appear hidden, and not visible from a network browse.
Q. How do I connect to a network share?
A. You can connect to a network share using the command prompt:
net use <drive letter>: <UNC>
e.g. net use f: \\johnpc\john
A share can also be connected to using explorer:
The advantage of using the "net use" command is you can connect to hidden shares, i.e. john$ (although you can also connect by manually typing the address in explorer), and also this can be used from within command files.
Q. How do I configure the boot menu to show forever?
A. The timeout is changed by editing the boot.ini file which is on the boot partition and changing the timeout parameter:
Q. How can I configure the machine to reboot at a certain time?
A. There is a command line utility shipped with the resource kit called SHUTDOWN.EXE that can be used to reboot the local machine
shutdown /l /r /y /c
Where /l tells it to shutdown the local machine, /r to reboot, /c to close all programs and /y to avoid having to say yes to questions. You can then combine this with the AT command (don't forget you need the Schedule service to be running (Start - Settings - Control Panel - Services) to use the AT command) to make this happen at a certain time:
AT <time> shutdown /l /r /y /c, e.g.
AT 20:00 shutdown /l /r /y /c
Additions to the at command could be /every:M,T,W,Th,F so it happens every day, e.g. AT 20:00 /every:M,T,W,Th,F shutdown /l /r /y /c
You will then be given 20 seconds before the machine is shutdown, to abort the shutdown type
shutdown /l /a /y
Q. How can I configure Explorer to start with drive x: ?
A. The procedure below is used to change the shortcut for Explorer in the start menu, however you could just as easily create a new shortcut on the desktop and then edit the properties of it and change the target.
Q. How can I decrease the time my machine takes to shutdown/reboot?
A. It is possible to manually shutdown each service (well some of them) and then shutdown the machine. To identify which services are running enter the command
net start
(you can add > [filename] to the end to make it output to a file, i.e. net start > services.lst). You can then try to shutdown each of them by entering the command
net stop "<service name>" ,e.g. net stop "spooler". Some services will ask you to enter a y to confirm, and for these just add /y to the end. You will be able to build up a list of all the services that can be manually stopped, and you should put these in a .bat file, e.g.
net stop "Computer Browser""
net stop "Messenger"
.
.
net stop "Workstation"
To the end of the file add the command
shutdown /r /y /l /t:0
to reboot the machine (leave of the /r to just shutdown the machine). You may also want to add @echo off to the start of the file. You could add a check to accept an input parameter to reboot or shutdown, e.g. save this file as shutfast.bat, and call using shutfast reboot, or shutfast shutdown
@echo off
net stop "Computer Browser""
net stop "Messenger"
net stop "Net Logon"
net stop "NT LM Security Support Provider"
net stop "Plug and Play"
net stop "Protected Storage"
net stop "Remote Access Autodial Manager"
net stop "Server"
net stop "Spooler"
net stop "TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper" /y
net stop "Workstation"
if %1==reboot goto reboot
shutdown /l /y /t:0
exit
:reboot
shutdown /l /y /r /t:0
exit
You could add a shortcut on the desktop for this batch file with the relevant parameter.
You can also decrease the time NT waits for a service to stop before terminating it by performing the following:
I have been informed of an application TrapSD from http://www.pyzzo.com which helps close applications at shutdown.
Q. How can I change the startup order of the services?
A. Each service belongs to a Service Group, and it is possible to modify the order that the groups start:
See Knowledge Base Article Q102987 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q102/9/87.asp for more information
Q. How can I configure the system so that certain commands run at boot up time?
A. There is a utility called AUTOEXNT which is supplied in a zip file. You use perform the following:
When the system boots in future the AutoExNT service will check for the existence of the file autoexnt.bat and execute any commands in it.
A version of this is also shipped with the resource kit, however it is
better to use the downloadable version. To install the Resource kit
version you have to type
instexnt install
Q. What are the .cpl files in the system32 directory?
A. Each .cpl file represents one or more control panel applets (Start - Settings - Control Panel). Below is a list of common .cpl files and what Control Panel Applets they represent
| .cpl file name | Control Panel Applets |
| ACCESS.CPL | Accessibility options |
| APPWIZ.CPL | Add/remove programs |
| CONSOLE.CPL | Console |
| DESK.CPL | Display |
| DEVAPPS.CPL | PCMCIA, SCSI adapters and tape drives |
| INETCPL.CPL | Internet |
| INTL.CPL | Regional Settings |
| JOY.CPL | Joystick |
| MAIN.CPL | Fonts, keyboard, mouse and printers |
| MLCFG32.CPL | |
| MMSYS.CPL | Sounds and multimedia |
| MODEM.CPL | Modems |
| NCPA.CPL | Network |
| NTGUARD.CPL | Dr Solomons |
| ODBCCP32.CPL | ODBC |
| PORTS.CPL | Ports |
| RASCPL.CPL | Dial up monitor |
| SRVMGR.CPL | Server, services and devices |
| SYSDM.CPL | System |
| TELEPHON.CPL | Telephony |
| TIMEDATE.CPL | Date/time |
| TWEAKUI.CPL | TWEAKUI |
| UPS.CPL | UPS |
If you renames any of these files then the items they represent in the
Control Panel would not be shown, e.g.
rename timedate.cpl timedate.non
would remove the date/time control panel applet.
Also, setting HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer\NoSetFolders (REG_DWORD) to 1 will hide the Control Panel, Printers and My Computer in Explorer and Start Menu. You would normally need to create this value as it does not exist by default.
Q. How can I create a non-network hardware configuration?
A. You may have some machines that are not always connected to the network, and a solution is to create an alternate hardware profile which has all network devices and services disabled.
To actually use this configuration when you boot up the machine, after you select the operating system to load, e.g. "Windows NT Workstation 4.0" you will receive another menu with your hardware profile choices. Select the required and click enter.
Q. How can I remove the option "Press Spacebar for last known good config"?
A. The choice is hard coded into NT and therefore cannot be removed, however you can remove the functionality of what it does.
Several sets of configuration information are stored in NT, the current configuration and one or more sets of old configuration that are known to work. What NT does in the registry is to point to the current configuration and also a link to one of the other sets. It is possible to change the link to the last known good config, thus pressing space at bootup will have no effect.
The option "Press Spacebar for last known good config" has caused lots of trouble, because of use with the Novell IntranetWare for Windows NT, which is unavaiable after restoring the last known good configuration; the same is true for any self created hardware profile.
It has been found that an interesting solution for this and other related system crashes: Save the whole registration key from the regedit (interestingly, this method doesn't work with the more detailed regedt32) as a script file named for example save.reg, and if a system is damaged a simple double click on this executable file regenerates the whole configuration without loss of information. Moreover you can zip this file - usually as large as 5 MBytes - to a volume of nearly 500 KBytes. With these tools in hand it is possible, to restore a crashed system from disk with rdisk and afterwards regenerate it with the registry file to the last known standard.
Q. How can I disable the OS2/POSIX subsystems?
A. It is possible to disable one or both of these
Q. How can I configure NT to automatically refresh the screen?
A. Usually when you delete a file, create a new folder etc the screen does not update until you press F5 (for refresh), however you can automate this
This change is immediate and the next time you start Explorer the new auto update will be in effect.
Q. How can I run a control panel applet from the command line?
A. It is possible to run Control Panel applets from the command line by just typing
control <applet name>
There are some instances when the .cpl file represents more than one control panel applet when you need to pass a parameter of which applet to run, below is a list
e.g. control main.cpl printers
will run the printer control panel applet
However it is better to associate the .cpl extension with control.exe, which means you only need to type the applet name. This is accomplished using the assoc and ftype commands
assoc .cpl=ControlFile
ftype ControlFile=control.exe %1 %*
You can now just enter the command and it will run (be sure to include the .cpl extension).
For a full list of control panel applets to .cpl files see Q. What are the .cpl files in the system32 directory?
Q. How can I configure a program/batch file to run every x minutes?
A. NT comes with a powerful built in scheduling tool, the at command, however it is not really suitable for running a command every 5 minutes, to do this you would have to submit hundreds of at jobs to run at certain times of the day. There are a number of tools supplied with the Windows NT Resource Kit which will help.
The first is called sleep.exe, and is user to set a command file to wait
for n seconds (like the timeout command), and its usage is simply
sleep 300
which would make the batch file pause for 5 minutes, so if you wanted a
command file/program to run every 5 minutes you could write a batch file
with the following (name run5.bat)
<program name>
sleep 300
run5
There are a number of problems with this approach, the command session has to stay open, and the 5 minutes does not start until the program has closed (however this can be solved by running the program in a separate thread by putting the word "start" in front of the program, e.g. start <program>).
Another program is called SOON.EXE and this schedules a task to run in n
seconds from now, to use soon the scheduler service has to be running
(start - settings - control panel - services). Again you could create a
batch file to use it (runsoon.cmd)
soon 300 runsoon.cmd
notepad.exe
Run the command file using the at command or soon, e.g. from the command
line
soon 300 runsoon.cmd
to get it started
Once the SOON is scheduled to run, if you wanted to stop it you would use the AT command to get a list of current scheduled jobs
C:\>at
Status ID Day Time Command Line
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 Today 9:04 AM runsoon.cmd
Once its ID is known it can be stopped using
C:\>at [\\computer name] <ID> /delete
e.g. C:\>at 0 /delete
Q. What registry keys do the Control Panel applets update?
A. The table below shows the control panel applet and the corresponding registry area, those not shown are stored in multiple areas.
| Accessibility Options | HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Accessibility |
| Date/Time | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\TimeZoneInformation |
| Devices | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services |
| Display | HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Desktop and HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\RESOURCEMAP\VIDEO |
| Fonts | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Fonts |
| Internet | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings |
| Keyboard | HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Desktop |
| Modems | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Unimodem |
| Mouse | HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Mouse |
| Multimedia | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Multimedia |
| Ports | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\RESOURCEMAP |
| Printers | HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Printers |
| Regional Settins | HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\International |
| SCSI Adapters | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\RESOURCEMAP\ScsiAdapter |
| Services | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services |
| Sounds | HKEY_CURRENT_USER\AppEvents\Schemes\Apps\.Default |
| Tape devices | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\RESOURCEMAP\OtherDrivers\TapeDevices |
| Telephony | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Telephony |
| UPS | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\UPS |
Q. How can I run a script at shutdown time?
A. There is no direct way to accomplish this, however it is possable to write a script and then call the shutdown.exe utility that is shipped with the NT Resource kit
shutdown /l /y
You could then add a shortcut to this script on the desktop. An alternative is to use a utility called ShutUp which can be downloaded from http://www.zdnet.com/pcmag/download/utils/shutup-a.htm .
Q. How can I create my own tips to be shown when NT starts?
A. The tips that NT displays are stored in key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Tips, and can easily be edited using the registry editor. You will notice that the names of the values are incremented by one so to add a new tip just either edit an existing one or create a new value (of type string) and set its name to the next available number.
The tips are displayed sequentially and the counter is stored in HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Tips\Next and can be changed if you want. The values are stored in hexadecimal.
To control if tips are shown set the value HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Tips\show to 01000000 to display and 00000000 to not display.
Q. How can I change the location of the event logs?
A. In event viewer you will notice that there are 3 different logs, Application, System and Security and each of these are mapped to a .EVT file in the %systemroot%/system32/config directory, however for performance/disk space reasons you may wish to move them and this can be done by performing the following
Q. How can I configure the default Internet Browser?
A. When you start an Internet Browser they usually perform a check to see if they are the default browser, however you may have turned this check off and want to change the default browser
Q. How can I change the alert for low disk space on a partition?
A. By default when a partition has less than 10% free disk space an event ID 2013 is created with the following text
"The disk is at or near capacity. You may need to delete some files".
To view these events use Event Viewer, however it is possible to change the percentage that the alert is created
Q. Is it possible to delete/rename the Administrator account?
A. It is not possible to delete the Administrator account, if you try and delete it an error "Cannot delete built in accounts" will be displayed. You can however rename it, in fact it is recommended that the account be renamed to avoid the possibility of hacking, most hackers try to enter a system using an admin account. To rename the Administrator account perform the following
Q. How can I tell NT how much secondary cache (L2) is installed?
A. NT will try and detect how much L2 cache is installed at startup time however it cannot always tell and will use a default of 256. If you have more you can manually configure NT with your exact amount
Q. What switches can be used in boot.ini?
A. The boot.ini file has a number of lines and some of these relate to the Windows NT Operating system, e.g.
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(2)\WINNT="Windows NT Workstation Version 4.00"
There are a number of switches that can be appended to the Windows NT startup line to perform certain functions. To edit the file perform the following
The switches that can be added are as follows
| /3GB | New to Service Pack 3. This causes the split between
user and system portions of the Windows NT map to become 3GB for user
applications, 1GB for System. To take advantage of this the system must be part of the NT Enterprise suite and the application must be flagged as a 3GB aware application. |
| /BASEVIDEO | The computer starts up using the standard VGA video driver. Use this if you have installed a graphics driver that is not working. |
| /BAUDRATE | Specifies the baud rate to be used for debugging. If you do not set the baud rate, the default baud rate is 9600 if a modem is attached, and 19200 for a null-modem cable. |
| /BURNMEMORY= | Makes NT forget about the given amount of memory in MB. If /burnmemory=64 was given then 64MB of memory would be unavailable |
| /CRASHDEBUG | The debugger is loaded when you start Windows NT, but remains inactive unless a Kernel error occurs. This mode is useful if you are experiencing random, unpredictable Kernel errors. |
| /DEBUG | The debugger is loaded when you start Windows NT, and can be activated at any time by a host debugger connected to the computer. This is the mode to use when you are debugging problems that are regularly reproducible. |
| /DEBUGPORT= comx | Specifies the com port to use for debugging, where x is the communications port that you want to use. |
| /HAL=<hal> | Allows you to override the HAL used, for example using a checked version |
| /KERNEL=<kernel> | Same as above but for the kernel |
| /MAXMEM:n | Specifies the maximum amount of RAM that Windows NT can use. This switch is useful if you suspect a memory chip is bad. |
| /NODEBUG | No debugging information is being used. |
| /NOSERIALMICE=[COMx | COMx,y,z...] | Disables serial mouse detection of the specified COM port(s). Use this switch if you have a component other than a mouse attached to a serial port during the startup sequence. If you use /NOSERIALMICE without specifying a COM port, serial mouse detection is disabled on all COM ports. |
| /NUMPROC=n | Only enables the first n processors on a multiple processor system |
| /ONECPU | Only use the first CPU in a multiple processor system |
| /PCILOCK | Stops Windows NT from dynamically assigning IO/IRQ resources to PCI devices and leaves the devices configured by the BIOS. |
| /SOS | Displays the driver names while they are being loaded. Use this switch if Windows NT won’t start up and you think a driver is missing. This option is configured by default on the [VGA] option on the boot menu. |
You can then edit the boot.ini file and either add Windows NT startup entries or modify existing entries, for example you could add a debug entry in the file as follows
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(2)\WINNT="Windows NT Workstation Version 4.00 [debug]" /debug /debugport=com2
Q. How can I change the default editor used for editing batch files?
A. By default if you right click on a batch file and select Edit then the batch file will be opened in Notepad, however the application used can be changed as follows:
There is no need to reboot, the change take immediate affect. To reset back to notepad change the entry to
%SystemRoot%\System32\NOTEPAD.EXE %1
Q. What are the default protections on an NTFS boot partition?
A. Below is a list from Knowledge base article Q172008 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q172/0/08.asp
<root>:\-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\Msapps and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\Program Files and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\Temp-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\Users-
Administrators - Special (RWXD) Everyone - List (RX) System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\Users\Default-
Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Special (RWX) System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\Win32app-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Read (RX) Server Operators - Full Control System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%-
Administrators- Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Config-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Cookies-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Cursors-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Desktop-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Fonts-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Help-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\History-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Inf-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Java and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Media-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Nwspool-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Profiles-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\profiles\Administrators
Administrators - Full Control System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\profiles\All Users and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Everyone - Read System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\profiles\Default User and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Everyone - Read System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Profiles\<username> and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control <username> - Full Control System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Repair-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Read Server Operators - Full Control System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Shellnew-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Cache-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Dhcp-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Read (RX) Server Operators - Full Control System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Drivers and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Read (RX) Server Operators - Full Control System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Inetsrv and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Lls-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Logfiles-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Netmon and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Os2 and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Ras
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change (RWXD) Server Operators - Full Control System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Repl
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Read (RX) Server Operators - Full Control System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Repl\Export and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Read (RX) Replicator- Change (RWXD) Server Operators - Change (RWXD) System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\repl\import and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Read (RX) Replicator- Change (RWXD) Server Operators - Change (RWXD) System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Spool and <subdirectories>-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Read (RX) Print Operators- Full Control Server Operators - Full Control System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Viewers-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\System32\Spool\Wins-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change (RWXD) Server Operators - Change (RWXD) System - Full Control
<boot partition>:\%SystemRoot%\Temporary Internet Files and <subdirectories>
Administrators- Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
Any other directories-
Administrators - Full Control Creator/Owner - Full Control Everyone - Change Server Operators - Change System - Full Control
These permissions do not apply to a drive that is converted to NTFS using the CONVERT utility. A converted NTFS drive consists of all files and directories with Everyone - Full Control as the default permission. To reset to the normal protections see Q. How can I restore the default permissions to the NT structure?
Q. How do I configure the default keyboard layout during login?
A. You can change the keyboard layout using the keyboard control panel applet (start - settings - control panel - keyboard - Input Locales) however this does not affect the layout used during logon (which is by default English (United States)). To change this perform the following:
A table of the codes to the countries is given below:
| 00000402 | Bulgarian |
| 0000041a | Croatian |
| 00000405 | Czech |
| 00000406 | Danish |
| 00000413 | Dutch (Standard) |
| 00000813 | Dutch (Belgian) |
| 00000409 | English (United States) |
| 00000809 | English (United Kingdom) |
| 00001009 | English (Canadian) |
| 00001409 | English (New Zealand) |
| 00000c09 | English (Australian) |
| 0000040b | Finnish |
| 0000040c | French (Standard) |
| 0000080c | French (Belgian) |
| 0000100c | French (Swiss) |
| 00000c0c | French (Canadian) |
| 00000407 | German (Standard) |
| 00000807 | German (Swiss) |
| 00000c07 | German (Austrian) |
| 00000408 | Greek |
| 0000040e | Hungarian |
| 0000040f | Icelandic |
| 00001809 | English (Irish) |
| 00000410 | Italian (Standard) |
| 00000810 | Italian (Swiss) |
| 00000414 | Norwegian (Bokmal) |
| 00000814 | Norwegian (Nynorsk) |
| 00000415 | Polish |
| 00000816 | Portuguese (Standard) |
| 00000416 | Portuguese (Brazilian) |
| 00000418 | Romanian |
| 00000419 | Russian |
| 0000041b | Slovak |
| 00000424 | Slovenian |
| 0000080a | Spanish (Mexican) |
| 0000040a | Spanish (Traditional Sort) |
| 00000c0a | Spanish (Modern Sort) |
| 0000041d | Swedish |
| 0000041f | Turkish |
These can also be seen in the registry at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Keyboard Layout\DosKeybCodes
Q. How can I add my own information to General tab of the System Control Panel applet?
A. When you receive a PC from a manufacturer you may see extra lines of description text and a company logo in the General tab of a System Control Panel applet, and this can be changed or added as follows:
You do not need to reboot the machine, the system control panel applet will pick up the files when started. The information above would give the following:
Q. How can I change the program associated with a file extension?
A. The easiest way is to:
An alternative method is to:
Q. How do I set a process to use a certain processor?
A. This is called processor affinity where you set a process to use a specific processor on a multi-processor system.
You cannot set affinity for a service, or set affinity for a program which has not yet been started.
Q. I have duplicate entries on my boot menu.
A. This is easy to remedy and is usually caused by reinstalling Windows NT.
Q. How can I stop a service from the command line?
A. To get a list of the running services enter the command
net start
(you can add > [filename] to the end to make it output to a file, i.e. net start > services.lst). You can then try to shutdown each of them by entering the command
net stop "<service name>" ,e.g. net stop "spooler". Some services will ask you to enter a y to confirm, and for these just add /y to the end.
You can also use the Resource Kit SC.EXE command, use
sc query
to get a list of the services, and then
sc stop <service name>
to stop the service.
Q. How can I add the printer panel to the Start menu?
A. To add a Printer panel to the Start menu, perform the following:
The Printer Panel will now be on the start menu and will be cascading meaning all printers can be viewed as sub-objects of the menu item.
Q. How can I hide the Administrative Tools on the Start menu?
A. There are several options open to you:
1, Set the protections on the folder and its contents so only members of the Administrative group can read/execute it. This will only work if the boot partition is NTFS
Non-administrative users will now see an empty "Administrative Tools" menu. You could select different users if you wish.
2, You could also just move the Administrative Tools folder from the All Users section to a specific account area on the machine. There may be complications will roaming profiles etc.
The methods above just hide the items from the menu, however users could still run the applications from Run, however the operating system prevents unauthorized users altering the system using these tools so that is not a problem (you could always set the protections on the images as well if you don't want users to run them).
Q. How do I restrict access to the floppy drive?
A. The NT Resource Kit and the Zero Administration Kit come with FLOPLOCK service
With the service started on Windows NT Workstation, only members of the Administrators and Power Users groups can access the floppy drives. When the service is started on Windows NT Server, only members of the Administrators group can access the floppy drives.
To remove the service perform the following:
A. The easiest way is to install TWEAKUI, and goto the Network Tab and just fill in the boxes. It can be done manually through the registry by following the instructions below:
The instructions above should only be done by someone who is happy with using the registry editor.
It is also possible using a program called autolog.exe that comes with the resource kit. Just run the executable and you will be able to fill in the information.
To logon as a different user you need to hold down the shift key as you logoff.
You will have to use regedit32.exe to disable write permissions to "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\Current Version\Winlogon" if you want to be able to logoff and login as another user but still have the "original" user as the autologon.
Q. How do I disable AutoLogon?
A. Again use TWEAKUI, or in REGEDIT set AutoAdminLogon to 0, and clear the DefaultPassword
Q. How do I add a warning Logon message?
A. You need to use the registry editor
This can also be done via the policy editor (poledit.exe)
Alternatively, a text message can be displayed by creating the key LogonPrompt in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/SOFTWARE/Microsoft/Windows NT/CurrentVersion/Winlogon
Q. How do I stop the last logon name being displayed?
A. Set the registry setting HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\DontDisplayLastUserName from 0 to 1
This can also be done using the policy editor, and is under the Windows NT System - Logon tree, and tick "do not display last logged on username".
Q. How can I stop people logging on to the server?
A. If you want to disable an NT servers ability to handle authentication then it is possible to stop the "Net logon" service:
To disable all of NT's server services, click on Server and click stop, which will stop "Net Logon", "Computer Browser" and any other server services.
Q. Users fail to logon at a server.
A. By default members of Domain Users will not be able to logon to a server, i.e. a PDC or a BDC, and if they try the error "The local policy of this system does not allow you to logon interactively". If you want users to be able to logon to a server (why I don't know) follow the procedure below:
Q. How do I enable NumLock automatically?
A. The registry entry HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Keyboard. Change InitialKeyboardIndicators from 0 to 2 using the regedt32.exe registry editor. To set the numlock for before anyone logs on, change the .default user value from 0 to 2, e.g. HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Control Panel\Keyboard\InitialKeyboardIndicators to 2.
An easier way is to turn NumLock on and the logoff using Ctrl-Alt-Del Logoff which will preserve the state of Numlock (logoff from Start menu does not do this).
Q. How do I limit the number of simultaneous logons?
A. Perform the following:
Q. %SystemRoot% is not expanded when I use it in a command.
A. If when you type SET or PATH at a command prompt, you notice that the %SystemRoot% environment variable has not been expanded this is a problem and needs to be corrected:
You can also check HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SystemRoot and make sure that this REG_SZ value conains the proper path (e:\winnt).
Q. How can I disable the Win key?
A. To disable both Windows keys perform the following:
Once the machine has restarted the Win key will no longer work
You can automate this by placing the command in a regini file, create the file remove_win.ini with the following contents
\Registry\Machine\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Keyboard Layout
Scancode Map = REG_BINARY 24 \
0x00000000 0x00000000 3 \
0xE05B0000 0xE05C0000 \
0x0
To then run the script enter the command
regini remove_win.ini
Regini.exe is supplied with the Windows NT Resource kit.
To re-enable the Win key delete the "Scancode Map" value you created.
Q. How do I set the number of Cached logons a machine stores?
A. By default an NT machine (since version 3.5, 3.1 only stored the last 1) caches the last 10 succesful logons, however this can be changed from anywhere between 0 and 50.
If someone attempts to logon and the domain controller is not available but their information is cached they will received the message
"A domain controller for your domain could not be contacted. You have been logged on using cached account information. Changes to your profile since you last logged on may not be available."
but still be logged on succesfully. If their information is not cached they will get the message
"The system cannot log you on now because the domain <domain name> is not available"
and not be logged on.
Q. How can I configure the system to run a program at logon time?
A. The easiest way is to add it to the start-up folder, and you have two choices, the first is to add the program just to your start-up menu (%systemroot%\Profiles\<username>\Start Menu) or to the all users startup menu (%systemroot%\Profiles\All Users\Start Menu).
If you don't want to do it this way (if you don't want users to be able to remove it) there is a registry key which can be used to run programs.
If you want a program to run only once and then never run again, perform the above but add the values under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce. Once the program has run it gets deleted from the RunOnce key.
You can also configure programs for your account only by adding values to HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
Q. How can I install the Policy Editor on a Workstation?
A. The Policy editor is POLEDIT.EXE and a number of .adm files. To install the Policy Editor on a workstation perform the following:
You will now be able to run the Policy Editor on a Windows NT Workstation. You may want to create a shortcut to POLEDIT.EXE in your Administrative Tools folder.
Q. How can I delete the "My Computer" icon?
A. It is not possible to delete the icon, however you can make it invisible.
You could then move the icon to the bottom of the screen to hide the "My Computer" text.
Now, don't use autoarrange, and don't select a greater screen resolution and you will never see it again.
Q. How do I disable the file delete confirmation?
A. If you use the "Recycle Bin" then you can disable the delete confirmation
Q. How can I switch the time between 24 hour and 12 hour?
A. There are 2 ways to configure this.
The first is using the Regional Control Panel applet
The second is to directly edit the registry
Q. How can I suppress boot Error Messages?
A. If you are performing development or know of a problem you may decide you wish to suppress any of the error pop-ups that are displayed when there is a problem. An example would be a driver that can't be loaded or some other system component that is not acting correctly.
There pop-ups can be generated from either of the two main start-up phases, and a separate registry key needs to be set for each stage.
Errors that are displayed as a result of the boot phase can be disabled as follows:
To suppress error messages that are displayed as part of the post-boot start-up phase which includes most device driver messages perform the following:
Instead of a blanket ban on all error msgs, you may prefer to mark some services as "optional" and not to generate an error if they don't start correctly. This can be accomplished by setting HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\<service>\ErrorControl to 0. For more information see:
Q. How can I enable/disable the Ctrl-Alt-Del to enter logon information? - NT 5.0 only
A. Windows NT 5.0 introduces the ability to remove the necessity of pressing Ctrl-Alt-Del, the Security Attention Sequence (SAS) to logon. By default on a workstation this is no longer needed however on a server it is still necessary but this can be configured with a single registry entry.
Disabling this feature does not decrease the security of Windows NT. To gain access to the computer, users are required to log on to Windows NT with a valid user name and password. The Windows NT logon process suspends all other user-mode processes to protect the logon process and is the only process that can create the access tokens used by the Windows NT security system.
Q. How can I stop the last username to logon from being displayed?
A. There are two ways of doing this. The easiest is if you have the TweakUI utility installed perform the following:
If you don't have TweakUI or simply want to achieve the result through the registry (maybe so you can set it from a logon script):
Q. The screen saver can only be configured to start up to 60 minutes.
A. This is a hard coded restriction of Windows NT 4.0, however Service Pack 4 increases this to 999 minutes.
Q. I have lost the ADMIN$ share.
A. If you have configured the system to not automatically create system shares at start-up time by setting the relevant registry entry AutoSharexxx then this share will not be created as that is what you are asking.
If however you do not have this set and you have just lost the ADMIN$ share which points to the %SytemRoot% folder, e.g. d:\winnt then you can recreate it by entering the following command:
C:\> net share admin$
For more information on suppressing the system shares please see Q. How do I stop the default admin shares from being created?
Q. How can I configure Notepad to wrap?
A. By default Notepad will allow you to enter text and not wrap when the screen is full, rather it will just scroll right. This behaviour can be altered.
Under the Edit menu of Notepad you can check "Word Wrap" however this can also be configured using the registry is you wanted to set this as the default for policies, as part of a login script or an unattended installation.
Q. How do I modify the login timer for profiles?
A. When you logon and, for instance, your local profile is newer than the one stored on the profile server you have an option of which to use and a timer of 30 seconds is given. This 30 seconds can be modified as follows:
Q. How do I change the location for temporary files?
A. The are a number of "temp" variables, mainly temp and tmp and the values of these can be changed as follows:
Alternatively you can directly edit the registry to make these changes
A final method from the command line is to use the SET command
C:\> set temp=d:\temp
Most Windows applications such as Word check the variable 'tmp' for the location of temporary files and not 'temp' so make sure you modify 'tmp' and not just 'temp'.
Q. How do I modify system variables?
A. As with user variables, these can be changed using the system control panel applet:
Alternatively you can directly edit the registry to make these changes
A final method from the command line is to use the SET command
C:\> set OS=OS2 DON'T do this :-)
Q. How do System Policies work?
A. You have a different System Policy for Windows 95 machines, and Windows NT machines. The Windows NT Policy editor is shipped with Windows NT server, and the Windows 95 System Policy editor is on the Windows 95 CD-ROM in the \ADMIN\APPTOOLS\POLEDIT directory. Policies alter registry settings on the target machine, and once the registry settings have been changed, the changes remain until changed by something else, therefore if you implement restrictions they will remain even if the policy file is deleted. By default, Windows clients look for policy files in the NETLOGON share on the domain controller (for NT, the machine that validates the logon, for Windows 95 the PDC unless you implement load balancing). Windows NT looks for the policy file NTCONFIG.POL and Windows 95 machines CONFIG.POL.
An important thing to note, is that NTCONFIG.POL/CONFIG.POL are not copied to BDC's by default and you have to setup directory replication.
A. In this example we will modify the Logon Banner:
Q. How do I create my own Policy template?
A. When system policy editor is run you can select which templates to include. There are 3 which are supplied with NT, and are stored in the %systemroot%/inf directory
The only ones you will use normally are common.adm and winnt.adm. Windows.adm was supplied for compatibility with windows95 machines, however policies created with Windows NT will not work on Windows 95 so this template is not used.
To select which templates to use, select "Policy template" from the options menu.
The structure of an adm file is simple and follows the structure shown below
CLASS MACHINE or USER
CATEGORY !!<string for first level>
CATEGORY !!<string for second level> this is optional
POLICY !!<string for name to be displayed next to check box>
KEYNAME !!<string for the keyname where the value is, do not include the first
VALUENAME !!<actual value name>
VALUEON "1" VALUEOFF "0"
PART !!<displayed in the bottom of the system policy screen> TEXT
END PART
END POLICY
END CATEGORY
END CATEGORY
[strings]
<strings defined>="Windows NT Network"
Simple! The !! means what's after is a string and has to then be defined in the [strings] section. You don't have to use strings and can just put the entries directly be enclosing in quotes if it contains a space, it just might help for long key names if used repeatedly. For every keyword (except for class) there must be a end keyword, e.g. for category there must be a end category, same as an if and endif etc.
For examples, look at the common.adm and winnt.adm files and then compare to how they look in the system policy editor to get the display and effect you want. There are many other combinations and effects such as a drop down box which can be accomplished using the following
PART !!<string> DROPDOWNLIST
VALUENAME ""<actual value>
ITEMLIST
NAME "<string>" VALUE NUMERIC n
NAME "<string>" VALUE NUMERIC n
NAME "<string>" VALUE NUMERIC n
END ITEMLIST
END PART
Q. Where can I get information on Profiles and Policies?
A. There is an excellent page at http://www.usyd.edu.au/su/is/dts/DTSwinNTProfiles.html which covers the subject well.
A. Logon as the Administrator (or a member of the Administrators group) and perform the following
It is also possible to configure auditing on a file/directory. Right click on the file/directory, select properties, and select the security tab and then select auditing.
Q. How do I view/clear the security log?
A. Logon as the Administrator (or a member of the Administrators group) and perform the following
Q. Where can I get more information on the Event Viewer?
A. See http://www.heysoft.de/ for more information
Q. Where can I get information on NT security problems?
A. There are various sites:
Q. How can I restore the default permissions to the NT structure?
A. Follow the procedure below:
The procedure above will only work on an NT 3.51 system. To perform the above on an NT 4.0 system you require the Windows NT Resource Kit SUpplement 2 and should perform the following
FIXACLS sets the permissions to the values defined in %SYSTEMROOT%\INF\PERMS.INF. Therefore, access to this file is also required to run FIXACLS.
Q. How can I copy files and keep their security and permissions?
A. By default when you copy files from one NTFS
partition to another, the files inherit their protections from the parent
directory. It is possible to copy the files and keep their settings using
the SCOPY program that comes with the NT resource kit.
SCOPY can copy owner and security audit information:
SCOPY c:\savilltech\secure.dat d:\temp\ /o /a
would copy the owner and auditing information. You can also use /s to
copy information in subdirectories.
The restriction for this command is that both the origin and target drives must be NTFS or the command will fail.
Q. How do I enable auditing on certain files/directories?
A. Auditing is only available on NTFS volumes. Follow the instructions below:
You must ensure that File access auditing is enabled (Start - Programs - Administrative Tools - User Manager - Policies - Audit).
These events can then be viewed using the Event Viewer (Start - Programs - Administrative Tools - Event Viewer - Log - Security)
Q. How do I use the System Key functionality of Service Pack 3?
A. Service Pack 3 introduced a new feature in NT with the ability of increasing security on the SAM database. This is performed by introducing a new key in one of 3 modes
To generate the system key you use the syskey.exe, however be warned, once you activate the encryption you cannot turn it off without performing a system recovery using an ERD produced before syskey was enabled. To enable encryption perform the following
Once rebooted if you choose a password once the GUI phase of NT starts a dialog box will be displayed and you should enter the password you gave and click OK, after that you may log on as normal. If you choose floppy disk you will be prompted to insert the disk and then click OK
Although you cannot remove the system key, you can change the mode by running syskey.exe and click Update. You will be asked to either enter the existing password or insert the system key floppy if changing from one of these modes.
For more information see Q143475 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q143/4/75.asp
Q. How do I remove the System Key functionality of Service Pack 3?
A. As stated in the previous FAQ there is not a simple remove function however if you restore the SAM from an ERD that was taken before the system key was enabled, it will remove this feature from the system.
Q. How can I configure the system to stop when the security log is full?
A. To avoid security logs being lost you can configure the system to halt if the security log becomes full so that only Administrators can logon, they can then archive the log and purge
When this happens the OS will display a BSOD.
Q. How can I clear the pagefile at shutdown?
A. As you will be aware the pagefile contains areas of memory that were swapped out to disk, it may be in a secure environment you want this pagefile cleared when the machine is shutdown as parts of memory containing passwords/sensitive information may have been mapped out to the pagefile.
Q. How do I enable strong password filtering?
A. Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 2 introduced a new password filter, passfilt.dll, which implements the following new restrictions
To enable this functionality perform the following on all PDC's (and stand alone's if used). You do not need to install this on BDC's, however you should in case the BDC is promoted to a PDC.
It should be noted you will still be able to set passwords in User Manager that do not meet the criteria, this is by design as direct SAM updates are not filtered.
Q. How do I set what happens during a crash?
A. By default a crash dump file will be produced but there are two other items that can be configured.
The first option is to enter a log entry in the system log. This can be set using the Startup/Shutdown tab of the system control panel applet in NT 4.0 and the "Startup and Recovery" button under the Advanced tab of the system control panel applet in NT 5.0 by checking the "Write an event to the system log".
This can also be achieved by setting the registy key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl\LogEvent to 1.
The other option is to send an Administrative alert (you need the alerter service to be running to enable this option). Again using the same dialog as before check the "Send an administrive alert".
This can also be achieved by setting the registy key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl\SendAlert to 1.
Q. How can I configure the system to automatically reboot in the event of a crash?
A. This can be set using the Startup/Shutdown tab of the system control panel applet in NT 4.0 and the "Startup and Recovery" button under the Advanced tab of the system control panel applet in NT 5.0 by checking the "Automatically reboot".
This can also be achieved by setting the registy key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl\AutoReboot to 1.
Q. What backup software is available for Windows NT?
A. Windows NT ships with NTBACKUP.EXE which is suitable for backing up most installations however its features are quite basic, for the larger more complex installations one of the following may be worth a look
A. Before you can add a tape drive you should first ensure that the correct SCSI driver is loaded for the card the tape drive is connected to. Once the SCSI driver is loaded you should perform the following
Q. What types of backup does NTBACKUP.EXE support?
A. NTBACKUP.EXE supports 5 different types of backups
Q. What backup strategies are available?
A. The main backup strategy is on a weekly plan as follows
As you know an incremental backup only backs up those files that have changed since the last backup and then sets them as backed up so this type of backup should be quite fast. In the event of a failure you would have to first restore the normal backup and then any subsequent incremental backups.
An alternative would be as follows
Differential backups and incremental backups are the same except that differential does not mark the files as backed up, therefore files backed up on Monday will still be backed up on Tuesday etc. Therefore to restore the backup you would only need to restore the normal backup and the latest differential backup.
It is important to not just have on week's worth of tapes, you should have a tape rotation and have maybe 10 tapes and rotate on a fortnightly basis.
If you wanted an extra backup as a one off you would use a copy backup as this does a full backup but does not mark files as backed up and therefore would not interfere with other backup schemes in use.
Q. What options are available when using NTBACKUP.EXE?
A. Once you start NTBACKUP a list of all drives on the machine will be shown. You can either select a whole drive or double click on the drive and then select directories. Once you have selected the drives/directories click the Backup button.
When performing a backup there are a number of fields that should be completed.
Q. Can I run NTBACKUP from the command line?
A. NTBACKUP is fully usable from the command line using the format below
ntbackup <operation> <path> /a /b /d "text" /e /hc:<on/off> /l "<filename>" /r /t <backup type> /tape:n /v
The parameters have the following meanings
| <operation> | This will be backup . If you wanted to eject a tape you could enter eject (but must also include the /tape parameter) |
| <path> | The list of drives and directories to be backed up. You may not enter file names or use the wildcard character. To backup multiple drives just put a space between them, e.g. ntbackup backup c: d: etc... |
| /a | Append backup sets to the end of the tape. If /a is omitted then the tape will be erased |
| /b | Backup the local registry |
| /d "text" | A description of the tape |
| /e | Logs only exceptions |
| /hc:<on/off> | If set /hc:on then hardware compression will be used, if /hc:off then no hardware compression will be used. |
| /l "<filename>" | Location and name for the logfile |
| /r | Restricts access (ignored if /a is set) |
| /t <backup type> | The type of backup, normal, Incremental, Differential, Copy or Daily |
| /tape:n | Which tape drive to use (from 0 to 9). If omitted tape drive 0 is used |
| /v | Performs verification |
Q. How do I schedule a backup?
A. Before a backup can be scheduled, you must ensure the scheduler service is running on the target machine, it does not have to be running on the issuing machine. For information on the schedule service see Q. How do I schedule commands?
Once the scheduler service has been started it is possible to submit a backup command using the ntbackup.exe image (image is a name for an executable)
at 22:00/every:M,T,W,Th,F ntbackup backup d: /v /b
The command above would schedule a backup at 10:00 p.m. on weekdays of drive D: and the local registry with verification.
A. To restore a backup saveset is simple and will depend on what was backed up, however the basics are
Q. How do I backup open files?
A. Sometimes fills can be corrupted as a backup program will try to backup an open file and when restored the file is corrupt. To stop NTBACKUP from backing up open files perform the following
If you do have "Backup files in use" set to 1 then you should also set the following parameter
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Ntbackup\User Interface\Skip open files
The values for this are
0 - Do not skip the file, wait till it can be backed up
1 - Skip files that are open/unreadable
2 - Wait for open files to close for Wait time (which
is another registry value in seconds)
For more information have a look at Q159218 (http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q159/2/18.asp)
To backup open files without corruption you should look at Open File Manager software from http://www.stbernard.com (yeah the advert with the cute dog!). You can download a 15 day free trial.
Q. What permissions do I need to perform a backup?
A. The operator performing the backup requires the "back up files and directories" user right. This can be given directly using user manager, or the preferred way is to make the user a member of either the Administrators group or the backup operators group.
Q. How do I backup the registry?
A. Most of the registry hives are open, making them unable to be copied in the normal way, however there are several methods available to you
NT does not automatically rename the old Registry to .DA0 as does Windows 95. However, you can use RDISK, the Emergency Recovery Disk utility, to generate fresh duplicates of the Registry, and use this script to keep three old versions on hand:
REM REGBACK.BAT note: change M: to home directory on LAN
REM pkzip25 is a product of PKWARE, see www.pkware.com for details
rdisk /s-
if exist m:regback.old del m:regback.old
ren m:regback.sav regback.old
ren m:regback.zip regback.sav
pkzip25 -lev=0 -add -attr=all m:regback %systemroot%\repair\*.*
exit
Q. How can I erase a tape using NTBackup that reports errors?
A. When NTBackup starts and when a tape is inserted a scan of the device is performed and if any errors are found one of the following messages will be displayed
You will not be able to perform any actions on the tape including erasing it. It is possible to force NT to not check a tape when inserted using the /nopoll parameter, e.g.
c:\>ntbackup /nopoll
You will now be able to erase the tape within NTBackup. If you have multiple tape drives you may want to use the /tape:n parameter to instruct NTBackup to ignore a certain tape drive, otherwise no other parameters should be used.
Once you have erased the tape you should exit ntbackup and restart to use the tape (without specifying /nopoll).
Q. How do I create an Emergency Repair Disk?
A. From the Start Menu, select Run, and type RDISK. Click on Update Repair Info. It will then recreate the repair information stored in the winnt\repair directory. It will ask if you want to create a repair disk, insert a blank formatted disk and select Yes. RDISK /S updates the information in the %systemroot%/repair and also the SAM and SECURITY keys. Permissions on the repair should be strict as a user with access to the files could create a repair disk and use it to crack the system passwords.
Q. How do I create an NT Boot Disk?
A. Follow the steps below
You can then boot off of this disk, it will look at the existing NT partition and load the kernel as usual. This is useful for a mirrored system as you could edit the boot.ini file and change the disk, e.g.
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINNT="Windows NT Workstation Version 4.00"
could be changed to
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(1)partition(1)\WINNT="Windows NT Workstation Version 4.00"
if the mirror was the first partition on the second NT disk.
Q. I get the error "Can't find NTLDR"
A. This is a core file which must be in the root directory, and that fact that it cannot find it may mean other files are also missing, however to fix this problem perform the following:
Q. How do I recover a lost administrator password?
A. If there are no other accounts in the administrator group then the only way is to reinstall NT into a new directory (not the same, as it will upgrade and see the old password) and it will let you enter a new Admin password. Also if you have an old ERD that you knew the password at time of making, you could use this and restore the SAM and security portions of the registry.
There is also a piece of software from http://www.winternals.com that can break into an NT system (LockSmith) that will change any password. The software is not free, and will cost around US$100. Their new product, ERD Professional can also change passwords and is available from the same site.
A similar piece of software is also available from http://www.mirider.com that allows you to boot off of a set of disks and change the Administrator password.
Q. I have set a drive to no access, now no-one can access it.
A. Logon as an Administrator and then perform the following
Q. If I copy a file with Explorer or from the command line, the permissions get lost.
A. The only time a file keeps it permissions if is it is moved on the same partition. If it is copied it inherits the protection of the owning directory (a move across drives is a copy and delete). Also FAT does not support permissions so anything copied to FAT will lose protections.
Q. How can I get my taskbar back?
A. Press Ctrl-Alt-Del, then select Task Manager, click the applications tab, select New Task, and type Explorer.
Q. I get the error "NTOSKRNL.EXE missing or corrupt" on bootup.
A. This is usually due to an error in the boot.ini
file. The entry for NT is either missing or incorrect. Edit the boot.ini
file and check the entry for NT is correct, for example for an IDE disk
the entry should look something like
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(2)\winnt="Windows NT
workstation"
Check that disk and partition are correct. If you have recently added a
new disk or altered the partitions try changing the disk() and partition()
values. If you are sure everything is OK, then the actual file may be
corrupt so copy NTOSKRNL.EXE off of the installation CD onto the
%systemroot%/system32 directory.
Q. How do I configure Directory Replication?
A. Directory Replication is the process of replicating directories and their contents from one machine to one or more machines. The only machines that can be export servers are Windows NT Server machines. Import servers can be an NT server, NT workstation or OS/2 LAN Manager machine.
The main usage for Directory Replication is for the export of login scripts from the PDC to the BDC(s), where the PDC is the export server and the BDC the import server. This means when you login the BDC can also supply the login script as well as the authentication of the user, leaving the PDC free. This is the case that will be explained below.
The user has now been added to the domain, and the export server now needs to be configured
You may be wondering why you should keep your login scripts in the export area, when your NETLOGON share is import/scripts, well it will actually replicate to itself from the export/scripts to import/scripts so they will be the same.
Some people have problems with replication and adding Repuser to the Domain Administrators group may fix the problem. Also only directories directly under the /export directory will be replicated, files will not be, they have to be in a subdirectory of export.
Q. How do I remotely create an Emergency Repair Disk?
A. You can schedule an ERD creation using
at \\<machine name> <time> /interactive
/every:M,T,W,Th,F %windir%\system32\rdisk /s-
It may be preferable to store the contents of this disk on a location at the server, so the following batch script could be used:
%windir%\system32\rdisk /s-
net use z: \\<server name>\temp /persistent:no
if not exist z:\%computername% md z:\%computername%
copy %windir%\repair\*.* z:\%computername%\
net use z: /delete
exit
This would then be submitted as
at \\<machine name> <time> /interactive
/every:M,T,W,Th,F \\<server>\<share>\ERD.BAT
You could also just put the call to ERD.BAT in the login script so the contents of the repair disk will be updated every time the user logs on.
Q. How do I promote a Backup Domain Controller to the Primary Domain Controller?
A. When possible you should always promote a BDC to the PDC while the main PDC is still active, in this way the original PDC will be demoted to a BDC and no information will be lost, however sometimes the PDC will not be available (i.e. its crashed) and a BDC needs to be promoted, as in the absence of a PDC, a BDC does not automatically promote itself.
Q. How do I reinstate my old PDC back into the Domain as the PDC?
A. It is not possible to have 2 PDC's in a domain so assuming the machine crashed, i.e. has not been demoted to a BDC before being shutdown, then when it starts it will still be configured to be a PDC
Q. What tuning can be performed on Directory Replication?
A. There are a number of registry entries you can update.
These are all values under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Replicator\Parameters
| GuardTime | Sets the amount of time the export folder must have had no changes before files are replicated, by default 5 minutes. |
| Interval | How often an export server looks for changes in the replicator folders, by default 2 minutes |
| Pulse | Number of times the import computer repeats the change notice after the initial announcement. By default twice. |
Q. I am unable to perform a repair without a CD-ROM drive?
A. Performing any repair requires a CD-ROM in the drive, however this was fixed in Service Pack 2 and later
You will now be able to boot off of these disks and repair the registry/boot sector without a CD-ROM. Replacing system files without a CD-ROM is detailed in the procedure Q150497 which can be viewed from http://support.microsoft.com/support/
Q. Changing the Administrator password if you have forgotten it.
A. The instructions below require a second installation of NT on the machine you have forgotten the password to. I uses the srvany.exe resource kit utility.
You now need to correct the changes made
You may now delete the second installation of NT if you wish and remove it from the boot menu (edit boot.ini after removing the hidden, read only and system attributes attrib c:\boot.ini -r -s -h).
All this actually does is change the spooler service to use the SRVANY.EXE program which runs NET as the service with parameters "user Administrator password", which is the same as net user Administrator password which is a way to change the password. Check the resource kit for more information on SRVANY.
Q. Where is RDISK in NT 5.0? - NT 5.0 only
A. The RDISK.EXE utility has been replaced with an option in the NTBACKUP.EXE utility.
The recovery disk can no longer be used to restore user accounts etc. and you will need to backup/restore the Active Directory which will be covered in the backup section.
Q. I have installed Office 97 now I can no longer use Desktop Themes.
A. There was a bug with Office97 that corrupted the JPEG loader. Download the patch (ThemeFix.exe)
Q. I cannot delete a file called AUX.BAT or COM1!
A. A file of which the name (or a part of it) is equal to a DOS devices (NUL, COMx, AUX, LPTx, PRN...) cannot be deleted with Explorer or the usual DEL syntax. Use DEL \\.\drive:\path\AUX.BAT instead (replace drive and path with appropriate values). (The files may be the remains of a failed installation, you can create them e.g. with COPY some existing file \\.\drive:\path\COM1)
Q. The AT command does not work!
A. A sine qua non to use AT is a running Schedule service. To start it, type 'net start schedule' on the command line or use Control Panel/Services (if you want to use it regularly, set the Startup Type to Automatic). A common problem is that people try to use the example given in the online help: AT sometime CMD /C DIR > TEST.OUT.
Unfortunately, in NT 4.0, this does not work anymore. You must use AT sometime CMD /C "DIR > TEST.OUT" instead. The execution of the command starts by default in %systemroot%\system32, as can be seen from the output of the above example. You should specify the complete path if the command is in a different directory, e.g. AT sometime C:\TEMP\TEST.BAT. A further problem is that the command is executed in the security context of the LOCAL SYSTEM account, not the caller. However, the SYSTEM account does not have access to network resources, so your program cannot reside or access files on mapped drives (even if they are mapped from the local machine!). Also, environment variables (e.g. PATH) may be set differently. You can test the environment interactively with AT sometime /INTERACTIVE CMD.
Q. I can't format a disk/ create an Emergency Repair disk?
A. There are a number of possible problems. Firstly if using Service Pack 2 ensure you have the kernel fix applied. Also some virus killers (such as Dr Solomons) lock up drives making a format impossible as NT thinks the drive is locked (this is why you can't create an Emergency Repair disk). Stop the virus process using control panel - services and click on the Virus Killer process and press stop. Once the disk is formatted or the Emergency Repair disk go back to control panel and start the virus killer process again.
Q. When I change CD's/access the floppy drive NT crashes.
A. This is probably the bug in Service Pack 2. If you have service pack 2 then apply the KERNEL Fix.
Q. After a new installation of NT, I can logon but no shell starts.
A. Usually a normal user will have this problem, not an Administrator, as the problem is security on files. To cure this problem the security on the %systemroot% needs to be set so the Everyone group has RX access (Read, Execute)
If the shell does not start from any account you will need to:
For more information see http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q155/5/79.asp
Q. I have a Matrox Millenium graphics card and the windows blink and flash when moved.
A. If you are using the graphics card at 1600 x 1200 resolution in True Color (24-bit) or True Color (32-bit) mode, a window's frame may blink or flash when you drag the window across the screen. This is a known problem, and resolve, enable the Show Window Contents While Dragging option from the Plus tab on the Display control dialog (Start - Settings - Control Panel - Display)
Q. When I start NT I get NTDETECT twice.
A. This is caused by a missing or corrupt NTDETECT.COM. To resolve, copy the latest NTDETECT.COM from either the latest service pack, or if no service packs have been applied, from NT installation disk 1.
Q. My desktop disappears after a crash.
A. By default, if Explorer crashes it automatically restarts, however this may have been corrupted or changed so using the registry editor change the value HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\AutoRestartShell to 1.
Q. I have installed a second CPU, however NT will not recognize it.
A. When moving from a single CPU to dual-CPU,
multiprocessor versions of a number of NT files, including the HAL and the
OS kernel, must be installed. The UPTOMP.EXE utility, contained in
the NT Resource Kits, installs the multiprocessor files. The files
can be installed manually (see the MS Knowledge Base articles Q156358 "How
to Manually Add Support for a Second Processor" and Q168132 "After
Applying Service Pack NT Reports Single Processor").
The MS Knowledge Base article
Q142660
(http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q142/6/60.asp
) "Upgrade from Uni- to Multiprocessor (Uptomp.exe) and Win32k.sys"
describes a known problem when using UPTOMP.EXE on a version 4.0 NT
system. The fix, described in the article, adding the following line
to the file uptomp.inf, located at the base directory of the Resource Kit
installation, e.g., reskit.
win32k.sys = 0, 2, win32k.sys
Finally, if you install the multiprocessor files on a system to which a Service Pack has been applied, you probably need to reapply the Service Pack after running UPTOMP.EXE and before rebooting. Until you reapply the Service Pack your disk contains a mix of file versions, with the multiprocessor files at the revision level of the distribution media and files already present at the Service Pack revision level. Such a mix of versions can cause your reboot to fail.
Q. I reinstalled NT, now I cannot logon.
A. When you reinstall NT, a new SID is created. It is therefore necessary to remove the computer account for the machine from the NT server, and then add a new entry.
Q. I have Windows 95 installed, and I am trying to start the NT installation but it fails.
A. If you want to install NT with 95 installed, start
a DOS session (command.com) and first type
lock
which enables direct disk access for the NT installation program.
Remember also to use winnt.exe (not winnt32.exe)
Q. An Application keeps starting every time I start NT.
A. Applications can be started from a number of places
The easiest way would be to search the registry using REGEDIT on the application name
Q. Each time I start NT I get a file delete sharing violation?
A. There is a problem with TweakUI and the clear document history at startup option which can result in an error "Cannot delete <filename>, there has been a sharing violation". Disable the TweakUI Document History clear option or live with pressing OK each time.
Q. Sometimes when I run a program or Control Panel applet it says "no disk in drive a:".
A. It is possible the NT path statement has an "a:" included. Check the following
A. Run the "RDISK /S" a few times and this error will fix itself.
Q. I have installed Service Pack 3, now I cannot run Java programs.
A. Download the latest version of Internet Explorer which includes the latest virtual machines. There is also a hotfix for Service Pack 3 available from Microsoft ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/fixes/usa/nt40/hotfixes-postSP3/archive/java-fix/JAVAFIXI.EXE .
Q. Every time I start NT, explorer is started showing the system32 directory.
A. This is caused by an incorrect program call at startup, search the areas a program can be started from for an incorrect entry, these are listed at An Application keeps starting every time I start NT.
Q. I have removed my IDE CD-ROM drive, now NT will not boot.
A. Unless it is hardware related, such as you have not connected the cable correctly or you have not set the master/slave correctly you need to perform the actions below before disconnection the CD-ROM drive. Therefore if you have already disconnected the CD-ROM you should reconnect it temporarily.
You should now be able to boot normally. See Knowledge base article Q125933 for more information.
Q. I get the error, WNetEnumCachedPasswords could not be located in MPR.DLL
A. This is usually caused by an incorrect mapi32.dll, sometimes software installs the Windows95 version. Copy mapi32.dll from your NT installation CD-ROM to %systemroot%/system32.
Q. What information is shown in the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) ?
A. The NT operating system has 2 basic layers, the user mode and kernel mode. The user mode cannot directly access hardware, is limited to an assigned address space and operates at Ring 3 (lower priority). If a user mode program has an error, then NT just halts the programs process and generates an Operation error, and as the application runs in its own virtual address it cannot affect any other program. Common components that run in user mode are
NT 4.0 introduced a change in the NT architecture as Kernel mode process run much faster (Ring 0) they moved Video and Printer drivers from User mode to Kernel mode. Kernel mode is a privileged processor mode, allowing direct access to the memory and hardware. Kernel mode errors are not usually recoverable and a reboot of the system will be required. The BSOD is a built in error trapping mechanism which is used to halt any further processing to avoid system/data corruption. This means a faulty graphics/print driver could now crash NT. Components in kernel mode are
But what does the BSOD (or STOP message screen) show? Below is the basic structure of the BSOD, however what you see will differ and you may not have some of the sections as I'll explain below
--------------------------------------------------
Section 1: Debug Port Status Indicators
DSR CTS SND
--------------------------------------------------
Section 2: BugCheck Information
*** STOP: 0x0000000A (0x00000002,0x00000000,0xDB30442D)
IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL *** Address db30442d has base at db300000 -
matrxmil.SYS
CPUID: GenuineIntel 5.2.4 irql:1f SYSVER 0xF0000565
--------------------------------------------------
Section 3: Driver Information
| Dll Base | DateStmp - Name | Dll Base | DateStmp - Name |
| 80100000 | 2cd348a4 - ntoskrnl.exe | 80400000 | 2cd348b2 - hal.dll |
| 80010000 | 2cd348b5 - ncrc810.sys | 80013000 | 2cda574d - SCSIPORT.SYS |
etc..
--------------------------------------------------
Section 4: Kernel Build and Stack Dump
Address dword dump Build [1381] -Name
xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx -
matrxmil.SYS
xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx -
ntoskrnl.exe
xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx -
ntoskrnl.exe
etc..
--------------------------------------------------
Section 5: Debug Port Information
Restart and set the recovery options in the system control panel
or the /CRASHDEBUG system start option if this message reappears,
contact your system administrator or technical support group
OR if you system is started with /debug or /crashdebug
Kernel Debugger Using : Com2 (Port 0x2f8, Baud Rate 9600)
Beginning Dump of physical memory
Physical memory dump complete. Contact your system administrator or
technical support group
Section 1: This section will only be shown if the system was start /debug or /crashdebug. To tell if your system is debugger enabled, just look at the boot menu when you start the machine and the words [debugger enabled] will be shown next to the Windows NT menu choice. To enable /debug follow the instructions below:
The 3 letter words are signals, e.g. RTS is Ready to Send, DSR Data Send Ready, CTS Clear to Send, and SND means data is being sent to the COM port
Section 2: This sections contains the error (or BugCheck) code with up to four developer-defined parameters (defined in the KeBugCheckEx() function call). In this case the BugCheck was 0x0000000A IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL which means a process attempted to access pageable memory at a process level that was to high and is usually caused by a device driver.
For example, a BugCheck of 0x00000077 or 0x0000007A mean the pagefile could not be loaded into memory. The second hexadecimal value will help you diagnose the cause, e.g.
| 0xC000009A | STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES, caused by lack of non-paged pool. |
| 0xC000009C | STATUS_DEVICE_DATA_ERROR, generally due to bad block on the drive. |
| 0xC000009D | STATUS_DEVICE_NOT_CONNECTED, bad or loose cabling, termination, or controller not seeing drive. |
| 0xC000016A | STATUS_DISK_OPERATION_FAILED, also caused by bad block on the drive. |
| 0xC0000185 | STATUS_IO_DEVICE_ERROR, caused by improper termination or bad cabling on SCSI devices. |
For a full list of what the codes mean see knowledge base article Q103059 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q103/0/59.asp .
Section 3: This lists out all drivers that were loaded at the time of the crash. It is split into 2 sides, with 3 columns to each site. The first column is the link time stamp (in seconds since the year 1970) and can be converted into real time using the cvtime.exe application (f$cvtime on VMS :-) ).
Section 4: This shows the build number of the Operating System and a stack dump that shows the addresses that were used by the failed module. The top lines may show the offending code/driver, however not always as kernel trap handlers may execute last to preserve error information.
Section 5: This will depend on if you have the /debug setup, but it basically just shows the communication settings and if a .dmp file has been created.
Q. I have created my own application service, however when the user logs off the application stops.
A. When a user logs off, a number of messages are sent. For graphical applications the messages WM_QUERYENDSESSION and WM_ENDSESSION are sent, and to console (character mode) applications the message CTRL_LOGOFF_EVENT is sent. If your application responds to these messages then it may cause it to stop. You will need to modify your program to either ignore or handle the messages differently. There is more information on this in the resource kit.
Q. I can't install any software.
A. Sometimes the file config.nt can become corrupted, specifically the files= line, therefore:
Q. I get an error "This application is not supported by Windows NT".
A. This can sometimes be caused by the files
%SystemRoot%\system32\config.nt
%SystemRoot%\system32\autoexec.nt
not having everyone:full access protection if the boot partition is NTFS. To check/change this protection
Q. I have installed IE 4.0 now my shortcut icons are corrupt.
A. This is caused my an incompatibility between the final version of Internet Explorer 4.0 and TweakUI. To fix this you will need to uninstall TweakUI.
If you get an error saying it was unable to be removed you can manually remove it by entering the following command
rundll32 syssetup.dll,SetupInfObjectInstallAction DefaultUninstall 4 e:\winnt\inf\tweakui.inf
You should then reboot the computer.
Another method to try is to delete the hidden file '%SystemRoot%\ShellIconCache' and restart Windows NT. The 'correct' desktop icons will be recreated when you login.
C:\> attrib %systemroot%\shelliconcache -h
C:\> del %systemroot%\shelliconcache
If you find after the reboot the icons are still corrupt, install TweakUI again and then remove. TweakUI can be downloaded from http://www.microsoft.com/windows95/info/powertoys.htm
Q. I have lost access to the root of the boot partition, now I can't logon.
A. If you set the root of the boot partition to no access then you will be unable to logon. To get round this perform the following
Q. I receive the error: WNetEnumCachedPasswords could not be located in MPR.DLL:
A. This problem is caused by the file mapi32.dll being replaced by an application installation, usually with the Windows 95 version. To correct the problem reinstall the mapi32.dll file from the NT installation CD-ROM
Be aware that if you have applied service packs, mapi32.dll was redelivered in some of the service packs so you should take mapi32.dll from the service pack delivery (expand the service pack and then copy the file over).
Q. How can I perform a kernel debug?
A. To perform a kernel debug, the computer should be connected via a null modem cable or a modem connection for dial in purposes. The computers will be referred to as "Host" for the machine that will perform the debug, and "Target" for the machine that has the problem and is being debugged.
The computers should both be running the same version of Windows NT and the symbol files for the Target machine should be installed on the Host computer. The symbol files are supplied on the Windows NT installation CD-ROM in the Support\Debug directory.
The Target computer's boot.ini entry needs to be modified to allow debugging as follows:
In the example above the Target machine will allow debug connection using Com2: at a speed of 9600 bps.
The host computer needs to be configured with the information it needs to perform the debug and the installation of the symbol files.
To install the symbol files move to the \support\debug directory on the CD-ROM and enter the command
expndsym <CD-ROM>: <target drive and directory>
e.g. expndsym f: d:\symbols
This may take some time. Remember if you have installed service packs on the target machine the symbol files for these will also need to be installed on the host computer. The symbol files for service packs need to be download from Microsoft separately.
The next stage is to configure the environment variables needed for the debugging, such as the symbol file location etc., these are outlined below.
| _NT_DEBUG_PORT | COM port to be used, e.g. COM2: |
| _NT_DEBUG_BAUD_RATE | Speed for the connection, e.g. 9600, make sure this matches the /baudrate specified on the target machine |
| _NT_SYMBOL_PATH | Location of the symbols files (where you expanded them to using the expndsym utility) |
| _NT_LOG_FILE_OPEN | Name of the file used for the log of the debug session (optional) |
It may be worth putting the definition of the above into a command file to avoid having to type in the commands every time, e.g.
echo off
set _nt_debug_port=com2
set _nt_debug_baud_rate=9600
set _nt_symbol_path=d:\symbols\i386
set _nt_log_file_open=d:\debug\logs\debug.log
Next you should copy over the kernel debug software which is located in the support\debug\<processor> directory on the NT installation CD-ROM, e.g. support\debug\I386. It is easier just to copy over the entire directory as it is not very large (around 2.5MB). The actual debugger for the I386 platform is I386KD.EXE and you would just enter I386KD to start the debugger. To enter a command press CTRL+C and wait for the kd> prompt.
Q. How do I configure remote debugging?
A. If you find you do not have the knowledge to debug a Windows NT problem you may need to get Microsoft to perform the debug for you, and in this scenario 3 computers will be involved, the computer at Microsoft, the host machine and the target.
The Microsoft machine will need to connect via RAS to either the host machine, or a computer on the same network, so one machine will need to run the RAS server service.
The configuration is the same as in the previous FAQ, except that on the host machine instead of entering the command I386KD.EXE the command
remote /s "I386KD -v" debug
where debug is the name of the session (this can be anything). At the Microsoft end once they had connected to the network they would enter the command
remote /c <computer name of the host> debug
again debug is the name of the session and must match that configured at the host machine.
Q. I get the error "Not enough server storage is available to process this command".
A. This problem may be due to the machines having a non-zero PagedPoolSize in the registry. This can be set by performing the following:
If PagedPoolSize is 0 then it allows NT to dynamically allocate memory, the installation of software such as ARCServe is known to cause this problem.
Another cause for this error is if you installed Service Pack 3 before installing any network components. If this is the case then re-apply Service Pack 3 and any subsequent hotfixes.
Q. I can't delete a directory called con.
A. CON is a reserved name, so to delete you must use the UNC,
rd \\.\<drive letter>:\<dir>
e.g. rd \\.\c:\john\con
Q. I get an error when I try to export a profile other than Administrator.
A. This is usually due insufficient privilege on the Protected Storage System Provider\<SID> key. To be able to export your profile perform the following:
You should now be able to export this profile. To be able to export someone else's profile perform the following:
You will now be able to export this users profile.
Q. I have chosen a screen resolution that has corrupted the display and now I can't change it back.
A. When you try and change screen resolution, Windows NT asks you to test it, if you ignore this and set the display to a resolution that causes a problem your only course of action to to boot in VGA mode, and then once in VGA mode set the resolution back to something you know works.
Q. I get error "Boot record signature AA55 not found (1079 found)".
A. If Windows NT is installed on a logical drive in an extended partition (the 4th partition is usually the extended start), after you select the OS choice and NTDETECT runs, this error message will appear:
"OS Loader 4.0 Boot record Signature AA55 Not Found, xxyy Found. Windows NT could not start because of a computer disk hardware configuration problem. Could not read from the selected boot disk. Check boot path and disk hardware. Please check the Windows NT Documentation about hardware disk Configuration and your hardware reference manuals for additional information. "
The Master Boot Record consists of boot code that is used by the system BIOS to read the partition table. From data contained in the partition table, the MBR can determine which partition is set to be bootable (active) and also the starting sector of that partition. Once that location is determined , the BIOS jumps to that sector and begins the next phase of the boot process by executing additional code that is operating-system specific.
If you have files required for boot located above 1024 cyl, it will fail. If you're running scsi, there's a chance you can get around it by using the scsi driver as ntbootdd.sys. If you're on IDE you're out of luck.
Windows NT 5.0 gets round the boot failure if any files needed for boot are above cylinder 1024 with an updated NTLDR. This file can be copied to a Windows NT 4.0 installation on the active partition without any ill effects, just make sure you have Service Pack 4 applied to the system before copying the NT 5.0 NTLDR.
If the only thing wrong with sector zero was that the last two bytes are not 55AA, this can be fixed with a disk editor such as Norton Diskedit. However, this message is usually indicative of something overwriting or destroying the entire boot sector (sector zero) including the partition table entries.
When you install Windows NT on a logical drive in an extended partition - OSLOADER needs to "walk the extended partition table" through BIOS calls in order to get to the partition you have Windows NT installed in. Each of these logical drives are addressed in a "daisy chain" of partition tables. Each sector that contains a partition table entry MUST end with a 55AA as the last 2 bytes in the sector.
The best way to determine how to recover is to use a disk editor to see if the partition table entries are still intact. Each sector occupies 512 bytes. The first 446 bytes of sector zero contain the MBR boot code followed by the partition table entries, and ends with 55AA. If the partition table entries are still intact at offsets 1BE through 1FD, manually record their values, then write 55AA starting at offset 1FE. Once the signature 55AA is written the MBR boot code can be regenerated by using the Fdisk.exe program from MS-DOS version 5.0 or later.
FDISK /MBR
WARNING: This process will repair the bootstrap code and the 55AA signature by rewriting sector zero but will also overwrite the partition table entries with all zeros, rendering your logical drives useless (unless, that is, the 55AA signature is manually entered using a disk editor prior to your performing the FDISK /MBR).
If the partition table entries are not intact or were overwritten with unreadable characters, the problem is more involved and entails locating the master boot sector (MBS) for each partition and manually rebuilding the partition table entries. This process is beyond the scope of this article.
To speed recover from future MBR corruption, use the Windows NT 4.0 Resource Kit utility Disksave.exe to save a copy of the MBR to a floppy disk. This can be used if needed at some future date to restore the MBR using Disksave.exe.
In the case where Windows NT is installed on a logical drive in an extended partition, you will need a disk editing utility like Norton Diskedit to examine each sector containing an extended partition logical drive entry to make sure it ends with a 55AA. This process is beyond the scope of this article.
Most of this information is from Knowledge base article 149877.
Q. When I boot up NT, it pauses for about 30 seconds on the blue screen.
A. Each dot is part of the boot-time chkdsk (autochk.exe), and each 3 dots represent one drive so there should be 3*<number of drives> dots. Sometimes if something is wrong with that drive the startup will be delayed. However there is a known problem with NT if your computer has one or more IDE disks and one or more SCSI disks which results in a pause of around 30 seconds. The problem is due to the detection code used by NT and is currently being investigated by Microsoft.
Q. I receive a RDISK error, disk is full.
A. When you run the rdisk.exe it updates the directory %systemroot%\repair with the following files
| File | Registry Hive |
| AUTOEXEC.NT | This is not a registry hive but rather a copy of the autoexec.nt file located in the %systemroot%\system32 directory |
| CONFIG.NT | As above |
| DEFAULT._ | HKEY_USERS\.Default |
| NTUSER.DA_ | New user profile |
| SAM._ | Parts of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Security |
| SECURITY._ | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Security |
| SETUP.LOG | Details of location of system and application files along with cyclic redundancy check information for use with a repair |
| software._ | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software |
| system._ | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System |
As the system is used the files setup.log, sam._ and security._ will grow. The sam._ and security._ files are only updated if rdisk.exe is run with /s qualifier, e.g. rdisk /s.
If the contents of the %systemroot%\repair directory exceeds 1.44 MB then you will receive the error "The Emergency Repair disk is full. The configuration files were saved in your hard disk". You should look at the contents of the repair directory and ascertain which file is the problem, i.e. setup.log is 1MB!
If setup.log if the problem then you can perform the following.
If the problem is not setup.log and is that the sam._ and security._ files are too large then the problem is there are too many accounts on the system so you need to delete some of your user accounts :-) Only joking!
What you can do is locate an ERD that was created early in the computers life where the sam._ and security._ files are small and copy these to the %systemroot%\repair directory and in future do not run rdisk.exe with /s option. This does mean that account information will not be recoverable and you will need to know what the Administrator password was when the original ERD was created (as if it was used accounts would be set back to this state).
Obviously you will still want to be able to restore accounts in the event of a disaster so I would suggest one of the following
For more information see Knowledge base article Q130029 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q130/0/29.asp
Q. My Shortcuts try and resolve to UNC paths?
A. Shortcuts when created are automatically created with an UNC with \\<Computer name>\<file> in .lnk file. This is usually a problem if you copy shortcuts to other machines, however there are a number of ways to fix this.
To fix a single shortcut you can use the shortcut.exe program supplied with the Windows NT Resource Kit supplement 1 kit.
To dump out a shortcut use shortcut -u <file>.lnk
To alter the shortcut to not track the machine before you copy it to others use the command
shortcut -c -s -n <shortcut name>.lnk
To change the target and working directory on a moved shortcut use
shortcut -c -t d:\www.ntfaq.com\index.html -d d:\www.ntfaq.com -n ntfaq.lnk
To disable link tracking for all shortcuts perform the following:
Q. When I select a hyperlink or open a channel system32 folder opens?
A. A fix for this can be requested from Microsoft support, 338.exe. The fix has not been fully tested which is why it cannot be downloaded from their site. This fix will be in Service Pack 4.
As a work around you should either remove the Active Desktop or when the Logon box is displayed wait 1 minute before logging on.
Q. When I try and use WinAT I get a Dr Watson error.
A. This is usually caused by the Resource Kit being installed in a long file name directory, e.g. d:\program files\reskit. To get rid of this problem install the resource kit in a short name directory (8 characters or less).
Q. Drive mappings are being created by themselves.
A. One known cause of this behavior is the FINDFAST.EXE application that is supplied with Office 97. If either set of the following conditions are both true then drive mappings may be created automatically:
Condition set 1
Condition set 2
There are a number of resolutions to this
My experience with FindFast is that is uses up a great deal of system resources and is not worth the resource usage for what it does so option 4 may be your best bet.
See Knowledge Base article Q150604 (http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q150/6/04.asp) for more information.
Q. I can't create a partition over 1GB on an Adaptec 2940 SCSI controller.
A. As you boot up, you should be able to do a ALT-A, this takes you into the SCSI BIOS, under "Advanced Host Adaptor Settings" "Extended BIOS Translation for DOS Drives >1Gb" must be enabled.
Q. I get a STOP 0x00000078 error.
A. This can be caused by a bug in Windows NT where the error is produced if the NonPagedPoolSize is greater than 7/8 of your physical memory. To correct this perform the following:
Q. A file Testdir.tmp is created on a shared volume which cannot be deleted.
A. When a file/folder is copied to a shared NTFS volume, a file Testdir.tmp is created and then automatically deleted. Sometimes the user performing the copy does not have delete permission on the shared NTFS volume and so the file is not deleted and has to be manually deleted by someone who has the delete privilege.
To fix this, give the Delete permission to the user or group who perform the copies.
Q. How can I replace an in use NT system file?
A. If you attempt to replace any of the core NT system files a message will be displayed saying the file is currently locked. The Windows NT Resource Kit ships with MV.EXE which is a 32 bit version of the POSIX MV utility which allows file moves to be scheduled for the next reboot which will mean the system files will not be locked by the operating system.
The basic format of MV is as follows:
c:\>mv /x /d d:\temp\ntfs.sys d:\winnt\system32\drivers\ntfs.sys
The /x means do not save a copy of the file that is replaced. If you do not specify /d a hidden,system subdirectory "deleted" will be created under the destination directory and a copy of the original file placed there.
The /d means do not copy the file until reboot time. The first file name is the file to be copied and the second the the destination name and directory of the copy.
You can do this without using the MV.EXE utility by just manually updating the registry (which is all MV does)
Below is an example value for PendingFileRenameOperations
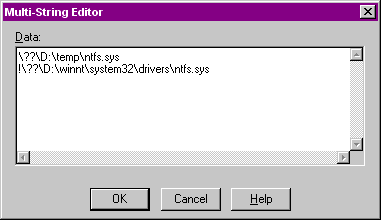
Once the reboot is complete and the file replaced the PendingFileRenameOperations value will be deleted from the registry.
Q. I removed my folder association and cannot open any folders!
A. That was silly :-)
Fortunately this can be fixed with two simple commands which should be run from a command session (cmd.exe)
The first command creates a new file type, folder, and the action associated with it. The second command creates the association between the "extension" and its file type.
Q. The batch file I schedule to run does not work with the /every switch.
A. You may find that if you submit a batch file with out the /every switch it works fine, e.g.
at 22:00 /interactive command.bat
however if you try
at 23:00 /every:M,T,W,Th,F /interactive command.bat
it fails. To correct this add cmd /c "<batch file>", e.g.
at 23:00 /every: M,T,W,Th,F /interactive cmd /c "command.bat"
Q. I have a volume of type Unknown in Disk Administrator.
A. If you have a partition in Disk Administrator that is of type unknown it does not necessarily mean the partition is corrupt. If the user has no permissions on the root of the drive then Unknown will be shown as the file type. To correct this perform the following:
The file system type of the partition will now be visible in Disk Administrator.
Q. I am unable to use Start from the command line with files with spaces in.
A. The Windows NT Start command allows the user to create separate window/process to run a specified program. If you try and run something that consists of a long file name with a space in quotes if fails and just brings up an empty cmd.exe window, e.g.
C:\> start "d:\documents\ntfaq book\contents.doc"
fails. In order to make it work only the part that has the long name should be in quotes, e.g.
C:\> start d:\documents\"ntfaq book"\contents.doc
will work OK. This applies to anything such as a server, share etc, e.g.
C:\> start \\"<server with space>"\"<share
with space>"\"<dir with space>"\"<file
with space>"
e.g. C:\> start \\"johns server"\"docs share"\"ntfaq
dir"\"table of contents.doc"
This is basically down to the fact that the first item in quotes should be the title of the window, and so a better way to work round the problem is to use
C:\> start "" "d:\documents\ntfaq book\contents.doc"
which will now work fine and there can be as many spaces as you want in any part.
Q. I am not offered the option to install from an INF context menu.
A. The options given from a context menu are derived from its file type entry under HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\inffile. The first item to check is that .inf is associated with inffile, and this can be checked with
C:\> assoc .inf
.inf=inffile
If you do not get the above response enter the command
C:\> assoc .inf=inffile
The next step is to check the context menu item "install" exists for inffile:
You should now have an install option for .inf files.
Q. How can I deallocate corrupt Memory?
A. If you get the blue screen or Dr. Watson often. Your Memory may be corrupt or you have mixed the Memory.
For testing this FAQ I have mixed two EDO-SIMM (2x16 MB) with two normal SIMM (2x16 MB) on a ASUS-Board P55 TP4-XE (This board can use mixed Memory). After this I often received Dr. Watson errors.
You should use the MAXMEM-Switch in Boot.ini to deactivate the corrupt memory bank until such time mixed memory is not longer in the mother-board. The MAXMEM switch will always use the lowest physical memory addresses, and therefore always uses bank0+. During the NT boot process NT probes the memory hard to make sure that it is really there and working -- generating a blue-screen if any memory tests fail.
Windows NT uses this switch and limits the whole memory from 64 to 32 MB and chooses only the good memory bank. You can also use this Switch to observe the swapping process if limiting the whole memory.
Q. I am unable to run certain 16 bit applications.
A. Certain 16-bit applications won't run under Windows NT, for example if they try and directly access hardware but if you are receiving any of the following errors then you may be able to do something about it:
A possible cause for these errors are if any of the following dynamic link libraries are missing, corrupt or simply the wrong version.
To fix expand/copy the files from the latest service pack/hotfix you have applied or if not found in the latest service pack, from your Windows NT installation CD-ROM.
Q. I have a service stopping NT from booting.
A. Normally you can modify the start-up of services using the Services control panel applet or Computer Management MMC snap-in - System Tools - Services in Windows NT 5.0. When you modify the start-up of a service it actually changes a value, Start, under the Services registry key, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services.
The first action to try is when Windows NT boots select "Last Known Good configuration" however if this does not work you can use the following.
The Start value of a service can have a number of values as defined in Q. What are the ErrorControl, Start and Type values under the Services subkeys?
In order to modify the start-up state of a service from outside of NT you will need to install a second copy of Windows NT on the machine (or if you can get the System file from the machine onto another machine using a tool like ERD Commanded (from http://www.winternals.com) the extra copy is not necessary).
You can now deleted your second copy of NT if you wish however it is always useful and takes up a minimal amount of space.
Another solution is to use ERD Professional which allows you to specify startup options for services/drivers from outside of NT, have a look at http://www.winternals.com.
Q. If I run winfile d: it starts Explorer?
A. If you try and pass WINFILE.EXE (the old File Manager pre 4.0) a drive, expecting it to start by default on that drive, you will find that it starts WINFILE as normal and then opens an Explorer view of the drive specified, e.g.
C:\> winfile d:
would start a File Manager session and an Explorer session which points to d:
This behavior is not a bug and is caused by a misunderstanding of the parameters expected by WINFILE.EXE. Any parameters passed to WINFILE.EXE are interpreted that it should run as a program, e.g. you could type
C:\> winfile notepad c:\file.txt
and it would start a File Manager session and a notepad session editing file.txt.
The reason Explorer starts if you specify a drive letter is that under NT and 95/98 any directory listings are executed by Explorer. Try typing C: from Run and it will start Explorer pointing to C:
Q. How do I create a queue to a Network Printer?
A. If you have a printer that has its own network card and IP address, you can create a queue to the device by following the instructions below
Q. How do I delete a network port (e.g. LPT3:)?
A. Network ports are defined in the registry at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Ports. Select the port you wish to delete and from Edit Menu select Delete.
You can also delete from the command line
net use lpt3: /del
Q. How do I configure my print jobs to wait until out of hours?
A. If you have large print jobs that you would rather run out of hours it is possible to configure usage hours on a print queue:
Jobs submitted to this print queue will now only be printed between the hours specified. If you wanted some jobs to be printed straight away you should define 2 queues, one for overnight, one for all hours.
Q. How can I disable the Printer PopUp message?
A. Start the Registry editor, and change KHEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Print\Providers and set the entry NetPopup to 0. You should then reboot Windows (however stopping and restarting the print spooler will suffice). If the printer is on an NT server, than this setting needs to be set on the Server which controls the print queue.
This can also be done from the Printers Control applet
Q. How do I change the Print Spool location?
A. Using the registry editor change the value HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Print\Printers\DefaultSpoolDirectory by double clicking on it and set it to the required area. This will change the print spool area for all printers, to change the print spool for only one printer move down to a printer key and create a value of type REG_SZ called SpoolDirectory and set this as where the spool files should be.
Q. How do I enable Print Auditing?
A. If you need to check what is being printed, then you can enable Print Auditing:
Print events will now be sent to the Security log which can be read from the Event Viewer (Start - Programs - Administrative Tools).
If you experience problems with events not being audited try enabling File and Object Access as well.
Q. How do I enable drag and drop printing?
A. To enable drag and drop printing, all you have to do is create a shortcut to the printer on your desktop
You can then just drag files over the printer and they will be printed (providing they are registered file types that NT knows how to print)
Q. How do I configure a Print Separator Page?
A. A printer separator page is configured by creating a text file using a number of special control codes. The basic format of the separator page is as follows
$ ---- this can be any character, and must be the
first character on the first line. Choose a character not normally used to
be the control character, in this case $
$LUser Name $N ---- $L is used to display
normal test until another code is found, $N displayed the username
$L, Job Number $I ---- $I displays the job
number
$E ---- $E means end of page
Other characters you can use are
$B$S ---- Turn on block character printing
$D ---- Data job printer
$F<filename> ---- A file to print
$H ---- Printer specific control code
$x ---- Where x is a number of blank lines to print
$T ---- Time job was printed
$U ---- Turns off block character printing
$Wxx ---- Width of the separator page
To configure the printer to use the separator file:
Q. How can I restrict which users can install local printer drivers?
A. It is possible to restrict print driver installation so that only Administrators and Print operators (on a server) or Power Users (on a workstation) can install local printer drivers
Q. How many printers can be on one NT Server?
A. You are only limited by how large the registry grows. I know of sites with 990 print queues, all lpr, on one NT server with no performance problems - NTS 4.0/SP3 dual P200 Pro, 256MB, FDDI.
There are some variables, but each queue adds about 30-35 KB to the registry. By periodically eliminating the wasted space and removing LastKnownGood as above, the limit is probably somewhere around 3500. I would expect performance to be a problem before this limit is hit.
Q. How can I print to an ascii text file?
A. A print driver "Generic/Text only" exists, which can be used with the file output ability as its default.
To use the ascii print driver go into your application and print, select the "Generic / Text Only" printer and click OK. A dialog will be displayed. Enter the file name you want the output to and click OK. You will not be able to view the file using Notepad or the like.
Q. How do I set security on a printer?
A. There are various levels of security you can set on a printer.
No Access - User may not print to the device
Print - User may print to the device and pause,resume and delete their own
jobs
Manage Documents - Enables the user to change the status of ANY print job
submitted by any user. The user may not change the status of the printer
Full - Enables complete access and administrative control of the printer
By default all users have Print access (the Everyone group) and also the "CREATOR OWNER" name has "Manage Documents" access. Creator Owner is the user that printed the document which means users have the ability to delete their own entries on the print queue.
To change print permissions perform the following:
Q. I get the error "The print processor is unknown" when installing a printer.
A. There are 2 causes for this.
If the winprint.dll is not found you should expand Winprint.dl_ from your Windows NT installation CD using the EXPAND command
expand -r <cd-rom drive>:\i386\winprint.dl_ %systemroot%\system32\spool\prtprocs\w32x86
If the file is there then you need to check the registry
Q. Where in the registry is the default printer set?
A. The default printer is set on a per user basis and so is part of the HKEY_USERS hive. To view the default printer for the currently logged on user view the
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows\Device
value. It is of the format "\\LN014\LN.S651.CSP001.HPLJ5,winspool,Ne01:", where the first part is the actual printer share, then the spooler and finally the connection, e.g. network or parallel port.
To view a different user or view remotely you would view HKEY_USERS\<SID of user>\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows\Device. To check which user has which SID see Q. How can I tell which User has which SID?
If no default printer is manually defined then the first printer alphabetically will be set as the default.
Q. When I try to print to a parallel device (lpt1) I receive error: System could not find the file.
A. This is usually caused by the parallel service not running. To check/fix perform the following:
If you still have problems also check the Parport and ParVdm services under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ as theses are also needed for parallel printing.
Another cause for this error is if LPT1 is disabled via the system BIOS so you should also check this.
Q. How can I allow members of the Printer Operators group to Add Printers?
A. While members of the Print Operators group can stop and restart the Print Spooler, modify jobs and other admin functions they cannot add or modify the actual printers. This can be changed by performing the following:
Stop and start the machine for the change to take effect. Alternatively just stop and start the print spool service,
C:\> net stop spooler
C:\> net start spooler
Q. How can I configure NT as a print server for UNIX systems?
A. The Windows NT Server that will be acting as the print service must have the following:
Once all of this is completed it is necessary to add a registry key as for UNIX to successfully pass data to an NT server the data type must be set to RAW.
The default value for SimulatePassThrough is 0, which informs LPD to assign data types according to the control commands.
You should now shutdown and restart the server. Once the start has completed the NT box will be able to accept UNIX print jobs. At the UNIX end you would need to use the following commands (example only for SCO Open Server 5).
On the SVR system you would use.
An example would be NT server name SAVPDC and print HP4SI the unix command would be
# lpadmin -p p0 -sSAVPDC!HP4SI
Thanks to Steven Vobes for this Unix information
Q. What Newsgroups are good for NT information?
A. The ones I subscribe to are:
Before posting to any of the Microsoft newsgroups, please read the Microsoft policy on Newsgroup posting, a HTML version of this can be viewed at http://www.ntfaq.com/ntfaq/MSNews.html.
Q. Where can I get more information?
A. There are various sites on the web that have extra information
Q. Where can I go for Training in Microsoft Products?
A. To find a training center in you area goto http://www.microsoft.com/isapi/train_cert/locator/locator0.idc.
Q. Where is information about becoming a MCSE?
A. Goto http://www.microsoft.com/train_cert
Q. Where can I find the resource kit?
A. It is available from most large book shops. Workstation is around US$50, Server US$150. You can purchase it online from a number of sources such as http://www.jsiinc.com and http://www.amazon.com. Updates to the Resource Kit tools are available from ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/reskit/.
Q. How do I run an application as a service?
A. The NT Resource Kit includes a utility called SRVANY.EXE which runs an applications as a service. There is more information on this at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q137/8/90.asp, also read the file that comes with the resource kit (Start - Resource Kit - Configuration - Running an application as a service).
Q. How can I shutdown a computer remotely?
A. Use the Shut Down workstation utility supplied with the NT Resource Kit.
Q. Where can I find a Unix su (substitute user) like utility?
A. Background for those unfamiliar with Unix: It is a good idea for system administrators to do everyday's work with a low privileged account and only change to an account which is a member of the Administrators group if you really have to do administrative work. To avoid closing all open applications and log off, it is useful to have a utility that allows you to temporarily start applications running in the security context of a different account.
The Resource Kits ships SU.EXE, a free equivalent is SU.ZIP (on Cica in /admin <LINK>). Both require setting system privileges for the caller. An alternative is SUSRV.ZIP (also from Cica), which has to be installed as a service, but does not require privileges. There is no equivalence to Unix suid programs (i.e. a file attribute which achieves that the file is run in the security context of the owner instead of the caller, without specifying a password).
Q. I'm running NT on Alpha - Can I run INTEL programs?
A. Digital have produced a special on-the-fly binary translator available at http://www.service.digital.com/fx32/.
A. TWEAKUI is part of the Power Toys set released for Windows95, however TWEAKUI (and a number of the other utilities) also runs on NT4.0. The utility basically puts a graphical front end to some of the more useful Registry settings and allows the user to remove icons from the desktop (such as Rubbish Bin), automatically login and many other useful config options. Download it from http://www.microsoft.com/windows95/info/powertoys.htm , then run the file and a number of files will be created. Right click on the TWEAKUI.INF and select install, and a TWEAKUI option will be in the control panel.
A. Below are some sites that are worth a look
Q. Do Windows 95 Powertoys work in NT?
A. Some of them do, and I suspect as time goes on they all will. The ones that currently work on NT 4.0 are
As part of the Powertoys for Windows 95 there is also a QUICKRES utility that allows a change of resolution without a reboot, however this does not work in NT, but the NT resource kit includes an identical utility (called QUICKRES.EXE).
Q. Is there a X-terminal for NT?
A. There is a very good free X-server called MIX at http://www.microimages.com
A. It is still shipped with NT 4.0, just run WINFILE.EXE
Q. Where do I get Themes for NT?
A. Desktop Themes are supplied on the NT Resource kit, however if you have Windows95 installed with the plus pack you can copy the files themes.cpl and themes.exe to the %systemroot$/system32 directory and reboot your machine. These files are contained in Plus_3.cab on the Windows 95 CD-ROM.
Q. Where can I get UNIX tools for NT?
A. There is an excellent selection of utilities available for download from http://www.cygnus.com/misc/gnu-win32/ .
Q. How can I fix/replace/copy files on an NTFS partition from outside Windows NT?
A. NT Internals has released ERD Commander which allows you to perform read and write operations on NTFS/FAT and CDFS partitions. ERD Commander can be purchased from http://www.winternals.com/erdcmndr.htmlor a free read-only version from http://www.sysinternals.com/erdcmndr.htm.
Once downloaded just run the executable erdcmndr.exe and it will self install to a directory of your choosing. It will also create a program group "ERD Commander". Once installed it will ask if you want to create the ERD Commander disks. ERD Commander works by altering a set of NT installation disks with its own special versions of certain files so instead of installing NT it brings up a DOS like command prompt. You can either modify an existing set of installation disks or let ERD Commander create a new set (you will need to insert you NT installation CD-ROM). The instructions below are for creating the disks.
When the creation has completed you can insert disk 1 and reboot the machine to boot into ERD Commander. You will then be prompted to insert disk 2 then disk 3 and then finally disk 2 again.
There is a pause of about 30 seconds when it first displays the "Microsoft (R) Windows NT", don't worry, this is normal. You will then be shown a list of all the drives.
Pay attention to the drive letters, they may not match your usual drive assignments, this is because Windows NT grants letters on active partitions of each disk first, where as ERD Commander assigns them as it comes across them from floppy disk 0, hard disk 0 and then CDRom 0 onwards. For example if you had 2 harddisks, harddisk 0 and harddisk 1, with harddisk 0 having 2 partitions, Windows NT would assign the letters as
Harddisk 0, partition 1 c:
Harddisk 1, partition 1 d:
Harddisk 0, partition 2 e:
This is because active partitions are assigned drive letters first. ERD Commander would label the partitions as
Harddisk 0, partition 1 c:
Harddisk 0, partition 2 d:
Harddisk 1, partition 1 e:
This is not a problem, just be aware, don't panic that your files have disappeared :-)
You can now enter normal commands like dir, rename, copy etc. When you are finished Ctrl-Alt-Del does not work, just remove the ERD Commander disk and type exit.
Q. What are the "Windows NT Support Tools"?
A. These are a set of tools used to aid debugging and diagnosis of Windows 3.51 and 4.0 systems.
The current version is 1.0 and these tools are free and can be downloaded from ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/tools/OEMSupportTools/OEMTools.exe (5.29MB).
The support tools consist of 3 programs
The download file is self-extracting and detailed instructions are provided in the readme.txt file.
Q. Does application x work with NT 4.0?
A. See the list below
Q. Does game x work with NT 4.0?
A. See http://www.cris.com/~dstaines/nt40games for an extensive lists of games that work with NT4.0, and tips to make them work.
Q. Does NT run 16bit applications?
A. There is no definitive answer. NT does not allow an application to directly access hardware, so any application that directly tried to access hardware would cause a violation, also private device drivers are not supported (such as a VXD). A VXD is usually a .386 file.
Besides direct hardware access, some 16 bit apps will not run under NT because they use a 16 bit API function call that either has no 32 bit equivalent, or the 32 bit equivalent has a completely different function call (different number/types of arguments) and NT can't convert the 16 bit version to the 32 bit version. If either of these things occur, NT will halt execution of the 16 bit app and throw some sort of error similar to the one it throws when direct hardware access occurs. This doesn't happen very often, but it seems that NT 4.0 has more problems with 16 bit code than NT 3.51 due to the 16 bit to 32 bit conversion process.
As a side note, this conversion of 16 bit code to 32 bit code is one of the reasons that NT will run 16 bit code slower than Win95 given all other things held equal. This has nothing to do with the Pentium Pro's problem with 16 bit code, it is an NT problem.
Q. Will NT 3.51 drivers work with NT 4.0?
A. Standard NT drivers will automatically be upgraded from the NT CD. 3rd party drivers may not work and the supplier should be contacted. In particular Video drivers and Printer drivers were moved for NT4.0 from Win32 to the NT executive to improve performance and reduce memory use (basically moved from Ring 3 - user mode to Ring 0 - kernel mode). This does have the effect that a graphics driver could crash NT.
Q. How do I change the letter associated with a drive?
A. From the Start Menu, select Administrative Tools and Disk Administrator. Right Click on the partition and choose "Assign Drive Letter", then just select the drive letter you wish to use. It is a good idea to recreate the Emergency Repair Disk after changing any drive information.
Q. How can I get NT to recognize my second harddisk?
A. Sometimes the Enhanced IDE (EIDE) adapter is misidentified as an ATAPI controller which loads the ATAPI.SYS driver. Disable this driver (Control Panel - Devices - Startup - Disable) and load the correct EIDE driver.
Q. How do I install a HP scanner?
A. There is full information on this at http://pw2.netcom.com/~gmelendz/index.html
Q. How do I install dual screens?
A. NT 5.0 will have support for this, however in the mean time you are limited to certain graphics cards with specialty drivers, such as two Matrox Millenium cards. Multi monitor support is also provided by #9, Diamond MM, Dynamic Pictures and STB. Some even have single PCI slot solutions, such as some STB cards and Diamond FireGL 3000.
Q. How much memory can NT support?
A. NT is a 32-bit operating system which means it can support 2^32 amount of memory (4 Gigs). However NT splits memory into 2 parts, 2 gigs for the programs and 2 gigs for the Operating System. There are known to be some problems when having more than 64MB even in NT4.0, please see Q117373
Q. How much memory do I need for NT?
A. For NT Workstation on Intel 12MB is the minimum, however 16MB is the recommended min, 24MB will reduce virtual memory usage and increase performance. For RISC based processors 24MB is recommended, and 32MB to improve performance. Most NT people will say the real acceptable performance numbers are 40MB for NT Workstation and 64MB for NT Server. It really does depend on what you will be running on the server.
For NT Server 16MB is the minimum, however most sites have 32MB.
Q. I cannot see my CD-ROM drive from NT?
A. If it is a IDE CD-ROM Drive ensure you have the ATAPI CD-ROM driver installed (or one supplied with drive).
If it is a SCSI CD-ROM ensure the correct SCSI driver is loaded.
Q. What are the IRQ's used for?
A. An Interrupt allows the piece of hardware to get the CPU's attention. For something like a Network card this is important as the card has limited buffer space so unless the CPU does not move the data out of the buffer it will get lost. Below is a table of the common IRQ uses.
| IRQ Level | Common Use | Comments |
| 0 | Timer | Hard-wired on motherboard |
| 1 | Keyboard | Hard-wired on motherboard |
| 2 | Cascade from IRQ 9 | May be available depending on Motherboard |
| 3 | COM2 or COM4 | |
| 4 | COM1 or COM3 | |
| 5 | LPT2 | This is usually free as not many people have 2 parallel ports. Sound blaster cards usually use this. |
| 6 | Floppy disk controller | |
| 7 | LPT1 | Sound blaster cards can use this |
| 8 | Real-time clock | Hard-wired on motherboard |
| 9 | Cascade to IRQ 2 | Wired directly to 2, sometimes tell software 9 when mean 2 |
| 10 | Unused | This is usually used by Network cards, many of them not allowing it to be changed |
| 11 | Unused | Usually used by SCSI controllers |
| 12 | PS/2, Bus mouse | If you are not using a PS/2 or bus mouse this can usually be used by another device |
| 13 | Math Coprocessor | Used to signal errors |
| 14 | Hard disk controller | If you are not using an IDE hard disk you may use this for another device |
| 15 | Some computers use this for the secondary IDE controller | If you do not use the secondary IDE controller you may use this for another device |
Note about attempting to free IRQ's used by unused motherboard devices: if your BIOS lets you disable the device manually and doesn't get reset by any Plug-and-Play software you have (for instance, Windows 95), you are probably okay. Otherwise, you'll just have to experiment to determine whether you can really use the IRQ occupied by the unused motherboard device.
Q. How Many CPU's does NT support?
A. NT Workstation can support 2 CPU's, NT Server supports 4 CPU's, however the OEM version of NT Server can support up to 32 CPU's.
Q. Is there a list of hardware NT supports?
A. Microsoft has a NT hardware compatibility list at http://www.microsoft.com/hwtest/hcl/
Q. Can I test my hardware to see if it is compatible with NT?
A. It is possible to create an NT Hardware Qualifier Disk. Boot to DOS, and insert the NT CD-ROM and a blank formatted floppy disk. On the CD-ROM goto \SUPPORT\HQTOOL and run makedisk. Then just boot off of the floppy disk.
Q. Can I test my SCSI devices?
A. A tool is provided on the NT installation CD that will test SCSI adapters from Adaptec and BusLogic, to use this tool perform the following:
Q. How do I disable mouse detection on a COM port (for UPS usage)?
A. Follow the steps below after first removing the UPS from the computer
The /NoSerialMice switch only disables the Microsoft Serial Mouse device driver.
If you have installed any third-party mouse drivers, go into Control Panel - Devices and disable their Serial Mouse drivers as well. For example, if you installed the Logitech Mouseware V8.0 for a Trackman Marble, you must also disable the "Logitech Serial Mouse" device, called "lsermous" (note that the Arial lower-case l looks like a capitol i).
Q. Where can I get a driver for x?
A. If you have a piece of hardware that does not have a driver with NT you should check in two places, the maker of the hardware, i.e. for the Iomega Ditto goto www.iomega.com . If there is nothing there you should try the Microsoft site as they make the drivers for some hardware, for example the HP NT 4.0 drivers are made by Microsoft. If you cannot find the driver in either of these places then e-mail the technical support of the hardware maker, asking them for the driver, in some cases the driver is not on the web site, but they will e-mail it to you (makes a lot of sense :-))
For Iomega drivers can be downloaded from 1-800-998-0037.
Q. My U.S. Robotics 56K modem only connects at 19200.
A. The USR .inf that is supplied with NT defaults to and has a limit of 19200. Download the latest mdmusr.inf from USR which will allow the top speeds.
Q. Can I user the IDE interface on my sound card?
A. It depends if it is ATAPI 1.2 compliant. If it is, there should be no problems, however if it is not, it will not work and you will be unable to use this port.
Q. Does NT support Plug and Play?
A. In a limited sense. There is a driver that can be installed that will detect Plug and Play devices, however it is not supported and you will receive no support. To install the driver
Installing the driver sets the following registry values:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\pnpisa\Enum\Type -
0x1
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\pnpisa\Enum\Start -
0x1
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\pnpisa\Enum\ErrorControl
- 0x0
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\pnpisa\Enum\DisplayName
- "Pnp ISA Enabler Driver"
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\pnpisa\Enum\ImagePath
- "system32\DRIVERS\pnpisa.sys"
A. Follow the instructions below:
Q. How do I give my tape drive a letter so it is visible from explorer?
A. NT on its own cannot do this, however there is a 3rd party "driver" that gives this functionality. For more information see http://www.tapedisk.com.
Q. How can I force NT to use a mouse on a given port?
A. When NT boots its hardware detection component checks all hardware and updates the registry, sometimes it may not detect the mouse however it is possible to force NT to use a mouse on a given port:
For more information see knowledge base article Q102990 at http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/Q102/9/90.asp
Q. How can I view which resources devices are using under NT?
A. The easiest way to view resource usage by devices is to use the built in WINMSD.EXE utility supplied with Windows NT:
You could also use the winmsdp.exe utility that is supplied with the resource kit. The command
winmsdp /i
will output the IRQ usage information to the file msdrpt.txt.
A. The warnings are there for a reason however if you want to stop them perform the following:
Q. How can I tell if I am using the Compaq Hardware Abstraction Layer?
A. Compaq have their own HAL.DLL, designed in conjunction with Microsoft the Compaq version of the HAL.DLL takes advantage of the Compaq's hardware more effectively than the shipped Windows NT HAL.DLL.
This special HAL.DLL can be downloaded from http://www.compaq.com or from their download area at 713-518-1418. The current version is 1.20A and the filename is sp2465.exe.
To check which version of the HAL.DLL you have perform the following.
Q. How do I get a dual monitor Matrox Millenium system to not split dialog boxes across the screens?
A. Perform the following:
Q. How can I suppress the error message generated if my ZIP drive is not connected?
A. This is a function of the Iomega Zip service (PPA3NT, obvious name!) and error announcement can be disabled by performing the following:
Q. Does Windows NT 4.0 support USB?
A. Universal Serial Bus is the new external bus standard for the connection of PC peripherals. The idea behind USB is it will be plug and play and as devices are connected they will automatically be detected and installed.
Windows NT 4.0 does not provide built in USB support, you will need to wait for Windows NT 5.0 or switch to Windows 98. Some boxes convert the USB devices into serial ports.
Q. Why can't I hot swap my PCMCIA card with Windows NT 4.0?
A. Windows NT 4.0 does not support hot swap capabilities for PCMCIA cards -- the card must be inserted at boot. This support will be supported Windows NT 5.0. If you need these capabilities with Windows NT 4.0, you can use a third party package, such as SystemSoft's CardWizard product. For more information, check out their web site at www.systemsoft.com.
Q. How do I install a ZIP drive under NT?
A. There are different types of ZIP drivers, internal, external, ZIP-PLUS and all of this will work under Windows NT 4.0.
If you have an internal ZIP drive just ensure you have Service Pack 3 or later installed which provide built in support for internal ZIP drives and will display the drives in Explorer as "Removable drive".
If it is an external ZIP drive you will need to download and install the correct drivers from http://www.iomega.com/support/software/winnt.html. All downloaded drivers/tools are self extracting and contain good install instructions.
Q. How do I enable Bus Mastering in Windows NT?
A. Windows NT 4.0 has native bus mastering support with Service Pack 3. To enable bus mastering in Windows NT 4.0 perform the following:
So Intel and Microsoft do officially support DMACHECK. See also
DMACHECK.EXE IDE BusMaster is very important : you can read or write on disk without using 100% of CPU (like SCSI)
Q. I said no to a PNPISA device now I want to install it.
A. If you have installed the PNPISA driver which enables NT to use some plug and play devices and upon reboot said no to install some devices it will not ask you again.
If you later decide you DO want to install the device it is necessary to make NT "forget" that it has ever seen it before. Each PNPISA device has an entry under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\pnpisa and so do make NT forget about a device just delete its key.
Upon reboot you will be able to install the device.
For more information on installing the driver see Q. Does NT support Plug and Play?
A. A batch file is just a text file with a .bat or .cmd extension that adheres to a syntax and a set of valid commands/instructions. To run a batch file just enter the name of the file, you don't need to enter the .cmd or .bat extensions. In line with program the first batch file we write will output "Hello World".
Q. What commands can be used in a batch file?
A. Windows NT 4.0 introduced some extensions to cmd.exe, so to use these make sure HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor\EnableExtensions is set to 1. The following is a list of the more common commands you will use
| call <batch file> | This is used to call one batch from inside another. The execution of the current batch file is suspended until the called batch file completes |
| exit | Used to stop batch file execution. If a batch file is called from inside another and exit is called both batch files are stopped |
| findstr <string> <filename(s)> | Used to find a string in a file. There are a number of parameters from this and is quite powerful |
| for | Standard for loop for /L %n IN (1,1,10) DO @ECHO %n Would print 1 to 10 |
| goto <label> | Causes the execution of a program to skip to a given
point. The actual label name must be preceded with a colon (:), e.g. goto label1 ... :label1 ... |
| if <condition> .. | The if statement has a great deal of functionality.
Some of the more common ones are: if /i <string1> <compare> <string2> <command> The /i makes the comparison case insensitive and compare can be one of: EQU equal NEQ not equal LSS less than LEQ less than or equal GTR greater than GEQ greater than or equal if errorlevel if exists <file name> |
| rem <string> | A comment |
| start <window title> <command> | Starts a new command session and runs a given command. Unlike call the execution of the current batch file is not halted and continues |
There are some extra utilities supplied with the NT Resource Kit which can be useful.
Q. How can I perform an action depending on the arrival of a file?
A. This is a common request as users on hosts have files FTP'd from a host and need to action it when it arrives. Below is a simple batch file to do this:
:filecheck
if exist e:\upload\file.txt goto actionfile
sleep 100
goto filecheck
:actionfile
...
This would check for file.txt every 100 seconds. The program sleep.exe is supplied with the resource kit so you would need the resource kit installed.
Q. How can I access files on other machines?
A. You can use the UNC naming conventions, e.g. \\<server name>\<share name>\<dir>\<file>. Alternatively you could map the drive, access the file using a drive letter and then unmap the drive, e.g.
net use g: \\savilltech\filetosee
... g:\dir\file.txt
net use g: /d
Q. How can I send a message from a batch file?
A. Use the NET SEND command, e.g.
net send <machine> "<message>"
Q. The command I enter asks for input, can I automate the response?
A. Most commands have a switch to confirm an action however if a command requires a response when run, for instance a logon may want you to enter a password try the following:
echo <password> | logon savillj
This runs the command "logon savillj" and assuming it then asked for a password, the echo would then echo the password with a return thus entering your password for you.
Q. How can I pass parameters to a batch file?
A. When you call a batch file you may enter data after the command which the batch file refers to as %1, %2 etc, for example the batch file hello.bat
@echo hello %1 boy
Would output
hello john boy
if called as "hello.bat john" (you don't need to enter .bat extension, I just use it here as I used bad file names :-) )
You can actually modify the passed parameter in the following ways
| Parameter | Description |
| %1 | The normal parameter. |
| %~f1 | expands %1 to a fully qualified path name. If you only passed a file name from the current directory it would expand to the drive/directory as well |
| %~d1 | extracts the drive letter from %1. |
| %~p1 | extracts the path from %1 |
| %~n1 | extracts the file name from %1 without the extension |
| %~x1 | extracts the file extension from %1 |
| %~s1 | changes the meaning of n and x options to reference the short name. You would therefore use %~sn1 for the short file name, or %~sx1 for the short extension |
You can combine some of the above as follows
| Parameter | Description |
| %~dp1 | expands %1 to a drive letter and path only. |
| %~nx1 | expands %1 to a file name and extension only. |
To see all of these in actions put this into a batch file testing.bat
@echo off
echo fully qualified name %~f1
echo drive %~d1
echo path %~p1
echo file name %~n1
echo file extension %~x1
echo short file name %~sn1
echo short file extension %~sx1
echo drive and directory %~dp1
echo file name and extension %~nx1
Run the file with a long file name, for example the batch file run on file c:\temp\longfilename.long would produce output
fully qualified name c:\TEMP\longfilename.long
drive c:
path \TEMP\
file name longfilename
file extension .long
short file name LONGFI~1
short file extension .LON
drive and directory c:\TEMP\
file name and extension longfilename.long
Obviously all the above also work on the second, third parameter etc, and you just substitute 1 for the parameter, e.g. %~f2 for the second parameters fully qualified path name.
Q. How can I stop my batch files outputing the command to screen as it runs it?
A. This is stopped by just placing
@echo off
at the top of your batch file. To stop a single command being output to the screen just put @ in front of the command.
Q. How do I call a batch file from within another batch file?
A. It is possible to just enter the name of the batch file in a batch file which will run the called batch file however once completed it will not pass control back to the calling batch file leaving the rest of the calling batch file unrun. For example suppose we had the batch files
calling.bat
@echo off
echo Calling bat here
called.bat
echo Back to Calling bat
called.bat
@echo off
echo called bat here
If you then run calling.bat you would not get the line "Back to
Calling bat" displayed as after called.bat terminates it does not
return to calling.bat. To call a batch file and have it return to the
calling batch file once completed use call . For example
if calling.bat was modified to have "call called.bat" instead of
"called.bat" the line "Back to Calling bat" would be
displayed as once called.bat was completed control would return to
calling.bat.
Q. .bat files have lost their association.
A. This is easily fixed. Enter the commands:
ftype batfile="%1" %*
assoc .bat=batfile
Q. How do I search files for a string from a batch file/command line?
A. There is the basic find command which allows you to search one file at a time for string, however findstr is far more versatile. The command has the following switches
FINDSTR [/B] [/E] [/L] [/R] [/S] [/I] [/X] [/V] [/N] [/M] [/O] [/F:file] [/C:string] [/G:file] [strings] [[drive:][path]filename[ ...]]
| Parameters | Meaning |
| /b | Match pattern if at the start of a line |
| /e | Match pattern if at the end of a line |
| /l | Search literally |
| /r | Use text as a regular expression (default) |
| /s | Search current directory and all sub-directories |
| /i | Ignore case |
| /x | Selects lines that are an exact match |
| /v | Selects lines that do not match |
| /n | Displays the line number before the matched line |
| /m | Displays only the matching file names |
| /o | Displays the offset of the match before the matched line |
| /g:<file> | Gets the search string from the specified file. /g:argument.txt |
| /c:"<string>" | Use text as a literal. /c:"string" |
| /f:<file> | Gets the file list from the specified file. /f:filelist.txt |
| strings | The search string (in double quotes if multiple words) |
| files | Files to be searched |
Use spaces to separate multiple search strings unless /c is used
findstr "Windows NT FAQ" ntfaq.html - searchs for
Windows, NT or FAQ in ntfaq.html
findstr /c:"Windows NT FAQ" ntfaq.html - searchs for "Windows
NT FAQ" in ntfaq.htm
A. Samba is a suite of programs which work together to allow clients to access to a server's filespace and printers via the SMB (Server Message Block) protocol. Initially written for Unix, Samba now also runs on Netware, OS/2 and VMS. For more information goto http://samba.anu.edu.au/samba/
Q. Why disk spanning function of PKZIP (command line version) not work under NT?
A. Because NT command processor CMD.EXE uses '&'
character for separating several commands on the same command line and
PKZIP uses the same character for creating multi-disk archives. Solution
is to enclose '&' in quotes like this:
C:>pkzip "-&" -pr <archive.zip> <files...>.
There is now a Win32 console (line command) PKZip 2.5 with disk span support. Check http://www.pkware.com
Q. What virus killers are available for NT4.0?
A. Below is a table of virus killers I know about.
| Cheyenne Software InocuLAN | http://www.cheyenne.com |
| Data Fellows F-PROT Professional | http://www.datafellows.com |
| McAfee Anti-Virus | http://www.mcafee.com |
| Panda Anti-Virus | http://www.pandasoftware.com |
| Symantec's Norton Anti-Virus for NT | http://www.norton.com |
| Ontrack Computer Systems VirusScan | http://www.ontrack.com |
| Dr. Solomon's Anti-Virus Toolkit | http://www.sands.com/prods/toolkit/ |
| SOPHOS | http://www.sophos.com |
| Vet | http://www.vet.com.au |
Q. Does NT support the LS120 (adrive)?
A. Yes, see http://www.ortechnology.com/adrive.html for more information.
A. Yes as long as the system has Service Pack 3 and the Year 2000 hot fixes applied. For more information see the Microsoft Year 2000 Information Centre at http://www.microsoft.com/y2k . Also see http://www.microsoft.com/ithome/topics/year2k/default.htm
A. See the table below
| ACL | Access Control List | A list that controls the access to an object |
| API | Network Applications Interface | A set of commands that allow programmers to build network-aware programs |
| BDC | Backup Domain Controller | An NT Server machine that receives a copy of the master user-database from the PDC and can validate logons |
| COLD | Computer Output to Laser Disk | |
| DHCP | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol | A service that automatically assigns IP-addresses to clients from a given range (scope) |
| DLC | Data Link Control | International standard protocol IEEE 802.2
Used with mainframe gateways and to control printers with a JetDirect-card |
| FAT | File Allocation Table | The DOS way of organizing a harddisk
Lots of wasted space on large disks Little file security |
| HPFS | High Performance File System | The OS/2 way of organizing a harddisk |
| IPX/SPX | Internetwork Packet Exchange / Sequenced Packet Exchange | Novell NetWare protocol
Based on the Xerox protocol XNS(Xerox Networking Services) |
| MAC-addresses | Media Access Control layer addresses | 48-bit address that is hardwired into the
netcard
DHCP, among others, use this to identify a machine requesting a certain IP-address within its lease duration |
| NBT | NetBIOS over TCP/IP | NetBIOS built on top of the TCP/IP suite |
| NDIS | Network Driver Interface Specification | Microsoft binding standard (interface
between netcard driver and protocol)
Can load into high memory on DOS systems |
| NetBEUI | NetBIOS Extended User Interface | The actual NetBIOS transport protocol |
| NetBIOS | Network Basic Input/Output System | An API of 18 networking-related commands |
| NIC | Network Information Center | The organization that assigns domain names and IP-addresses to Internet hosts |
| NTFS | New Technology File System | The NT way of organizing a harddisk
Efficient storage High level of security |
| ODI | Open Data-link Interface | Novell binding standard (interface between
netcard driver and protocol)
Can not load into high memory on DOS systems |
| PDC | Primary Domain Controller | The NT Server machine that stores the master user-database in a domain |
| RAID | Redundant Array of Inexpensive Drives | A number of disks with data distributed
all over them to allow for faster access
Can also provide data-recoverability NT supports RAID level 0,1 and 5 |
| RIP | Routing Internet Protocol | The protocol that takes care of routing on the Internet |
| SID number | Security IDentification number | Every object in an NT domain have a SID
number
Reinstalling will not give the same SID number |
| SPS | Standby Power Supply | Device that is installed between the wall
outlet and the computer inlet
The power goes directly into the computer with a branch to the batteries When the power fail, the batteries take over, but with a delay The delay should be 4 ms or better for proper operation |
| TCP/IP | Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol | The protocol used for Inter- and Intranet communications |
| UDP | User Datagram Protocol | Part of the TCP/IP suite
It is used for communicating with DHCP-servers before IP-addresses are assigned |
| UPS | Uninterruptible Power Supply | Device that is installed between the wall
outlet and the computer inlet
The power is directed through the batteries, thus stabilizing the variance of the power from the outlet Because of this, the switch delay is 0 ms |
| WINS | Windows Internet Naming Service | A dynamic IP-to-name database |
Q. What are the shortcuts available with the "Win" key?
A. See the table below
| WIN + R | Display the Run dialog |
| WIN + M | Minimize all windows |
| WIN + Shift + M | Undo minimize all windows |
| WIN + F1 | Help |
| WIN + E | Explorer |
| WIN + F | Find Files |
| Ctrl +WIN + F | Find Computer |
| WIN + TAB | Cycle through minimized taskbar icons |
| WIN + BREAK | Systems Properties |
Q. How can I open a file with an application, other than the one it is associated with?
A. Usually you can right click on the file, and select open. If you hold down shift and right click on the file you will have "open with."
Q. How do I change the icon associated with a short cut?
A. Follow the steps below:
Q. Is it possible to map a drive letter to a directory?
A. You can use the SUBST command to
map a pseudo drive letter to drive/directory
subst r: d:\winnt\system32
would map the letter r to the directory winnt\system32 on the d:
drive.
Q. What keyboard shortcuts are available?
A. See the table below
| F1 | Help |
| F2 | Rename |
| F3 | Find |
| F4 | Display combo box in Explorer |
| F5 | Refresh |
| F6 | Switch panes in Explorer |
| F10 | Menu Mode |
| ALT + ENTER | Properties |
| CTRL + Drag a file | Copy |
| CTRL + G | Goto |
| CTRL + U | Undo |
| CTRL + A | Select All |
| CTRL + ESC | Start Menu |
| CTRL + SHIFT + ESC | Task Manager |
Q. How do I schedule commands?
A. Windows NT has a built in scheduler service which enables applications to be started at specified times. To schedule events the schedule service must be started:
The scheduler service only needs to be started on the target
machine, not the issuing machine. If the scheduler service is not started
on the target machine the error
The service has not been started
will be displayed.
To schedule a command you use the AT utility. AT is used with the following syntax:
at [<computername>] <time> [/interactive]
[/every:date/day..] [/next:date/day..] <command>
e.g. at \\savmain 22:00 /interactive /every:M,T,W,Th,F sol.exe
The example would start the solitaire game on the SAVMAIN machine at 10:00 p.m. every weekday. The /interactive means the application can interact with the desktop, i.e. the currently logged on user. If /interactive is omitted and the application requires user interaction it will just start and finish instantly.
When a command is submitted it will be given an ID. To delete a scheduled command use:
at [<computername>] <id> /delete /yes
e.g. at \\savmain 3 /delete /yes - The /yes skips
confirmation of the delete
The above may seem quite a lot to take in if all you want to do is a backup (see Q. How do I schedule a backup? for an example of using AT with a backup), so a utility called WINAT is shipped with the NT Resource Kit that puts a graphical interface to the AT command which you may find easier, however the functionality is the same. The advantage with WINAT is that it automatically starts the Schedule service on the target machine.
Q. What are the long path names in the boot.ini file?
A. The pathnames in the boot.ini file are the ARC (Advanced RISC Computing) pathnames, and are used to locate the NT system partition. There are two main types of ARC names depending on if the disks are IDE or SCSI. For IDE they will follow the convention below:
multi(x)disk(x)rdisk(x)partition(x)\%systemroot%
Both the multi and disk are not really used for IDE and should always be 0. The rdisk is the physical drive and will be 0 or 1 on the first IDE controller, or 2 and 3 on the second IDE controller. Partition() is the partition number on the disk and starts from 1.
The scheme is slightly different for SCSI:
scsi(x)disk(x)rdisk(x)partition(x)\%systemroot%
Scsi() is the controller number of the SCSI identified in the Ntbootdd.sys. Disk() is the SCSI ID of the physical disk. RDISK() is the SCSI logical unit number (LUN), which will nearly always be 0. Partition is the same is with IDE and is the partition number starting with 1.
The multi() designation means that the drive can respond to INT 13 calls, and most SCSI drives can so you may use multi() with a SCSI drive also.
In a pure IDE system, the MULTI() syntax will work for up to the four drives maximum on the primary and secondary channels of a dual-channel controller.
In a pure SCSI system, the MULTI() syntax will work for the first two drives on the first SCSI controller (that is, the controller whose BIOS loads first).
In a mixed SCSI and IDE system, the MULTI() syntax will work only for the IDE drives on the first controller.
Q. How can I execute a batch file using WINAT with Administrator Permissions?
A. From the Services Control Panel Applet (Start - Settings - Control Panel) double click Scheduler. Change the account/password to that of a user in the Administrative group. It may be wise to create a new account just for this use which would require the following attributes:
After changing the Scheduler information you will need to stop and start the service.
Q. I have 95 and NT installed, how can I configure the applications to run on both?
A. While it is possible to add the windows95 system directory to the NT path (which would mean you would find any .dll's etc. associated with applications), many applications write a large amount of information to the registry which would be missing. The best approach, and one I have tested, is to just install the application twice to the same directory, once when you are booted into NT, and once when you are booted into 95. This has the effect of only having one set of exe's, but duplicates both .dll's and registry settings to both machines. Obviously the applications cannot be on an NTFS or FAT32 partition.
Q. How can I stop and start services from the command line?
A. This can be accomplished using the
net stop <service name>
net start <service name>
A full list of the exact services is found in the registry (run
regedit.exe) under the
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services key.
Alternatively, you can perform the stop and start using the name that is
showed in the Services Control Panel applet by putting the name in quotes,
i.e.
net stop "<service>"
net start "<service>"
A. To delete a service that has not been automatically removed by a software uninstall you need to edit the registry:
There is also a utility that is supplied with the NT resource kit called INSTSRV.EXE that can be used to install and remove services
instsrv <service name> remove
Alternatively, also with the resource kit is a utility SRVINSTW.EXE that again installs and removes services, but with a GUI wizard format allowing you to select the service either locally or remotely.
A. USER.DMP is created by Dr. Watson when a program crashes, and is there to help you fix the problem. It can be examined using \support\debug\i386\dumpexam.exe or using windbg -z user.dmp. You can delete this file without any worries. The syntax for dumpexam.exe is
dumpexam -y <symbol file location> <dumpfile name and
location>, e.g.
dumpexan -y d:\winnt\symbols d:\winnt\memory.dmp
The output from dumpexam will be placed at %SystemRoot%\MEMORY.TXT.
To stop this file from being created start the System Control Panel Applet and select the startup/shutdown tab and uncheck the "write debugging information to" checkbox.
Q. How in Notepad can I save a file without the .txt extension?
A. When you save the file, just put the file name in double quotes, e.g. "johns.bat" will save the file as johns.bat with no .txt extension.
Q. How can I move shares and their contents from one machine to another?
A. Moving the actual files and directories is simple, however share information is not contained in the directories, but rather is contained in the registry (under LanmanServer), it is therefore necessary to copy this registry information from the machine currently containing the shares, to the machine that will host the shares:
Q. How do I create a shortcut on the desktop to a directory/disk?
A. The procedure below works for and file/directory/disk (even the a: drive).
Q. How can I create a spare set of Windows95 disks?
A. Microsoft distributed Windows 95 using a new method, storing 1.68 MB of data on a normal disk, this makes copying impossible using normal methods, however there is a piece of software called CopyQM which can be downloaded from http://www.sydex.com which performs an image copy and using the command below can duplicate a windows 95 installation disk
copyqm a: bios blind silent tracks=80 sides=2 convert=1.68m
You will be prompted to insert the master disk and it will then read in the information and ask you to insert the target disk.
Q. What FAX software is available for Windows NT?
A. There is an excellent site at http://www.stonecarver.com/ntfax-faq.html which has a full list of FAX servers for Windows NT.
Q. How can I delete files that are over x days old?
A. There is a utility called DELOLD which is used in the form of
delold <location>\*.* n
where n is the number of days old the files need to be for them to be deleted. This utility can be downloaded from ACI Software (http://www.michna.com/software.htm)
Q. How can I speed up the performance of my OS/2 applications?
A. Many applications written for OS/2 will run faster under a Virtual DOS Machine (VDM), this is because NT allocates more resources to a VDM than to the OS/2 subsystem. You should therefore disable the OS/2 subsystem as follows:
Q. How can I install a font from the command line/batch file?
A. When you install a font all it does is copy the .ttf file to the %systemroot%\fonts and add an entry in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Fonts. This can be automated with a batch file as follows
Rem fontinst.bat
copy akbar.ttf %systemroot%\fonts
regedit /s font.reg
The font.reg would contain the following:
REGEDIT4
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
NT\CurrentVersion\Fonts]
"Akbar Plain (TrueType)"="akbar.ttf"
In this example it copies akbar.ttf which is called "Akbar Plain (TrueType)" (yes its the Simpsons font ;-) ). The reg scipt actually creates a value called "Akbar Plain (TrueType)" under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Fonts with its contents "akbar.ttf". The new font would be visable once the machine has been rebooted.
If you have some older 16bit applications you may want to add the font to win.ini as well in the [fonts] section. This could be accomplished using a .inf file, e.g.
[UpdateInis]
"E:\WINNT\WIN.INI","Fonts",,"Akbar Plain
(TrueType)=akbar.ttf"
Q. Information about Time Zones and daylight saving.
A. The following is some useful notes.
User crosses various timezones; uses Control Panel to change the timezone upon arrival.
Windows 95 - System will alter the offset from UTC. System clock is
unchanged. Displayed time will NOT be changed.
Windows NT - System will alter the offset from UTC. System clock is
unchanged. Displayed date/time WILL change.
Daylight Saving and the "Automatically Adjust for Daylight Saving Time" checkbox
A user arrives the morning of a Daylight Savings Period transition.
If the "Automatically Adjust For Daylight Saving Time" checkbox
HAS been enabled
Windows 95 - System will alter the offset from UTC. System clock will be
changed. Displayed clock time will change.
Windows NT - System will alter the offset from UTC. System clock is
unchanged. Displayed clock time will change.
If the "Automatically Adjust for Daylight Saving Time" checkbox has NOT been enabled
Windows 95 - System WILL alter the offset from UTC. System clock is
unchanged. Displayed clock time will NOT be changed.
Windows NT - System will NOT alter the offset from UTC. System clock is
unchanged. Displayed clock time will NOT be changed. If an NT user now
manually alters the system clock to show the 'true' time, the UTC time is
incorrect and any 'export' of time-data from this system will be
incorrect.
At some time/day within a Daylight Savings Period, if the user alters the "Automatically Adjust For Daylight Saving Time"
Windows 95 - System will NOT alter the UTC offset. System clock is
unchanged. Displayed clock time will NOT be changed.
Windows NT - System WILL alter the UTC offset. System clock is unchanged.
Displayed clock time WILL be changed.
Q. What are the ErrorControl, Start and Type values under the Services subkeys?
A. Each of the main 3 values and their contents are described below.
ErrorControl
This is used if the service fails to startup upon boot.
| Value | Meaning |
| 0x00 | If this driver can't be loaded or started ignore the problem and display no error |
| 0x01 | If the driver fails produce a warning but let bootup continue |
| 0x02 | Panic. If the current config is last known good continue, if not switch to last known good |
| 0x03 | Record the current startup as a failure. If this is last known good run diagnostic, if not switch to last known good and reboot |
Start
This defines when in the boot sequence the service should be started. You can also set these by using the Services control panel applet.
| Value | Start Type | Meaning |
| 0x00 | Boot | The kernel loaded will load this driver first as its needed to use the boot volume device |
| 0x01 | System | This is loaded by the I/O subsystem |
| 0x02 | Autoload | The service is always loaded and run |
| 0x03 | Manual | This service does not start automatically and must be manually started by the user |
| 0x04 | Disabled | The service is disabled and should not be started |
Type
This defines the kind of service or driver. They are loaded in the following order down the list.
| Value | Meaning |
| 0x01 | Kernel-mode device driver |
| 0x02 | Kernel-mode device driver that implements the file system |
| 0x04 | Information used by the Network Adapter |
| 0x10 | A Win32 service that should be run as a stand-alone process |
| 0x20 | A Win32 service that can share address space with other services of the same type |